ZHCSK67B June 2017 – August 2019 ADS1287
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5
Programming
- 8.5.1 Serial Interface
- 8.5.2
Commands
- 8.5.2.1 WAKEUP: Wake Up Command
- 8.5.2.2 STANDBY: Standby Mode Command
- 8.5.2.3 SYNC: Synchronize ADC Conversions
- 8.5.2.4 RESET: Reset Command
- 8.5.2.5 RDATAC: Read Data Continuous Mode Command
- 8.5.2.6 SDATAC: Stop Read Data Continuous Mode Command
- 8.5.2.7 RDATA: Read Data Command
- 8.5.2.8 RREG: Read Register Data Command
- 8.5.2.9 WREG: Write Register Data Command
- 8.5.2.10 OFSCAL: Offset Calibration Command
- 8.5.2.11 GANCAL: Gain Calibration Command
- 8.6
Register Map
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 8.6.1.1 ID/CFG: ID, Configuration Register (address = 00h) [reset = x0h]
- 8.6.1.2 CONFIG0: Configuration Register 0 (address = 01h) [reset = 52h]
- 8.6.1.3 CONFIG1: Configuration Register 1 (address = 02h) [reset = 08h]
- 8.6.1.4 High-Pass Filter Corner Frequency (HPFx) Registers (address = 03h, 04h) [reset = 32h, 03h]
- 8.6.1.5 Offset Calibration (OFCx) Registers (address = 05h, 06h, 07h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 8.6.1.6 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCx) Registers (address = 08h, 09h, 0Ah) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 8.6.1
Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
7.1 Noise Performance
SNR and input-referred noise are related parameters that define the ADC effective resolution. Use Equation 1 to calculate SNR from the input-referred noise data:
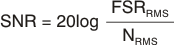
where
Table 1 through Table 4 list SNR and noise performance data. Noise performance data are listed for high-resolution and low-power modes, with and without chop enabled. The noise performance data are representative of typical ADC performance at TA = 25°C. The data are the standard deviation of consecutive ADC conversion results with the ADC inputs shorted over the signal bandwidth of 0.1 Hz to 0.413 fDATA. Repeated noise measurements can yield higher or lower noise results because of the statistical nature of noise.
Noise performance depends on several ADC operating parameters: high-resolution or low-power mode, data rate, PGA gain, and chop mode. Best noise performance is achieved by operating the ADC in high-resolution mode. Noise performance also depends on the data rate. For example, as the data rate decreases, the ADC bandwidth and thus total noise decreases. Using higher gain factors improves input-referred noise, but the calculated SNR decreases because of a 6-dB decrease of input range for each gain step. Chop mode improves noise performance by removing 1/f noise from the PGA. Chop mode is particularly important for lowest noise operation when used with low data rates or high gain. Chop mode is the recommended mode for geophone sensors.
Table 1. High-Resolution Mode Noise Performance (Chop Enabled)(1)
| fDATA (SPS) | SNR (dB) | INPUT-REFERRED NOISE (µVRMS) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAIN | GAIN | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | |
| 62.5 | 125 | 125 | 125 | 124 | 122 | 0.96 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.09 |
| 125 | 122 | 122 | 122 | 121 | 119 | 1.36 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.19 | 0.13 |
| 250 | 119 | 119 | 119 | 118 | 116 | 1.90 | 0.97 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.18 |
| 500 | 116 | 116 | 116 | 115 | 113 | 2.70 | 1.36 | 0.71 | 0.39 | 0.25 |
| 1000 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 112 | 110 | 3.85 | 1.95 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 0.36 |
Table 2. High-Resolution Mode Noise Performance (Chop Disabled)(1)
| fDATA (SPS) | SNR (dB) | INPUT-REFERRED NOISE (µVRMS) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAIN | GAIN | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | |
| 62.5 | 125 | 125 | 123 | 120 | 114 | 0.99 | 0.52 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| 125 | 122 | 122 | 121 | 119 | 114 | 1.36 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0.26 | 0.22 |
| 250 | 119 | 119 | 118 | 116 | 113 | 1.90 | 0.97 | 0.54 | 0.34 | 0.26 |
| 500 | 116 | 116 | 116 | 114 | 111 | 2.70 | 1.38 | 0.73 | 0.43 | 0.32 |
| 1000 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 111 | 109 | 3.85 | 1.95 | 1.03 | 0.60 | 0.41 |
Table 3. Low-Power Mode Noise Performance (Chop Enabled, Offset Enabled)(1)
| fDATA (SPS) | SNR (dB) | INPUT-REFERRED NOISE (µVRMS) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAIN | GAIN | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | |
| 62.5 | 123 | 123 | 122 | 121 | 118 | 1.33 | 0.66 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.14 |
| 125 | 120 | 119 | 119 | 118 | 115 | 1.86 | 0.96 | 0.50 | 0.29 | 0.20 |
| 250 | 117 | 116 | 116 | 115 | 112 | 2.65 | 1.36 | 0.70 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| 500 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 112 | 109 | 3.81 | 1.91 | 1.01 | 0.58 | 0.40 |
| 1000 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 109 | 106 | 5.50 | 2.79 | 1.48 | 0.84 | 0.58 |
Table 4. Low-Power Mode Noise Performance (Chop Disabled, Offset Enabled) (1)
| fDATA (SPS) | SNR (dB) | INPUT-REFERRED NOISE (µVRMS) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAIN | GAIN | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | |
| 62.5 | 122 | 122 | 121 | 118 | 113 | 1.36 | 0.71 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.24 |
| 125 | 119 | 119 | 118 | 116 | 112 | 1.90 | 0.97 | 0.53 | 0.36 | 0.29 |
| 250 | 116 | 116 | 115 | 114 | 110 | 2.67 | 1.38 | 0.74 | 0.46 | 0.35 |
| 500 | 113 | 113 | 113 | 111 | 108 | 3.75 | 1.93 | 1.02 | 0.62 | 0.46 |
| 1000 | 110 | 110 | 110 | 108 | 105 | 5.53 | 2.80 | 1.48 | 0.88 | 0.62 |