-
CC1352P7 具有集成功率放大器的SimpleLink™ 高性能多频带无线 MCU
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Power Supply and Modules
- 7.5 Power Consumption - Power Modes
- 7.6 Power Consumption - Radio Modes
- 7.7 Nonvolatile (Flash) Memory Characteristics
- 7.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 7.9 RF Frequency Bands
- 7.10 861 MHz to 1054 MHz - Receive (RX)
- 7.11 861 MHz to 1054 MHz - Transmit (TX)
- 7.12 861 MHz to 1054 MHz - PLL Phase Noise Wideband Mode
- 7.13 861 MHz to 1054 MHz - PLL Phase Noise Narrowband Mode
- 7.14 Bluetooth Low Energy - Receive (RX)
- 7.15 Bluetooth Low Energy - Transmit (TX)
- 7.16 Zigbee and Thread - IEEE 802.15.4-2006 2.4 GHz (OQPSK DSSS1:8, 250 kbps) - RX
- 7.17 Zigbee and Thread - IEEE 802.15.4-2006 2.4 GHz (OQPSK DSSS1:8, 250 kbps) - TX
- 7.18 Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 7.19 Peripheral Characteristics
- 7.20 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application, Implementation, and Layout
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- 重要声明
CC1352P7 具有集成功率放大器的SimpleLink™ 高性能多频带无线 MCU
1 特性
无线微处理器
- 功能强大的 48MHz Arm® Cortex®-M4F 处理器
- 704KB 闪存程序存储器
- 256KB ROM,用于协议和库函数
- 8KB 高速缓存 SRAM
- 具有奇偶校验功能的 144KB 超低泄漏 SRAM,可实现高度可靠运行
- 双频带 Sub-1GHz 和 2.4GHz 运行
- 动态多协议管理器 (DMM) 驱动程序
- 可编程无线电包括对 2-(G)FSK、4-(G)FSK、MSK、OOK、低功耗 Bluetooth® 5.2、IEEE 802.15.4 PHY 和 MAC 的支持
- 支持无线升级 (OTA)
超低功耗传感器控制器
- 具有 4KB SRAM 的自主 MCU
- 采样、存储和处理传感器数据
- 快速唤醒进入低功耗运行
- 软件定义外设;电容式触控、流量计、LCD
低功耗
- MCU 功耗:
- 2.63mA 有源模式,CoreMark
- 55μA/MHz(运行 CoreMark 时)
- 0.8μA 待机模式,RTC,144KB RAM
- 0.1μA 关断模式,引脚唤醒
- 超低功耗传感器控制器功耗:
- 2MHz 模式下为 25.2μA
- 24MHz 模式下为 701μA
- 无线电功耗:
- RX:5.4mA(在 868MHz 条件下)
- RX:6.4mA(在 2.4GHz 条件下)
- TX:21mA(在 +10dBm 和 2.4GHz 条件下)
- TX:24.9mA(在 +14dBm 和 868MHz 条件下)
- TX:64mA(在 +20dBm 和 915MHz 条件下)
- TX:101mA(在 +20dBm 和 2.4GHz 条件下)
无线协议支持
- Thread、Zigbee®、Matter
- 低功耗 Bluetooth® 5.2
- Wi-SUN®
- mioty®
- Amazon Sidewalk
- 无线 M-Bus
- SimpleLink™ TI 15.4-stack
- 6LoWPAN
- 专有系统
高性能无线电
- -121dBm(在 2.5kbps 远距离模式下)
- -110dBm(在 50kbps、802.15.4、868MHz 时)
- -104dBm(在低功耗 Bluetooth® 为 125kbps 时)
- 高达 +20dBm 的输出功率,具有温度补偿
法规遵从性
- 适用于符合以下标准的系统:
- ETSI EN 300 220 接收器类别1.5 和 2、EN 300 328、EN 303 131、EN 303 204、EN 300 440 类别2 和 3
- FCC CFR47 第 15 部分
- ARIB STD-T108 和 STD-T66
MCU 外设
- 数字外设可连接至任何 GPIO
- 四个 32 位或八个 16 位通用计时器
- 12 位 ADC、200ksps、8 通道
- 8 位 DAC
- 两个比较器
- 可编程电流源
- 两个 UART、两个 SSI、I2C、I2S
- 实时时钟 (RTC)
- 集成温度和电池监控器
信息安全机制
- AES 128 位和 256 位加密加速计
- ECC 和 RSA 公钥硬件加速器
- SHA2 加速器(包括至 SHA-512 的全套装)
- 真随机数发生器 (TRNG)
开发工具和软件
- LP-CC1352P7 开发套件
- SimpleLink™ CC13xx 和 CC26xx 软件开发套件 (SDK)
- 用于简单无线电配置的 SmartRF™ Studio
- 用于构建低功耗检测应用的 Sensor Controller Studio
- SysConfig 系统配置工具
工作温度范围
- 片上降压直流/直流转换器
- 1.8V 至 3.8V 单电源电压
- -40°C 至 +105°C
封装
- 7mm × 7mm RGZ VQFN48 (26 GPIO)
- 符合 RoHS 标准的封装
3 说明
SimpleLink™ CC1352P7 器件是一款多协议、多频带 Sub-1GHz 和 2.4GHz 无线微控制器 (MCU),支持以下协议:Thread、Zigbee®、低功耗 Bluetooth® 5.2、IEEE 802.15.4g、支持 IPv6 的智能对象 (6LoWPAN)、mioty®、Wi-SUN®、专有系统(包括 TI 15.4-Stack(Sub-1GHz 和 2.4GHz))和通过动态多协议管理器 (DMM) 驱动程序实现的并发多协议。CC1352P7 基于 Arm® Cortex® M4F 主处理器,针对电网基础设施、楼宇自动化、零售自动化、个人电子产品和医疗应用中的低功耗无线通信和高级传感功能进行了优化。
CC1352P7 具有由 Arm® Cortex®-M0 驱动的软件定义无线电,支持多个物理层和射频标准。 CC1352P7 支持在 287MHz 至 351MHz、359MHz 至 527MHz、861MHz 至 1054MHz、1076MHz 至 1315MHz 以及 2360MHz 至 2500MHz 频带内运行。通过动态多协议管理器 (DMM) 驱动程序,可在运行时完成 PHY 和频带切换。CC1352P7 具有高效的内置 PA,在 2.4GHz 频带中 TX 支持 +10dBm (21mA) 和 +20dBm (101mA) 的输出功率,在 Sub-1GHz 频带中 TX 支持 +20dBm (64mA) 的输出功率。
在保持 144KB RAM 时,CC1352P7 具有 0.9μA 的低待机电流。除了 Cortex® M4F 主处理器,该器件还具有能够实现快速唤醒功能的自主式超低功耗传感器控制器 CPU。例如,传感器控制器能够在系统电流为 1µA 时进行 1Hz ADC 采样。
CC1352P7 具有低 SER(软错误率)FIT(时基故障),可延长运行寿命。SRAM 奇偶校验功能始终开启,可更大程度地降低因潜在辐射事件导致的损坏风险。许多客户对产品生命周期的要求为 10 至 15 年或者更久,为了达到这一目标,TI 制定了产品生命周期政策,对产品的寿命和供货连续性作出承诺。
CC1352P7 器件是 SimpleLink™ MCU 平台的一部分,包括 Wi-Fi®、低功耗 Bluetooth®、Thread、Zigbee、Wi-SUN®、Amazon Sidewalk、mioty®、Sub-1GHz MCU 和主机 MCU。 CC1352P7 是可扩展产品系列(闪存为 32KB 至 704KB)的一部分,具有引脚对引脚兼容的封装选项。通用 SimpleLink™ CC13xx 和 CC26xx 软件开发套件 (SDK) 及 SysConfig 系统配置工具支持产品系列中各器件之间的迁移。SDK 随附了丰富的软件栈、应用示例和 SimpleLink™ Academy 培训课程。有关更多信息,请查看无线连接。
| 器件型号(1) | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| CC1352P74T0RGZR | VQFN (48) | 7.00mm × 7.00mm |
3.1 功能方框图
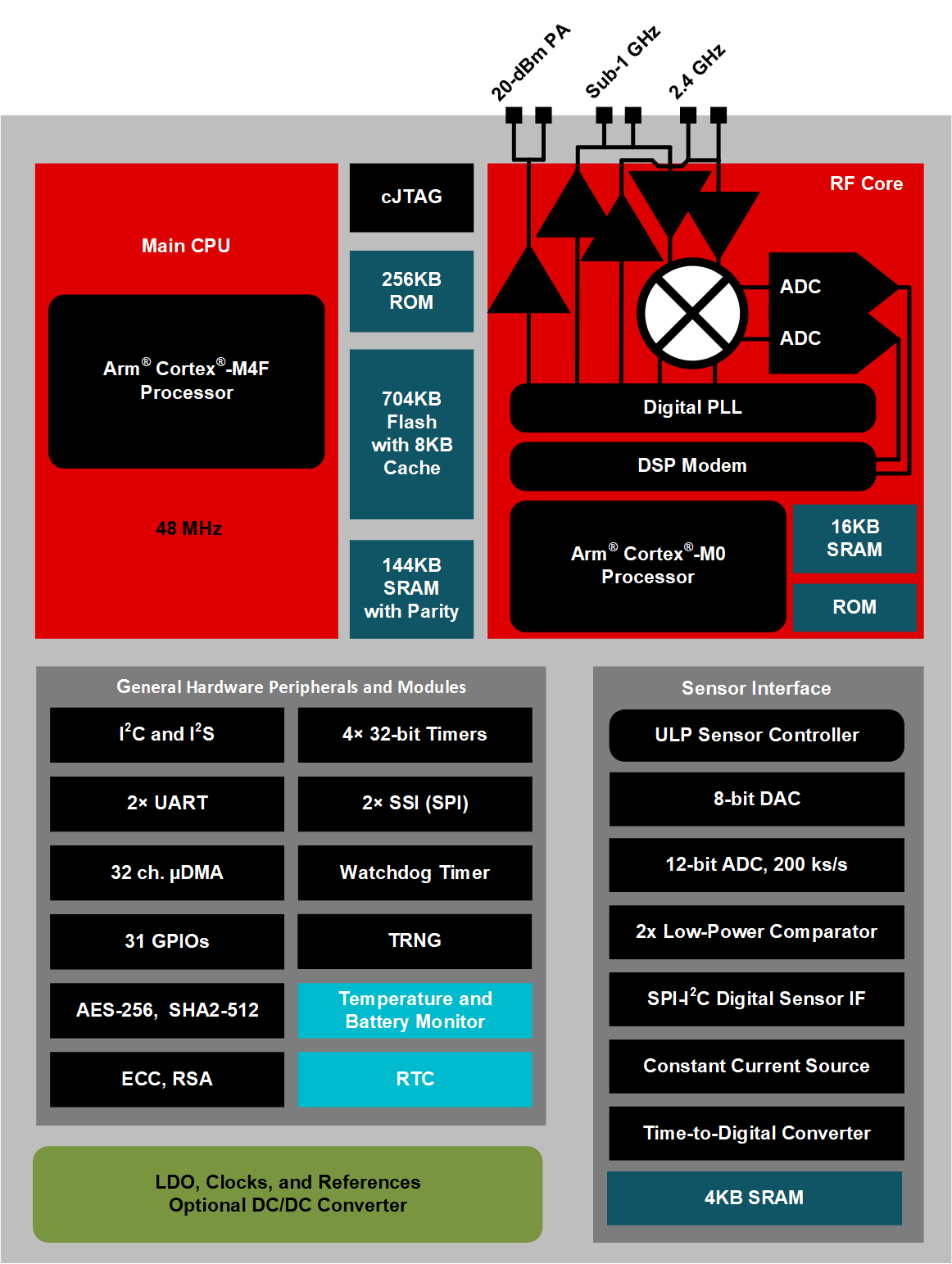 图 3-1 CC1352P7 方框图
图 3-1 CC1352P7 方框图4 Revision History
| DATE | REVISION | NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| November 2021 | * | Initial Release |
5 Device Comparison
| DEVICE | RADIO SUPPORT | FLASH (KB) |
RAM (KB) |
GPIO | PACKAGE SIZE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC1310 | Sub-1 GHz Wireless M-Bus |
32-128 | 16-20 | 10-30 | RGZ (7-mm ×
7-mm VQFN48) RHB (5 mm × 5 mm VQFN32) RSM (4 mm × 4 mm VQFN32) |
| CC1312R | Sub-1 GHz Wi-SUN® Amazon Sidewalk Wireless M-Bus |
352-704 | 80-144 | 30 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC1352P | Multiprotocol Sub-1 GHz Wi-SUN® Amazon Sidewalk Wireless M-Bus Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy Zigbee Thread 2.4 GHz proprietary FSK-based formats +20-dBm high-power amplifier |
352-704 | 80-144 | 26 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC1352R | Multiprotocol Sub-1 GHz Wi-SUN® Wireless M-Bus Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy Zigbee Thread 2.4 GHz proprietary FSK-based formats |
352 | 80 | 28 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC2642R | Bluetooth
5.2 Low Energy 2.4 GHz proprietary FSK-based formats |
352 | 80 | 31 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC2642R-Q1 | Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy | 352 | 80 | 31 | RTC (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC2652R | Multiprotocol Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy Zigbee Thread 2.4 GHz proprietary FSK-based formats |
352-704 | 80-144 | 31 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC2652RB | Multiprotocol Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy Zigbee Thread |
352 | 80 | 31 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
| CC2652P | Multiprotocol Bluetooth 5.2 Low Energy Zigbee Thread 2.4 GHz proprietary FSK-based formats +19.5-dBm high-power amplifier |
352-704 | 80-144 | 26 | RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm VQFN48) |
6 Terminal Configuration and Functions
6.1 Pin Diagram – RGZ Package (Top View)
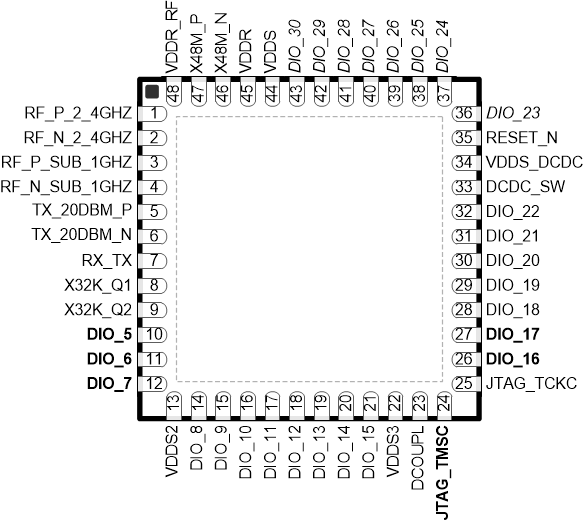 Figure 6-1 RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm) Pinout, 0.5-mm Pitch (Top View)
Figure 6-1 RGZ (7-mm × 7-mm) Pinout, 0.5-mm Pitch (Top View)
The following I/O pins marked in Figure 6-1 in bold have high-drive capabilities:
- Pin 10, DIO_5
- Pin 11, DIO_6
- Pin 12, DIO_7
- Pin 24, JTAG_TMSC
- Pin 26, DIO_16
- Pin 27, DIO_17
The following I/O pins marked in Figure 6-1 in italics have analog capabilities:
- Pin 36, DIO_23
- Pin 37, DIO_24
- Pin 38, DIO_25
- Pin 39, DIO_26
- Pin 40, DIO_27
- Pin 41, DIO_28
- Pin 42, DIO_29
- Pin 43, DIO_30
6.2 Signal Descriptions – RGZ Package
| PIN | I/O | TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAME | NO. | |||
| DCDC_SW | 33 | — | Power | Output from internal DC/DC converter(1) |
| DCOUPL | 23 | — | Power | For decoupling of internal 1.27 V regulated digital-supply (2) |
| DIO_5 | 10 | I/O | Digital | GPIO, high-drive capability |
| DIO_6 | 11 | I/O | Digital | GPIO, high-drive capability |
| DIO_7 | 12 | I/O | Digital | GPIO, high-drive capability |
| DIO_8 | 14 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_9 | 15 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_10 | 16 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_11 | 17 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_12 | 18 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_13 | 19 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_14 | 20 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_15 | 21 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_16 | 26 | I/O | Digital | GPIO, JTAG_TDO, high-drive capability |
| DIO_17 | 27 | I/O | Digital | GPIO, JTAG_TDI, high-drive capability |
| DIO_18 | 28 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_19 | 29 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_20 | 30 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_21 | 31 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_22 | 32 | I/O | Digital | GPIO |
| DIO_23 | 36 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_24 | 37 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_25 | 38 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_26 | 39 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_27 | 40 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_28 | 41 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_29 | 42 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| DIO_30 | 43 | I/O | Digital or Analog | GPIO, analog capability |
| EGP | — | — | GND | Ground – exposed ground pad(3) |
| JTAG_TMSC | 24 | I/O | Digital | JTAG TMSC, high-drive capability |
| JTAG_TCKC | 25 | I | Digital | JTAG TCKC |
| RESET_N | 35 | I | Digital | Reset, active low. No internal pullup resistor |
| RF_P_2_4GHZ | 1 | — | RF | Positive 2.4-GHz RF input signal to LNA during RX Positive 2.4-GHz RF output signal from PA during TX |
| RF_N_2_4GHZ | 2 | — | RF | Negative 2.4-GHz RF input signal to LNA during RX Negative 2.4-GHz RF output signal from PA during TX |
| RF_P_SUB_1GHZ | 3 | — | RF | Positive Sub-1 GHz RF input signal to LNA during RX Positive Sub-1 GHz RF output signal from PA during TX |
| RF_N_SUB_1GHZ | 4 | — | RF | Negative Sub-1 GHz RF input signal to LNA during RX Negative Sub-1 GHz RF output signal from PA during TX |
| RX_TX | 7 | — | RF | Optional bias pin for the RF LNA |
| TX_20DBM_P | 5 | — | RF | Positive Sub-1 GHz or 2.4-GHz high-power TX signal |
| TX_20DBM_N | 6 | — | RF | Negative Sub-1 GHz or 2.4-GHz high-power TX signal |
| VDDR | 45 | — | Power | Internal supply, must be powered from the internal DC/DC converter or the internal LDO(2)(4)(6) |
