ZHCSK03J August 1983 – November 2023 TLC555
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
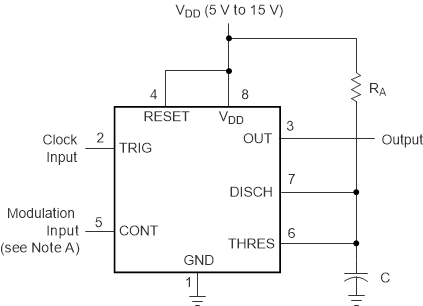
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.4 Thermal Information
- 5.5 Electrical Characteristics: VDD = 2 V for TLC555C, VDD = 3 V for TLC555I
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics: VDD = 5 V
- 5.7 Electrical Characteristics: VDD = 15 V
- 5.8 Timing Characteristics
- 5.9 Typical Characteristics
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
7.2.2 Pulse-Width Modulation
To modify timer operation, apply an external voltage (or current) to CONT to modulate the internal threshold and trigger voltages. Figure 7-3 shows a circuit for pulse-width modulation. A continuous input pulse train triggers the monostable circuit, and a control signal modulates the threshold voltage. Figure 7-4 shows the resulting duty cycle versus control voltage transfer function. Attempting to run under 10% duty cycle can result in inconsistent output pulses. Attempting to run close to 100% duty cycle results in frequency division by 2, then 3, then 4.