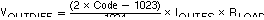ZHCSI68F September 2007 – October 2018 DAC5652A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: AC
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: Digital Input
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: Power Supply
- 6.9 Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RSL|48
订购信息
8.1.1 DAC Transfer Function
Each of the DACs in the DAC5652A has a set of complementary current outputs, IOUT1 and IOUT2. The full-scale output current, IOUTFS, is the summation of the two complementary output currents:
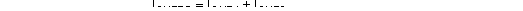
The individual output currents depend on the DAC code and can be expressed as:

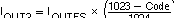
where Code is the decimal representation of the DAC data input word. Additionally, IOUTFS is a function of the reference current IREF, which is determined by the reference voltage and the external setting resistor (RSET).
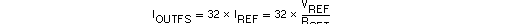
In most cases, the complementary outputs drive resistive loads or a terminated transformer. A signal voltage develops at each output according to:
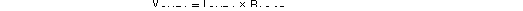
The value of the load resistance is limited by the output compliance specification of the DAC5652A. To maintain specified linearity performance, the voltage for IOUT1 and IOUT2 must not exceed the maximum allowable compliance range.
The total differential output voltage is: