ZHCSGZ1 October 2017 LMT84-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
1 特性
- LMT84-Q1 符合 AEC-Q100 标准且适用于汽车 应用:
- 器件温度等级 0:–40°C 至 +150°C
- 器件人体放电模型 (HBM) 静电放电 (ESD) 分类等级 2
- 器件 CDM ESD 分类等级 C6
- 非常精确:典型值 ±0.4°C
- 1.5V 低压运行
- -5.5mV/°C 的平均传感器增益
- 5.4µA 低静态电流
- 宽温度范围:–50°C 至 150°C
- 输出受到短路保护
- 具有 ±50µA 驱动能力的推挽输出
- 封装尺寸兼容符合行业标准的 LM20/19 和 LM35 温度传感器
- 具有成本优势的热敏电阻替代产品
2 应用
- 汽车
- 信息娱乐系统与仪表组
- 动力传动系统
- 烟雾和热量探测器
- 无人机
- 电器
3 说明
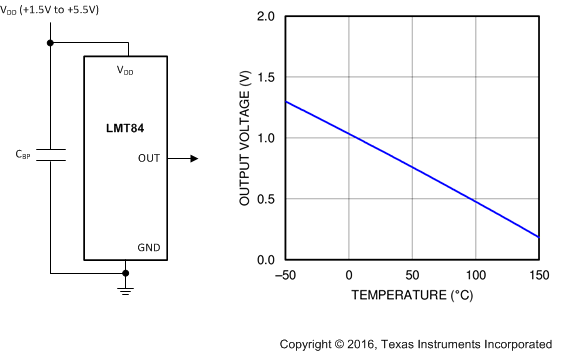
LMT84-Q1 是一款精密 CMOS 温度传感器,其典型精度为 ±0.4°C(最大值为 ±2.7°C),且线性模拟输出电压与温度成反比关系。1.5V 工作电源电压、5.4μA 静态电流和 0.7ms 开通时间可实现有效的功率循环架构,以最大限度地降低无人机和传感器节点等电池供电 应用 的功耗。LMT84-Q1 器件符合 AEC-Q100 0 级标准,在整个工作温度范围内可保持 ±2.7°C 的最大精度,且无需校准;因此 LMT84-Q1 适用于汽车 应用, 例如信息娱乐系统、仪表组和动力传动系统。 得益于宽工作范围内的精度和其他 特性, 使得 LMT84-Q1 成为热敏电阻的优质替代产品。
对于具有不同平均传感器增益和类似精度的器件,请参阅 类似替代器件
热时间常量
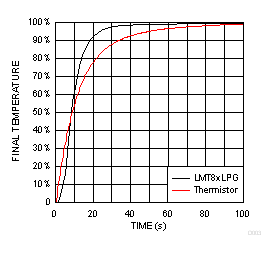
* 快速热响应 NTC
输出电压与温度间的关系