ZHCSIJ1E June 1999 – July 2018 LM2574 , LM2574HV
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics for All Output Voltage Versions
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics – 3.3-V Version
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics – 5-V Version
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics – 12-V Version
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics – 15-V Version
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics – Adjustable Version
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2 Typical Applications
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
10.1 Layout Guidelines
The layout is critical for the proper operation of switching power supplies. First, the ground plane area must be sufficient for thermal dissipation purposes. Second, appropriate guidelines must be followed to reduce the effects of switching noise. Switch mode converters are very fast switching devices. In such cases, the rapid increase of input current combined with the parasitic trace inductance generates unwanted L di/dt noise spikes. The magnitude of this noise tends to increase as the output current increases. This noise may turn into electromagnetic interference (EMI) and can also cause problems in device performance. Therefore, take care in the layout to minimize the effect of this switching noise.
The most important layout rule is to keep the AC current loops as small as possible. Figure 33 shows the current flow in a buck converter. The top schematic shows a dotted line which represents the current flow during the top switch ON-state. The middle schematic shows the current flow during the top switch OFF-state. The bottom schematic shows the currents referred to as AC currents. These AC currents are the most critical because they are changing in a very short time period. The dotted lines of the bottom schematic are the traces to keep as short and wide as possible. This also yields a small loop area reducing the loop inductance. To avoid functional problems due to layout, review the PCB layout example. Best results are achieved if the placement of the LM2574 device, the bypass capacitor, the Schottky diode, RFBB, RFBT, and the inductor are placed as shown in the example. In the layout shown, R1 = RFBB and R2 = RFBT. TI also recommends using 2-oz. copper boards or heavier to help thermal dissipation and to reduce the parasitic inductances of board traces. See the application note AN-1229 SIMPLE SWITCHER® PCB Layout Guidelines (SNVA054) for more information.
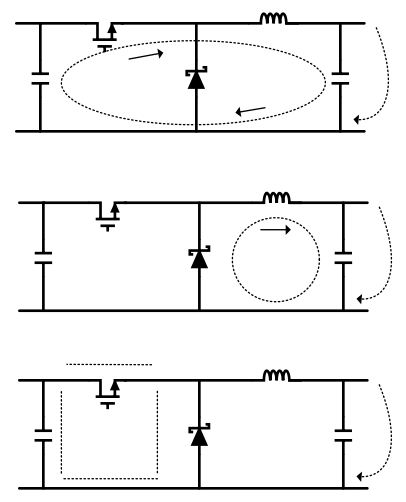 Figure 33. Buck Converter Current Flow
Figure 33. Buck Converter Current Flow