ZHCSH41A November 2017 – December 2021 TPS55160-Q1 , TPS55162-Q1 , TPS55165-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 说明(续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics — External Components
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics — Supply Voltage (VINP, VINL pins)
- 7.7 Electrical Characteristics — Reference Voltage (VOS_FB Pin) and Output Voltage (VOUT Pin)
- 7.8 Electrical Characteristics — Buck-Boost
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics — Undervoltage and Overvoltage Lockout
- 7.10 Electrical Characteristics — IGN Wakeup
- 7.11 Electrical Characteristics — Logic Pins PS, IGN_PWRL, SS_EN
- 7.12 Electrical Characteristics – Overtemperature Protection
- 7.13 Electrical Characteristics – Power Good
- 7.14 Switching Characteristics — Reference Voltage (VOS_FB Pin) and Output Voltage (VOUT Pin)
- 7.15 Switching Characteristics — Buck-Boost
- 7.16 Switching Characteristics — Undervoltage and Overvoltage Lockout
- 7.17 Switching Characteristics — IGN Wakeup
- 7.18 Switching Characteristics — Logic Pins PS, IGN_PWRL, SS_EN
- 7.19 Switching Characteristics – Power Good
- 7.20 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.4.3 Power-Up and Power-Down Sequences
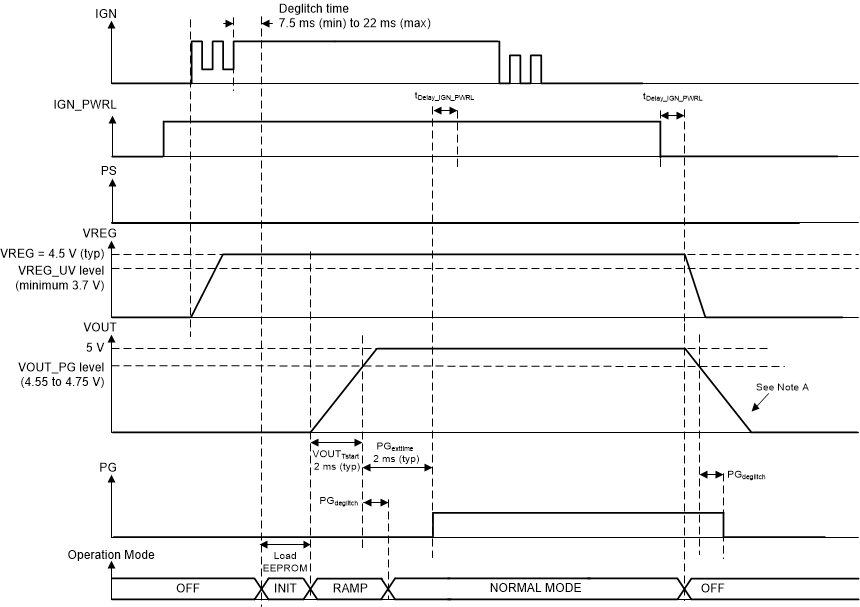
Figure 8-2 shows the power-up and power-down sequence without the usage of the IGN_PWRL pin.
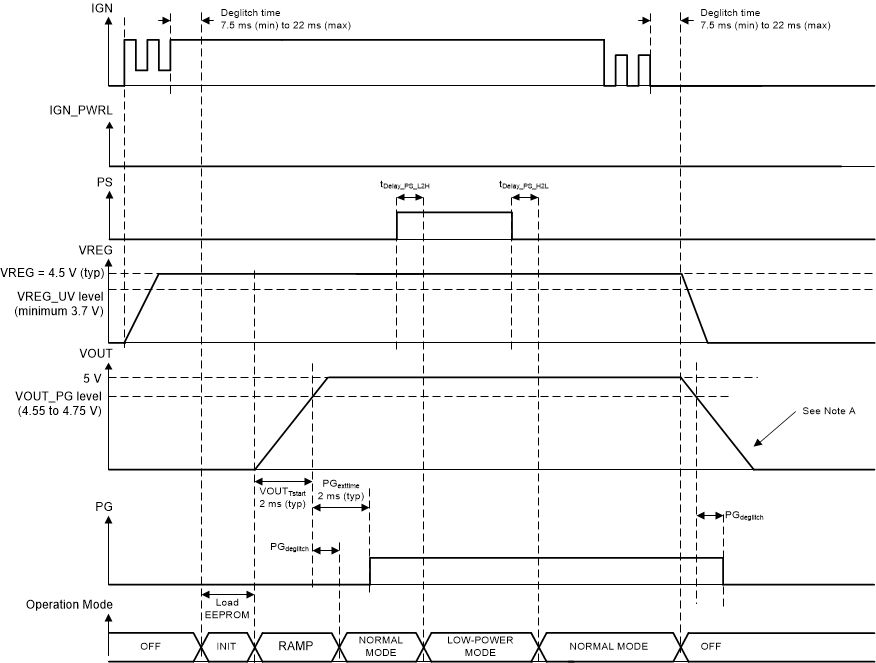
Figure 8-3 shows the power-up and power-down sequence with usage of the IGN_PWRL pin.
