SNAA333 April 2020 CDCE6214-Q1
- eAVB Media Clock Synchronization Using CDCE6214-Q1 Clock Generator
4.2 Listener and Media Clock Synchronization
A simplified Listener block diagram is shown below:
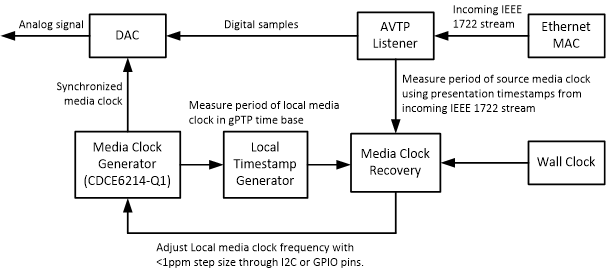 Figure 5. AVB Listener Simplified Block Diagram
Figure 5. AVB Listener Simplified Block Diagram This diagram explains how a Listener extracts presentation timestamps and recovers the source media clock from incoming 1722 streams generated by a Talker. The period of the source media clock in the gPTP time base can be estimated by the time difference between two presentation timestamps divided by the number of samples in between. Continually performing this calculation and applying appropriate filtering techniques yields an accurate measurement of the source's media clock period.
Similarly, the local media clock generator (CDCE6214-Q1) output can be timestamped with local time base which is then translated to gPTP time base, and its period can also be accurately measured. After comparing the two clock periods, the Media Clock Recovery module continually generates I2C/GPIO commands to increment or decrement output frequency of the CDCE6214-Q1 device so that the local media clock is synchronized to the source media clock.