ZHCSJ35C September 2016 – May 2021 CC3220R , CC3220S , CC3220SF
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 功能方框图
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 8.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.5 Current Consumption Summary (CC3220R, CC3220S)
- 8.6 Current Consumption Summary (CC3220SF)
- 8.7 TX Power and IBAT versus TX Power Level Settings
- 8.8 Brownout and Blackout Conditions
- 8.9 Electrical Characteristics (3.3 V, 25°C)
- 8.10 WLAN Receiver Characteristics
- 8.11 WLAN Transmitter Characteristics
- 8.12 WLAN Filter Requirements
- 8.13 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 8.14
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 8.14.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 8.14.2 Device Reset
- 8.14.3 Reset Timing
- 8.14.4 Wakeup From HIBERNATE Mode
- 8.14.5 Clock Specifications
- 8.14.6
Peripherals Timing
- 8.14.6.1 SPI
- 8.14.6.2 I2S
- 8.14.6.3 GPIOs
- 8.14.6.4 I2C
- 8.14.6.5 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
- 8.14.6.6 ADC
- 8.14.6.7 Camera Parallel Port
- 8.14.6.8 UART
- 8.14.6.9 SD Host
- 8.14.6.10 Timers
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.3 Security
The SimpleLink™ Wi-Fi® CC3220x Internet-on-a-Chip device enhances the security capabilities available for development of IoT devices, while completely offloading these activities from the MCU to the networking subsystem. The security capabilities include the following key features:
Wi-Fi and Internet Security:
- Personal and enterprise Wi-Fi security
- Personal standards
- AES (WPA2-PSK)
- TKIP (WPA-PSK)
- WEP
- Enterprise standards
- EAP Fast
- EAP PEAPv0/1
- EAP PEAPv0 TLS
- EAP PEAPv1 TLS EAP LS
- EAP TLS
- EAP TTLS TLS
- EAP TTLS MSCHAPv2
- Personal standards
- Secure sockets
- Protocol versions: SSL v3, TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2
- Powerful crypto engine for fast, secure Wi-Fi and internet connections with 256-bit AES encryption for TLS and SSL connections
- Ciphers suites
- SL_SEC_MASK_SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_SSL_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_MD5
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_RC4_128_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- SL_SEC_MASK_TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
- Server authentication
- Client authentication
- Domain name verification
- Runtime socket upgrade to secure socket – STARTTLS
- Secure HTTP server (HTTPS)
- Trusted root-certificate catalog—Verifies that the CA used by the application is trusted and known secure content delivery
- TI root-of-trust public key—Hardware-based mechanism that allows authenticating TI as the genuine origin of a given content using asymmetric keys
- Secure content delivery—Allows encrypted file transfer to the system using asymmetric keys created by the device
Code and Data Security:
- Network passwords and certificates are encrypted and signed.
- Cloning protection—Application and data files are encrypted by a unique key per device.
- Access control—Access to application and data files only by using a token provided in file creation time. If an unauthorized access is detected, a tamper protection lockdown mechanism takes effect.
- Encrypted and Authenticated file system (not supported in CC3220R)
- Secured boot—Authentication of the application image on every boot
- Code and data encryption (not supported in CC3220R)—User application and data files are encrypted in serial flash.
- Code and data authentication (not supported in CC3220R)—User Application and data files are authenticated with a public key certificate.
- Offloaded crypto library for asymmetric keys, including the ability to create key-pair, sign and verify data buffer.
- Recovery mechanism
Device Security:
- Separate execution environments—Application processor and network processor run on separate Arm cores
- Initial secure programming (not supported in CC3220R)—Allows for keeping the content confidential on the production line
- Debug security (not supported in CC3220R)
- JTAG lock
- Debug ports lock
- True random number generator
Figure 9-1 shows the high-level structure of the CC3220R device. The network information files (passwords and certificates) are encrypted using a device-specific key.
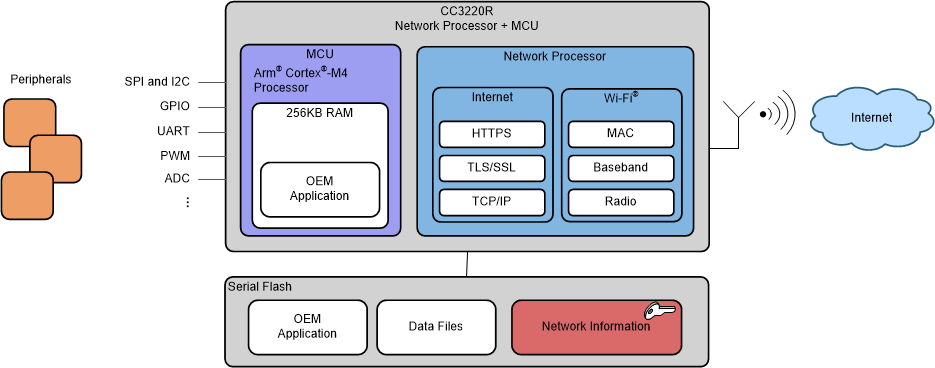 Figure 9-1 CC3220R High-Level Structure
Figure 9-1 CC3220R High-Level StructureFigure 9-2 shows the high-level structure of the CC3220S and CC3220SF devices. The application image, user data, and network information files (passwords, certificates) are encrypted using a device-specific key.
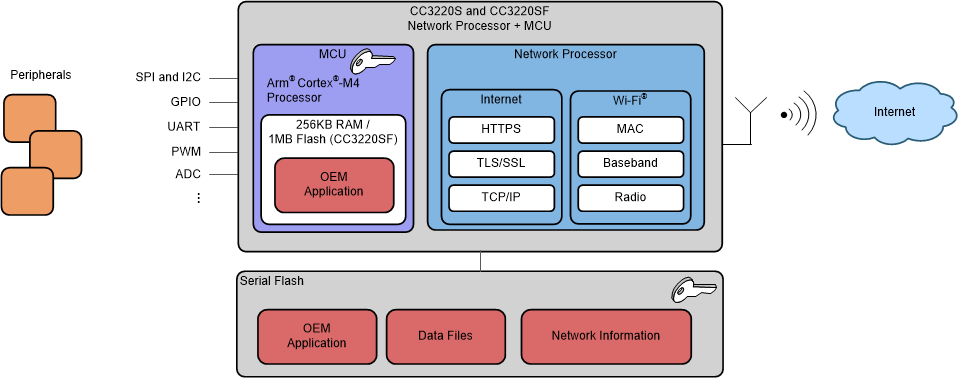 Figure 9-2 CC3220S and CC3220SF High-Level Structure
Figure 9-2 CC3220S and CC3220SF High-Level Structure