ZHCSOW3 September 2020 INA848
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.1.1.1 RC Filter Network
In environments where known high-frequency noise must be eliminated, use a low-pass filter containing a capacitor, and optionally, a resistor.
Figure 9-1 Low-pass Filter
The ‒3-dB cross frequency is determined given following equation:
Equation 2. 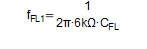
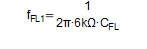
Where 6 kΩ represents the internal resistor network. Use the Analog Engineer's Calculator for fast and easy bode plot visualization.