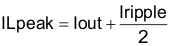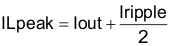ZHCSD91B January 2015 – January 2022 TPS65251-1 , TPS65251-2 , TPS65251-3
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Adjustable Switching Frequency
- 7.3.2 Synchronization
- 7.3.3 Out-of-Phase Operation
- 7.3.4 Delayed Start-Up
- 7.3.5 Soft-Start Time
- 7.3.6 Adjusting the Output Voltage
- 7.3.7 Input Capacitor
- 7.3.8 Bootstrap Capacitor
- 7.3.9 Error Amplifier
- 7.3.10 Slope Compensation
- 7.3.11 Power Good
- 7.3.12 3.3-V and 6.5-V LDO Regulators
- 7.3.13 Current Limit Protection
- 7.3.14 Overvoltage Transient Protection (OVP)
- 7.3.15 Thermal Shutdown
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.2.1 Loop Compensation Circuit
- 8.2.2.2 Selecting the Switching Frequency
- 8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
- 8.2.2.4 Output Capacitor
- 8.2.2.5 Input Capacitor
- 8.2.2.6 Soft-Start Capacitor
- 8.2.2.7 Bootstrap Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.2.8 Adjustable Current Limiting Resistor Selection
- 8.2.2.9 Output Voltage and Feedback Resistors Selection
- 8.2.2.10 Compensation
- 8.2.2.11 3.3-V and 6.5-V LDO Regulators
- 8.2.3 Application Curves
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.2.2.3 Output Inductor Selection
To calculate the value of the output inductor, use Equation 15. KIND is a coefficient that represents the amount of inductor ripple current relative to the maximum output current. In general, KIND is normally from 0.1 to 0.3 for the majority of applications.
For this design example, use KIND = 0.2 and the inductor value is calculated to be 3.6 µH. For this design, a nearest standard value was chosen: 4.7 µH. For the output filter inductor, it is important that the RMS current and saturation current ratings not be exceeded. The RMS and peak inductor current can be found from Equation 16 and Equation 17.
Equation 15. 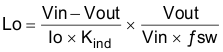
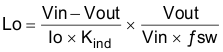
Equation 16. 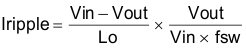
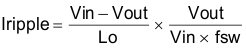
Equation 17. 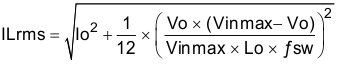
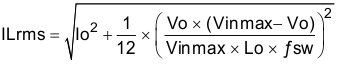
Equation 18.