ZHCSDI7A December 2012 – March 2015 SM74611
PRODUCTION DATA.
7 Detailed Description
7.1 Overview
The SM74611 is designed for use as a bypass diode in photovoltaic modules. The SM74611 utilizes a charge pump to drive an N-channel FET to provide a resistive path for the bypass current to flow.
7.2 Functional Block Diagram
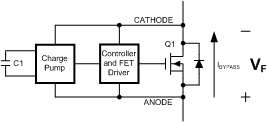
7.3 Feature Description
The operational description is described below. Please refer to Figure 4 and Figure 5.
From t0 to t1:
When cells in the solar panels are shaded, the FET Q1 is off and the bypass current will flow through the body diode of the FET as shown on Figure 4. This current will produce a voltage drop (VF) across ANODE and CATHODE terminal of the bypass diode. During this time, the charge pump circuitry is active and charging capacitor C1 to a higher voltage.
At t1:
Once the voltage on the capacitor reaches its predetermined voltage level, the charge pump is disabled and the capacitor voltage is used to drive the FET through the FET driver stage.
From t1 to t2 :
When the FET is active, it provides a low resistive path for the bypass current to flow thus minimizing the power dissipation across ANODE and CATHODE. Since the FET is active, the voltage across the ANODE and CATHODE is too low to operate the charge pump. During this time, the stored charge on C1 is used to supply the controller as well as drive the FET.
At t2:
When the voltage on the capacitor C1 reaches its predetermined lower level, the FET driver shuts off the FET. The bypass current will then begin to flow through the body diode of the FET, causing the FET body diode voltage drop of approximately 0.6V to appear across ANODE and CATHODE. The charge pump circuitry is re-activated and begins charging the capacitor C1. This cycle repeats until the shade on the panel is removed and the string current begins to flow through the PV cells instead of the body diode of the FET.
The key factor to minimizing the power dissipation on the device is to keep the FET on at a high duty cycle. The average forward voltage drop will then be reduced to a much lower voltage than for a Schottky or regular P-N junction diode.
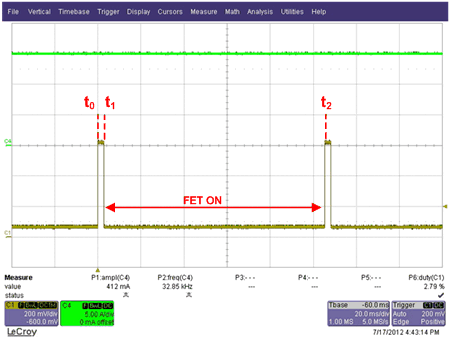 Figure 5. ANODE to CATHODE Voltage (Ch1) with IBYPASS = 15A (Ch4) for SM74611 in Junction Box at 85˚C Ambient
Figure 5. ANODE to CATHODE Voltage (Ch1) with IBYPASS = 15A (Ch4) for SM74611 in Junction Box at 85˚C Ambient