SLVAF70 September 2021 TPS62130
1 Introduction
Most enterprise SSDs, including server and data-center SSDs, rely on power failure functions that monitor the system power rail (12 V) from the host and generate an early warning signal to the SSD controller if the system voltage drops below a predetermined threshold. Additionally, a hold-up circuit is implemented to protect against loss of data upon power failures. The hold-up time is the amount of time that the system can continue to run without resetting or rebooting during a power interruption, and a high-capacity super capacitor or a bank of discrete capacitors can be used for the proper hold-up time function.
Figure 1-1 shows the typical application circuit of the TPS62130 to get 3.3-V output from 5-V input. The recommended input voltage range of the TPS62130 is from 3 V to 17 V, and the device will stop switching if the input voltage of the TPS62130 goes down to below 3.0 V. By adding a few external components, this application report shows how the buck converter with the TPS62130 is working even though the 5-V input voltage goes down to below 3 V, and this increases the hold-up time eventually regulating 3.3-V output properly.
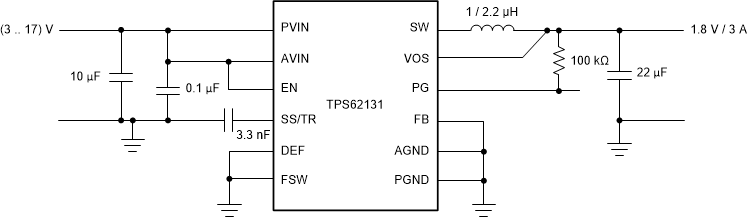
Figure 1-1 Typical TPS62130 Application Circuit