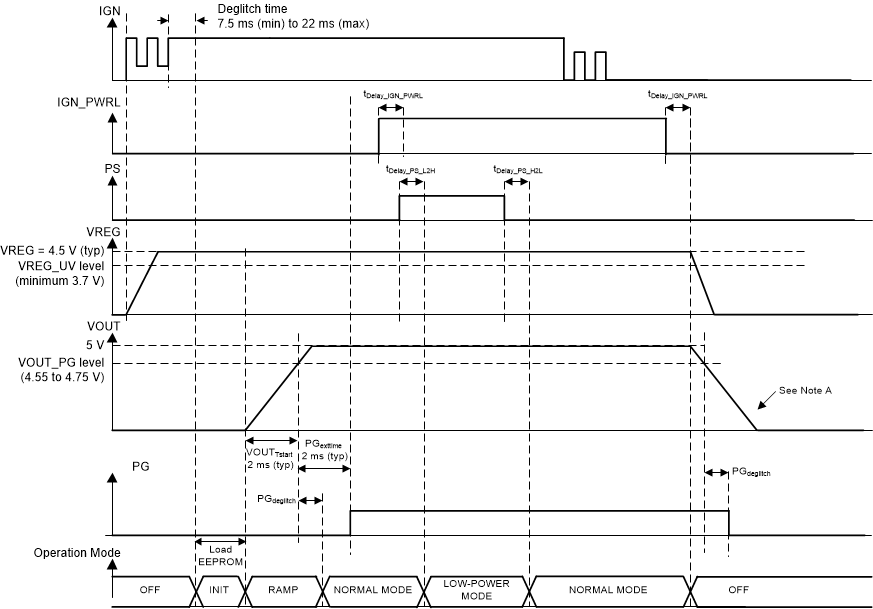
Figure 8-4 shows a power-up and power-down sequence in low-Power mode with the IGN pin low. Figure 8-4 shows that after the device is powered on in the OFF state, the device is in low-power mode when the PS pin is high regardless of what was applied on the IGN and IGN_PWRL input pins.
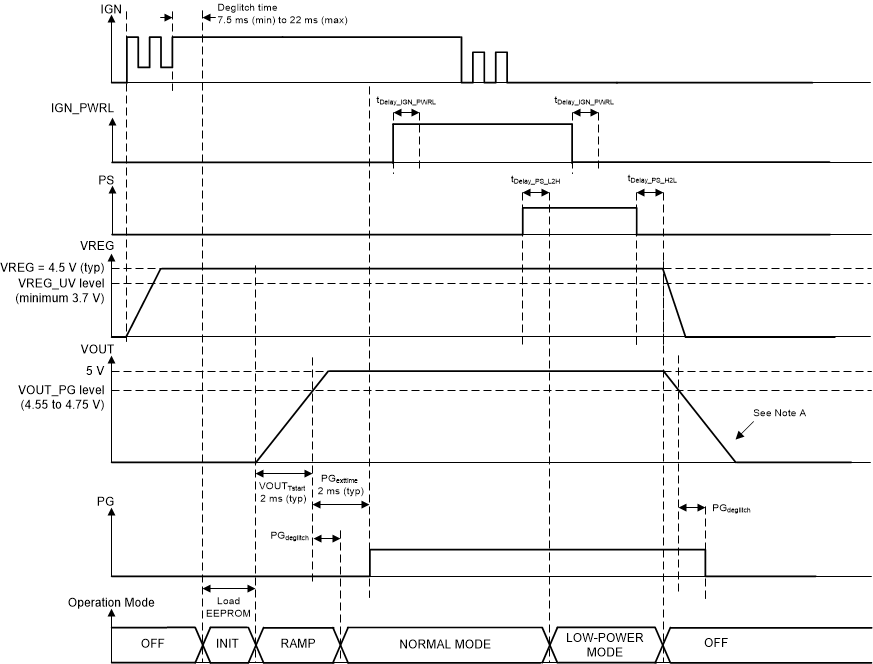
Figure 8-5 shows that when the device starts in the OFF state, the buck-boost converter always enters normal mode first, even when the PS pin was previously set high. The device can only enter low-power mode when the PG output pin is set high. Figure 8-5 also shows that the device does not start-up as long as the IGN pin is low.
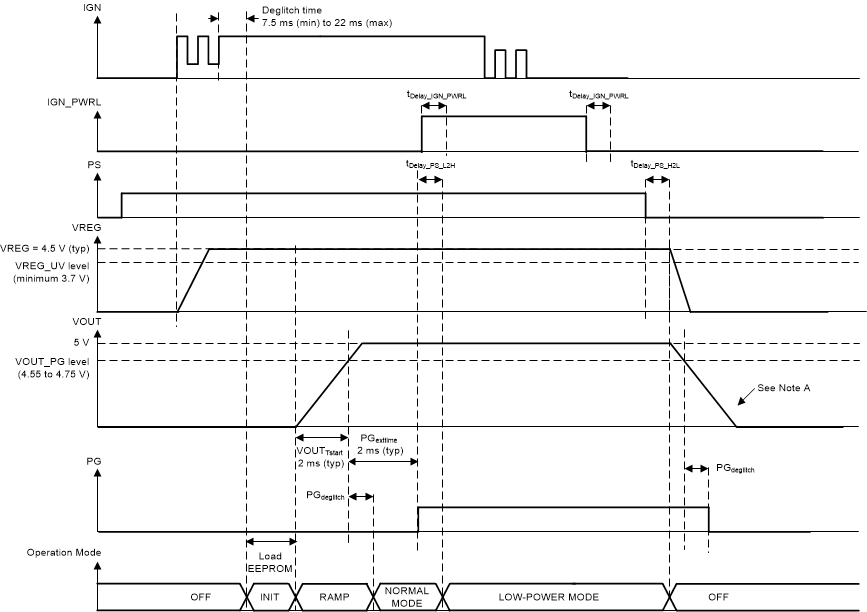
Figure 8-6 shows that the device only can start-up in the OFF state when the IGN pin is high. Setting the IGN_PWRL pin before the IGN pin is high does not start-up the device. Figure 8-6 also shows that the IGN_PWRL signal is only valid after the PG pin is high and the PGDeglitch time has elapsed.