TIDUEB2A July 2022 – July 2022
- Description
- Resources
- Features
- Applications
- 5
- 1System Description
-
2System Overview
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2
Design Considerations
- 2.2.1 Power Multiplexing Circuit Design Parameters
- 2.2.2 Input Connections and Filter
- 2.2.3 Reverse Polarity Protection
- 2.2.4 Battery Charger Input
- 2.2.5 Battery Ideal Diode-OR
- 2.2.6 Input and Battery Switchover Mechanics
- 2.2.7 LM74800 (U1) HGATE
- 2.2.8 Battery LM74800 HGATE
- 2.2.9 BQ25731 Design Considerations
- 2.2.10 BQ25731 Component Selection
- 2.2.11 ILIM Circuit
- 2.2.12 MCU and I2C Bus Design Considerations
- 2.2.13 MSP430FR2475
- 2.2.14 I2C Bus Overview
- 2.2.15 MSP430 Connectors
- 2.2.16 MSP430 Power Supply
- 2.2.17 Sensing Circuits
- 2.2.18 Current Sensing
- 2.2.19 Voltage Sensing
- 2.2.20 Input Comparators
- 2.2.21 Software Flow Chart
- 2.3 Highlighted Products
- 3Hardware, Testing Requirements, and Test Results
- 4Design and Documentation Support
- 5Revision History
2.2.18 Current Sensing
Two INA213B devices are used for current sensing in this design. The INA213 is a current-shunt monitor design for both high- and low-side current measurements. Both of these devices are supplied by 3.3 V, referenced to ground, and provide a gain of 50 V/V. U2 measures the current across the 2-mΩ sense resistor R1, which provides an input current measurement for both the system rail and battery charge currents. U4 measures the current across the 2-mΩ sense resistor R2, which provides a measurement of the current on the system output rail.
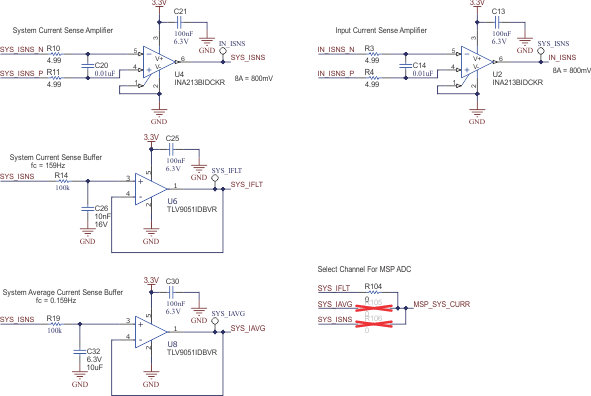 Figure 2-7 Current Sensing
Schematic
Figure 2-7 Current Sensing
SchematicThere are also two current-sense buffers that are used to filter the system current rail. The buffer including U6 includes a low-pass filter with a corner frequency of 159 Hz. This provides the MCU with an accurate measurement of the system current while mitigating high-frequency noise. The buffer including U8 includes a low-pass filter with a corner frequency of 0.159 Hz. This provides the MCU with an average current signal over about 6 seconds.
The MCU only has one ADC pin available for current sensing so a 0-Ω resistor was added in series with each of these outputs to provide the ability to manually select between which current sense output is delivered to the MCU.