SWRA654A December 2019 – April 2020 CC2652R , CC2652R7 , CC2652RSIP
3.1 Zigbee
Zigbee is a wireless communication system operating at 2.4 GHz, which targets battery-powered applications. There are three logical device types for Zigbee networks, Coordinator, Router, and End Device. The role of the Coordinator is to start a network and manage the keys; it also handles all devices entering and leaving the network. Besides that, it behaves like a Router device. The Router is active at all times to ensure that other devices can join the network. Routers also have child devices, End Devices, which they assist with the communication. The End Devices are usually asleep, except when communicating with its parent Router, because they have no responsibility for maintaining the network infrastructure. Figure 3 shows a typical Zigbee network with one Coordinator in black, multiple Routers in red, and multiple End Devices in white.
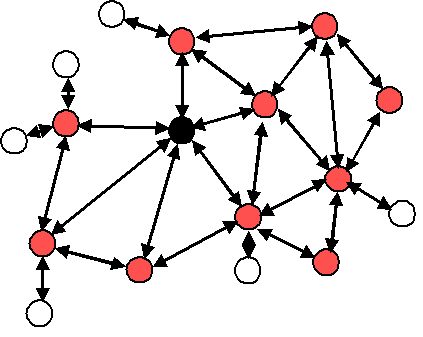 Figure 3. A Typical Zigbee Network
Figure 3. A Typical Zigbee Network Zigbee networks use a mesh structure to transmit data over long distances. The data passes through multiple intermediary devices to reach the final destination in the remote device. The remote devices can be different kinds of sensors, for example, temperature, smoke detector, audio detection, and so forth. They can also be used for smart home applications such as ventilation.
The TI implementation of Zigbee is called the Z-stack and is a part of the CC13x2/CC26x2 SDK. For more information, see the Z-Stack User's Guide.