ZHCSH86B December 2017 – February 2019 LMH5401-SP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8.1 Output Reference Nodes and Gain Nomenclature
- 8.2 ATE Testing and DC Measurements
- 8.3 Frequency Response
- 8.4 S-Parameters
- 8.5 Frequency Response with Capacitive Load
- 8.6 Distortion
- 8.7 Noise Figure
- 8.8 Pulse Response, Slew Rate, and Overdrive Recovery
- 8.9 Power Down
- 8.10 VCM Frequency Response
- 8.11 Test Schematics
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Application
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 10.3 Do's and Don'ts
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
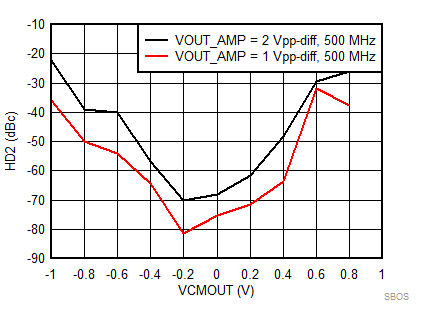
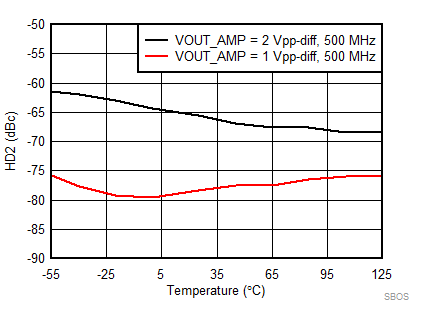
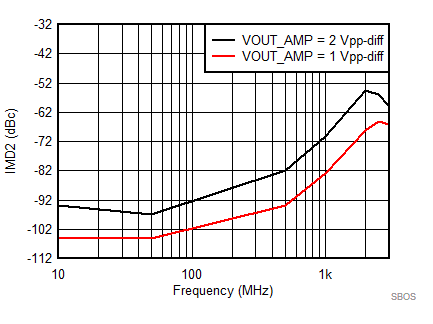
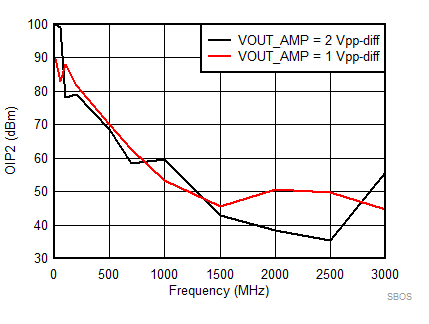
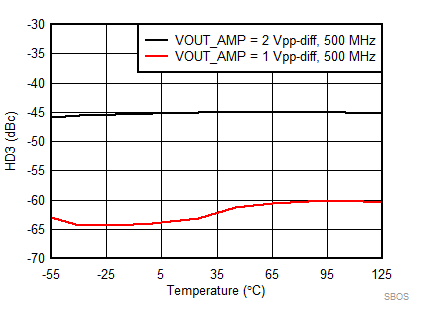
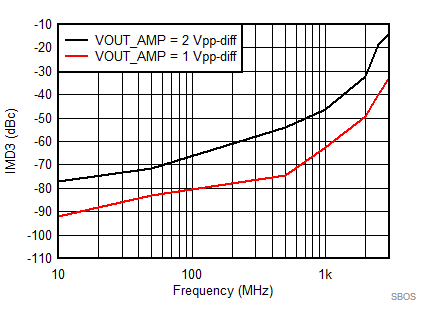
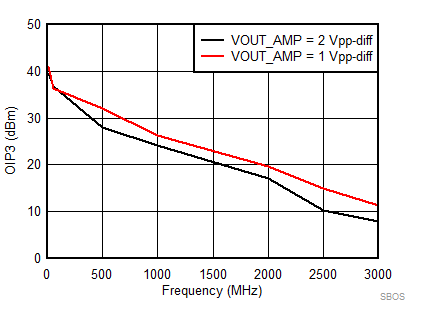
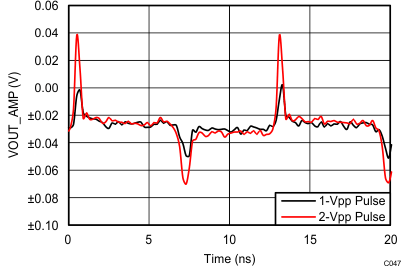