| VDDR_RF | 48 | — | Power | Internal supply, must be powered from the internal DC/DC converter or the internal LDO(2)(5)(6) |
| VDDS | 44 | — | Power | 1.8-V to 3.8-V main chip supply(1) |
| VDDS2 | 13 | — | Power | 1.8-V to 3.8-V DIO supply(1) |
| VDDS3 | 22 | — | Power | 1.8-V to 3.8-V DIO supply(1) |
| VDDS_DCDC | 34 | — | Power | 1.8-V to 3.8-V DC/DC converter supply |
| X48M_N | 46 | — | Analog | 48-MHz crystal oscillator pin 1 |
| X48M_P | 47 | — | Analog | 48-MHz crystal oscillator pin 2 |
| X32K_Q1 | 8 | — | Analog | 32-kHz crystal oscillator pin 1 |
| X32K_Q2 | 9 | — | Analog | 32-kHz crystal oscillator pin 2 |
6.3 Connections for Unused Pins and Modules
| FUNCTION | SIGNAL NAME | PIN NUMBER | ACCEPTABLE PRACTICE(1) | PREFERRED PRACTICE(1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPIO | DIO_n | 10–12 14–21 26–32 36–43 | NC or GND | NC |
| 32.768-kHz crystal | X32K_Q1 | 8 | NC or GND | NC |
| X32K_Q2 | 9 | |||
| DC/DC converter(2) | DCDC_SW | 33 | NC | NC |
| VDDS_DCDC | 34 | VDDS | VDDS |
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDDS(3) | Supply voltage | –0.3 | 4.1 | V | |
| Voltage on any digital pin(4) | –0.3 | VDDS + 0.3, max 4.1 | V | ||
| Voltage on crystal oscillator pins, X32K_Q1, X32K_Q2, X48M_N and X48M_P | –0.3 | VDDR + 0.3, max 2.25 | V | ||
| Vin | Voltage on ADC input | Voltage scaling enabled | –0.3 | VDDS | V |
| Voltage scaling disabled, internal reference | –0.3 | 1.49 | |||
| Voltage scaling disabled, VDDS as reference | –0.3 | VDDS / 2.9 | |||
| Input level, Sub-1 GHz RF pins (RF_P_SUB_1GHZ and RF_N_SUB_1GHZ) | 10 | dBm | |||
| Input level, 2.4 GHz RF pins (RF_P_2_4GHZ and RF_N_2_4GHZ) | 5 | dBm | |||
| Tstg | Storage temperature | –40 | 150 | °C | |
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VESD | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS001(1) | All pins | ±2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JESD22-C101(2) | All pins | ±500 | V | ||
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating ambient temperature(1)(3) | –40 | 105 | °C | |
| Operating junction temperaturehrefhref | –40 | 115 | °C | |
| Operating supply voltage (VDDS) | 1.8 | 3.8 | V | |
| Operating supply voltage (VDDS), boost mode |
VDDR = 1.95 V +14 dBm RF output sub-1 GHz power amplifier |
2.1 | 3.8 | V |
| Rising supply voltage slew rate | 0 | 100 | mV/µs | |
| Falling supply voltage slew rate(2) | 0 | 20 | mV/µs | |
7.4 Power Supply and Modules
