ZHCSHW2I June 2007 – September 2018 LM2735
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1 LM2735X SOT-23 Design Example 1
- 8.2.2 LM2735Y SOT-23 Design Example 2
- 8.2.3 LM2735X WSON Design Example 3
- 8.2.4 LM2735Y WSON Design Example 4
- 8.2.5 LM2735Y MSOP-PowerPAD Design Example 5
- 8.2.6 LM2735X SOT-23 Design Example 6
- 8.2.7 LM2735Y SOT-23 Design Example 7
- 8.2.8 LM2735X SOT-23 Design Example 8
- 8.2.9 LM2735Y SOT-23 Design Example 9
- 8.2.10 LM2735X WSON Design Example 10
- 8.2.11 LM2735Y WSON Design Example 11
- 8.2.12 LM2735X WSON SEPIC Design Example 12
- 8.2.13 LM2735Y MSOP-PowerPAD SEPIC Design Example 13
- 8.2.14 LM2735X SOT-23 LED Design Example 14
- 8.2.15 LM2735Y WSON FlyBack Design Example 15
- 8.2.16 LM2735X SOT-23 LED Design Example 16 VRAIL > 5.5 V Application
- 8.2.17 LM2735X SOT-23 LED Design Example 17 Two-Input Voltage Rail Application
- 8.2.18 SEPIC Converter
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DGN|8
订购信息
7.1.1 Theory of Operation
The LM2735 is a constant-frequency PWM boost regulator IC that delivers a minimum of 2.1 A peak switch current. The regulator has a preset switching frequency of either 520 kHz or 1.6 MHz. This high frequency allows the device to operate with small surface mount capacitors and inductors, resulting in a DC-DC converter that requires a minimum amount of board space. The LM2735 is internally compensated, so it is simple to use, and requires few external components. The device uses current-mode control to regulate the output voltage. The following operating description of the LM2735 refers to the simplified internal block diagram (Functional Block Diagram), the simplified schematic (Figure 13), and its associated waveforms (Figure 14). The LM2735 supplies a regulated output voltage by switching the internal NMOS control switch at constant frequency and variable duty cycle. A switching cycle begins at the falling edge of the reset pulse generated by the internal oscillator. When this pulse goes low, the output control logic turns on the internal NMOS control switch. During this on-time, the SW pin voltage (VSW) decreases to approximately GND, and the inductor current (IL) increases with a linear slope. IL is measured by the current sense amplifier, which generates an output proportional to the switch current. The sensed signal is summed with the corrective ramp of the regulator and compared to the error amplifier’s output, which is proportional to the difference between the feedback voltage and VREF. When the PWM comparator output goes high, the output switch turns off until the next switching cycle begins. During the switch off-time, inductor current discharges through diode D1, which forces the SW pin to swing to the output voltage plus the forward voltage (VD) of the diode. The regulator loop adjusts the duty cycle (D) to maintain a constant output voltage .
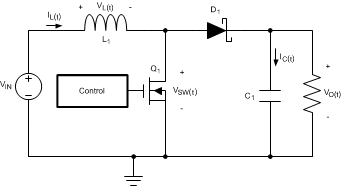 Figure 13. Simplified Schematic
Figure 13. Simplified Schematic 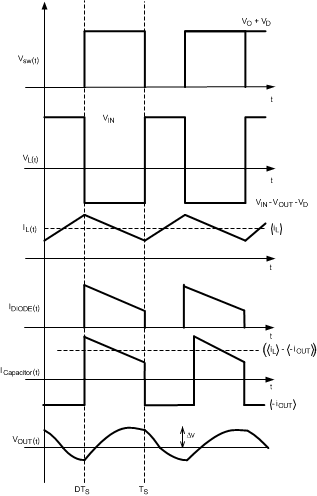 Figure 14. Typical Waveforms
Figure 14. Typical Waveforms