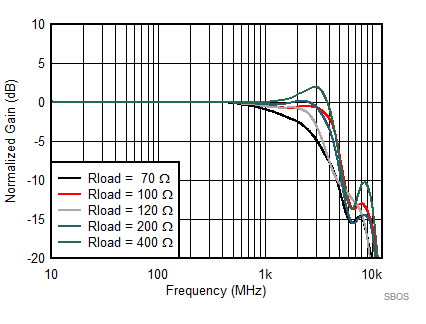
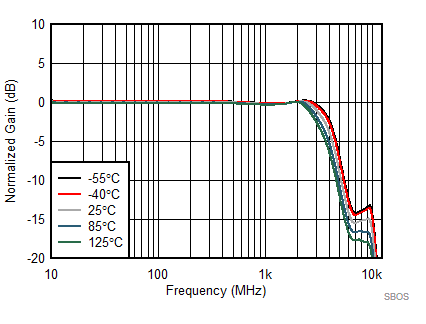
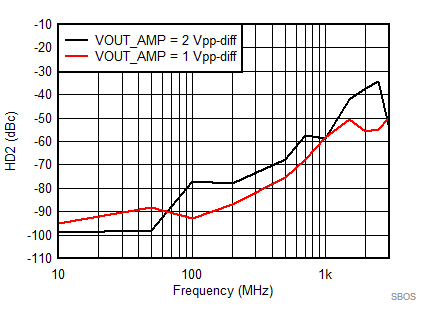
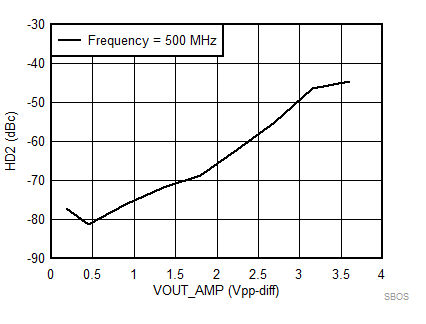
7.8 Typical Characteristics: 3.3 V
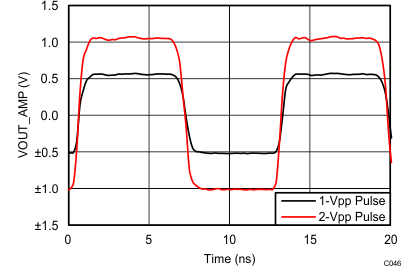
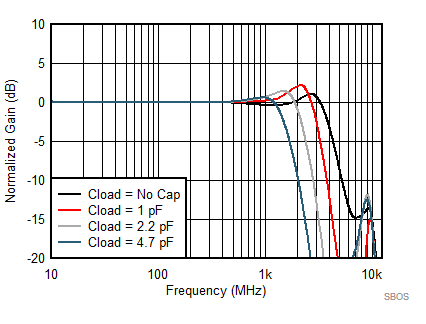
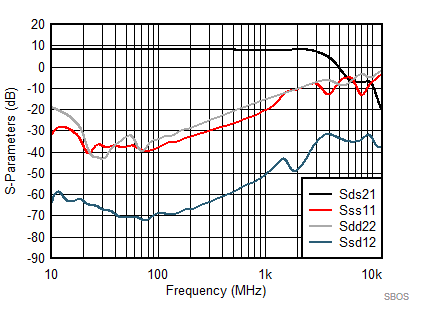
at TA = 25°C, VS+ = 3.3 V; VS– = 0 V; VCM = 1.65 V, RLtotal = 200-Ω differential(3) (RO = 40 Ω each), Gp = 8 dB (Gv = 17 dB), single-ended input and differential output, and input and output pins referenced to midsupply (unless otherwise noted); measured using an EVM as discussed in the section (see Figure 54 to Figure 57)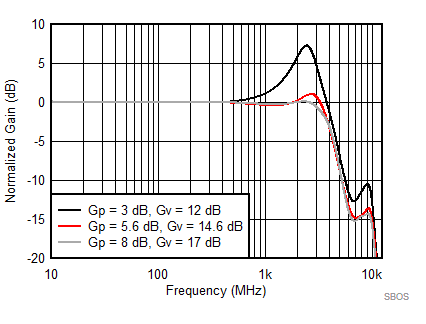
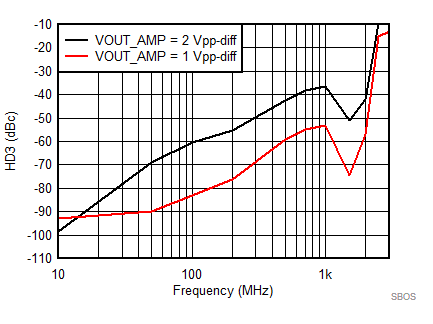
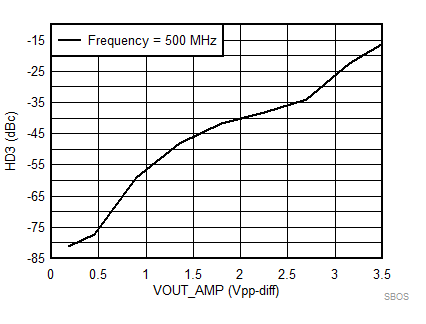
| Vout = pk-pk voltage swing per tone on 100-Ω effective load |
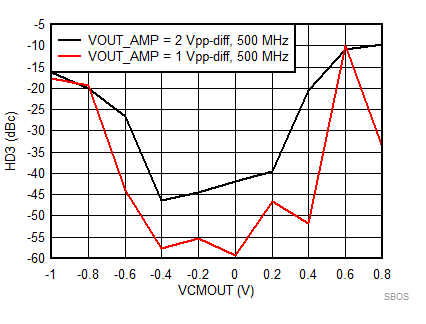
| VCM @ AMPOUT Node; VCM = (Vo+ + Vo–) / 2 |
| Vout = pk-pk voltage swing per tone on 100-Ω effective load |