SWRA725 November 2021 AWR2944 , IWR2944
3 Localization and Mitigation on the Hardware Accelerator (HWA)
With the theory in place, the methods available on devices like the AWR294x for localization and mitigation of interference are discussed. Localization is defined as the process of finding interfered regions in ADC data, while Mitigation refers to the process of healing the damaged region.
The radar hardware accelerator [2] (or HWA) is collection of accelerators for common radar signal processing options. These accelerators are divided into four different cores (Figure 3-1): FFT, CFAR, Compression/Decompression, and Local maxima. The interference modules are part of the FFT Engine – and are placed before the FFT engine. This is so that the process of interference mitigation is performed prior to and inline with the FFT. All modules are streaming engines – every cycle they take in one sample as input and give one sample as output. Hence, the additional cost of interference mitigation is only a few additional cycles.
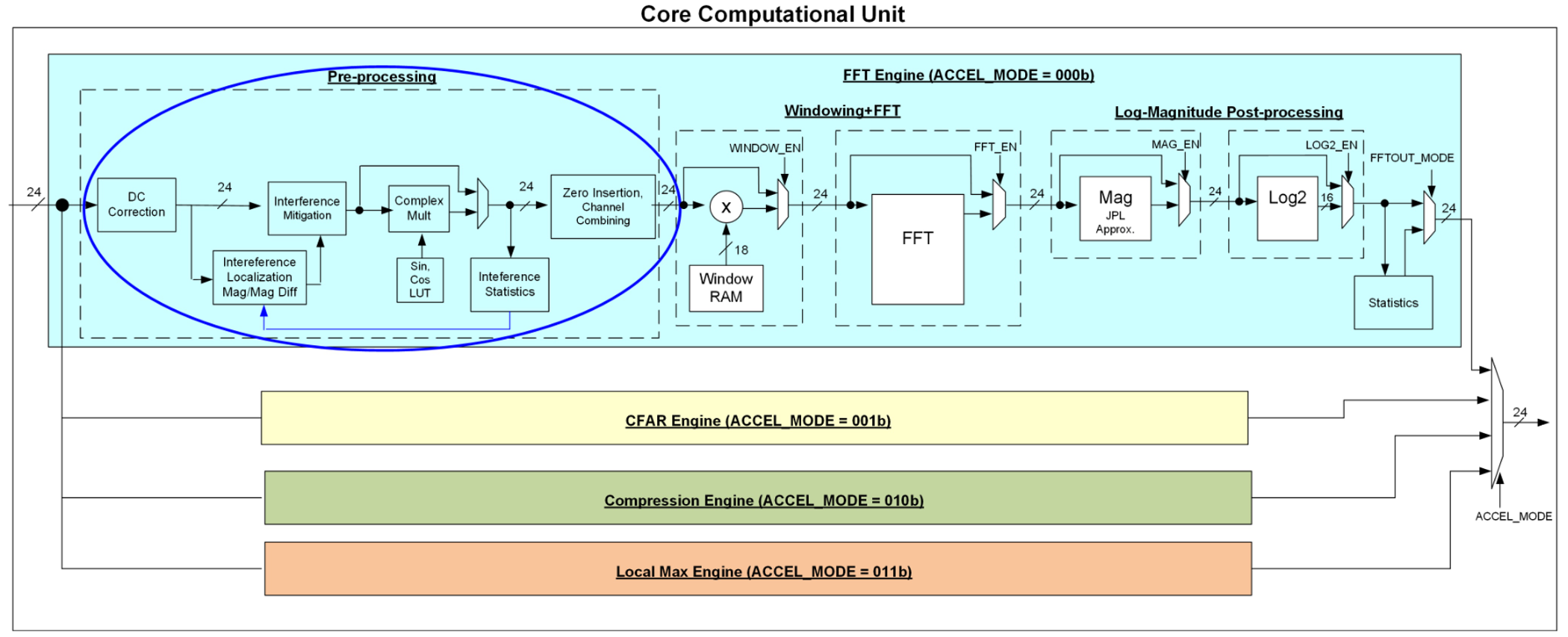
The modules related to interference are:
- Interference Statistics Module - computes statistics on the ADC data and generates thresholds.