| PARAMETER | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VDDS Power-on-Reset (POR) threshold | 1.1 - 1.55 | V | |||
| VDDS Brown-out Detector (BOD) (1) | Rising threshold | 1.77 | V | ||
| VDDS Brown-out Detector (BOD), before initial boot (2) | Rising threshold | 1.70 | V | ||
| VDDS Brown-out Detector (BOD) (1) | Falling threshold | 1.75 | V |
7.5 Power Consumption - Power Modes
| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | TYP | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core Current Consumption | ||||
| Icore | Reset and Shutdown | Reset. RESET_N pin asserted or VDDS below power-on-reset threshold | 110 | nA |
| Shutdown. No clocks running, no retention | 110 | |||
| Standby without cache retention |
RTC running, CPU,
144KB RAM and (partial) register retention. RCOSC_LF |
0.8 | µA | |
| RTC running, CPU,
64KB RAM and (partial) register retention. RCOSC_LF |
0.7 | µA | ||
| RTC running, CPU,
144KB RAM and (partial) register retention XOSC_LF |
0.9 | µA | ||
| Standby with cache retention |
RTC running, CPU,
144KB RAM and (partial) register retention. RCOSC_LF |
1.9 | µA | |
| RTC running, CPU,
144KB RAM and (partial) register retention. XOSC_LF |
2.0 | µA | ||
| Idle | Supply Systems and
RAM powered RCOSC_HF |
590 | µA | |
| Active | MCU running
CoreMark at 48 MHz RCOSC_HF |
2.63 | mA | |
| Peripheral Current Consumption | ||||
| Iperi | Peripheral power domain | Delta current with domain enabled | 39 | µA |
| Serial power domain | Delta current with domain enabled | 2.6 | ||
| RF Core | Delta current with
power domain enabled, clock enabled, RF core idle |
89 | ||
| µDMA | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle | 57 | ||
| Timers | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle(3) | 97 | ||
| I2C | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle | 9.2 | ||
| I2S | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle | 22 | ||
| SSI | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle(2) | 50 | ||
| UART | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle(1) | 110 | ||
| CRYPTO (AES) | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle | 16 | ||
| PKA | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle | 59 | ||
| TRNG | Delta current with clock enabled, module is idle | 20 | ||
| Sensor Controller Engine Consumption | ||||
| ISCE | Active mode | 24 MHz, infinite loop | 701 | µA |
| Low-power mode | 2 MHz, infinite loop | 25.2 | ||