ZHCSJH0C March 2019 – September 2022 OPA1655 , OPA1656
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Device and Documentation Support
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.1.1 Basic Noise Calculations
Low-noise circuit design requires careful analysis of all noise sources. External noise sources can dominate in many cases; consider the effect of source resistance on overall op amp noise performance. Total noise of the circuit is the root-sum-square combination of all noise components.
Figure 8-1 shows noninverting (A) and inverting (B) op amp circuit configurations with gain. In circuit configurations with gain, the feedback network resistors contribute noise. In general, the current noise of the op amp reacts with the feedback resistors to create additional noise components.
The selected feedback resistor values make these noise sources negligible. Low impedance feedback resistors load the output of the amplifier. The equations for total noise are shown for both configurations.
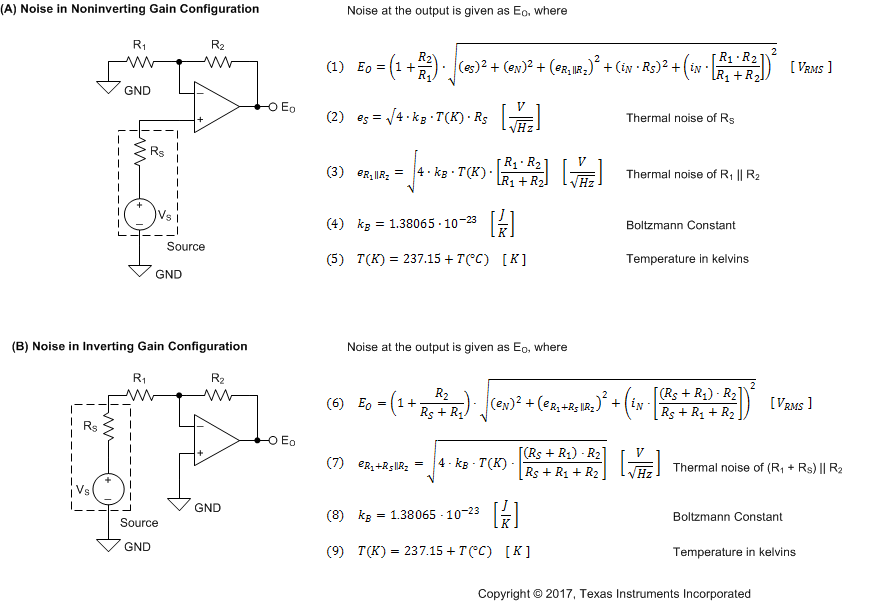
where
- eN is the voltage noise of the amplifier. For the OPA165x, eN = 4.3 nV/√Hz at 1 kHz.
- iN is the current noise of the amplifier. For the OPA165x, iN = 6 fA/√Hz at 1 kHz.