- Interference Localization Module – uses the thresholds to find outliers.
- Interference Mitigation Module - removes outliers using one of three methods.
The process of interference mitigation is a two pass process (Figure 3-2):
- In the first pass, statistics are computed on the ADC. Interference Localization and Mitigation is a two pass method.
- In the second pass, the statistics are used to generate thresholds. Then, samples that cross the threshold are marked as corrupted/interfered with in the interference localization module. This information is then provided to the interference mitigation module.
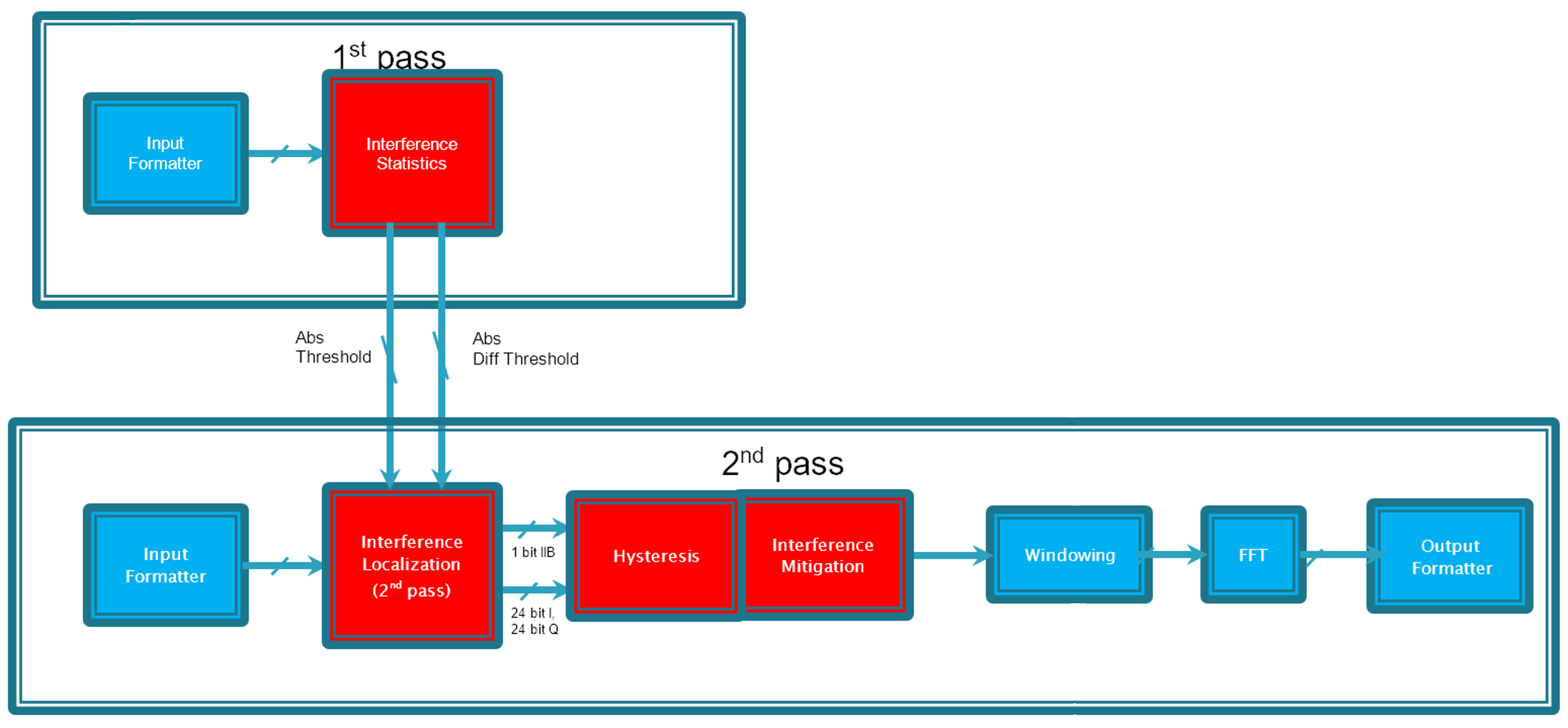 Figure 3-2 Interference Mitigation
Flow
Figure 3-2 Interference Mitigation
Flow