SLVAEJ1 January 2020 TPS25830-Q1 , TPS25830A-Q1 , TPS25831-Q1 , TPS25832-Q1 , TPS25833-Q1 , TPS25840-Q1 , TPS25842-Q1
2.2 Evaluating Loop Characteristics With Cable Compensation Function
When the cable compensation function is used, the setup shown in Figure 3 cannot cut off the loop completely. This method cannot measure the loop characteristic correctly when the cable compensation function is enabled. For this case, fast load transient is used to evaluate loop characteristics. Generally speaking, when the phase margin is greater than 45 °, the overshoot of the load transient will be smaller, and the overshoot callback will be smooth [1]. For poor loop design, its overshoot of load transient will be higher, and the overshoot callback may have ringing. The load transient performance of TPS2583x-Q1 is compared with and without cable compensation function. Figure 5 is the load transient result of no cable compensation function. Figure 6 is the load transient result with cable compensation function. The overshoots and undershoots are summarized in Table 1.
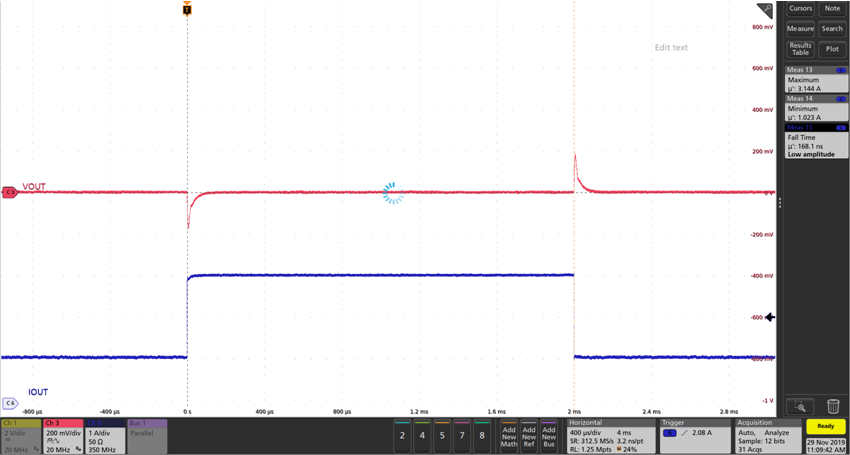 Figure 5. Load Transient Result of TPS2583x-Q1 Without Cable Compensation
Figure 5. Load Transient Result of TPS2583x-Q1 Without Cable Compensation 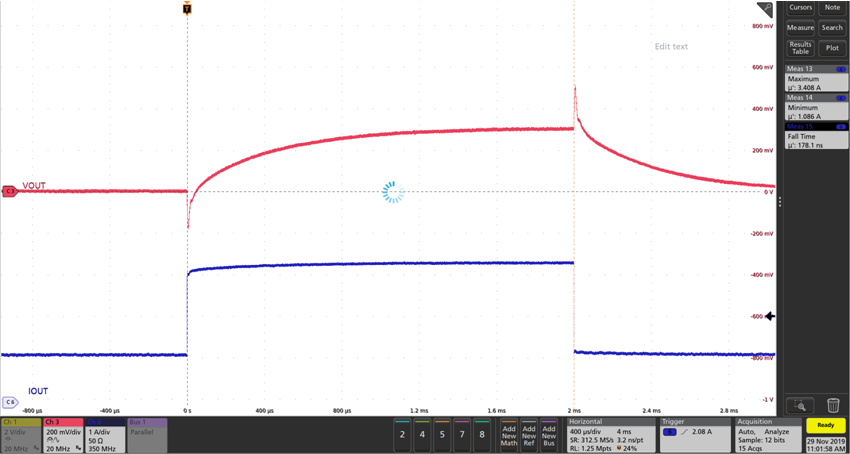 Figure 6. Load Transient Result of TPS2583x-Q1 With Cable Compensation
Figure 6. Load Transient Result of TPS2583x-Q1 With Cable Compensation Table 1. Overshoot and Undershoot Result
| Overshoot (mV) | Undershoot (mV) | |
|---|---|---|
| No cable compensation | 192.2 | 175.6 |
| With cable compensation | 201.2 | 183.6 |