ZHCSGX8E march 2017 – june 2023 TPS61253A , TPS61253E
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
9.2.2.2 Inductor Selection
A boost converter normally requires two main passive components for storing energy during the conversion, an inductor and an output capacitor. It is advisable to select an inductor with a saturation current rating higher than the possible peak current flowing through the power switches.
The inductor peak current varies as a function of the load, the input and output voltages. It can be estimated using Equation 4.
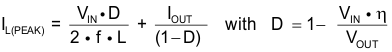
Selecting an inductor with insufficient saturation current can lead to excessive peak current in the converter. This could eventually harm the device and reduce its reliability. When selecting the inductor, as well as the inductance, parameters of importance are: the maximum current rating, series resistance, and operating temperature. The inductor DC current rating should be greater (by some margin) than the maximum input average current, refer to Equation 5 for more details.
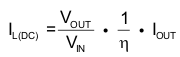
The TPS61253x series of step-up converters could support operating with an effective inductance in the range of 0.33 µH to 1.3 µH and with effective output capacitance in the range of 3.5 µF to 30 µF. The internal compensation is optimized for an output filter of the inductance between 0.56 µH and 1 µH and output capacitance from 5 µF to10 µF. Larger or smaller inductor and capacitor values can be used to optimize the performance of the device for specific operating conditions. For more details, see Section 9.2.2.5.
In high-frequency converter applications, the efficiency is essentially affected by the inductor AC resistance (that is, quality factor) and to a smaller extent by the inductor DCR value. To achieve high efficiency operation, care should be taken in selecting inductors featuring a quality factor above 25 at the switching frequency. Increasing the inductor value produces lower RMS current, but degrades transient response. For a given physical inductor size, increased inductance usually results in an inductor with lower saturation current.
The total losses of the coil consist of both the losses in the DC resistance, R(DC) , and the following frequency dependent components:
- The losses in the core material (magnetic hysteresis loss, especially at high switching frequencies)
- Additional losses in the conductor from the skin effect (current displacement at high frequencies)
- Magnetic field losses of the neighboring windings (proximity effect)
- Radiation losses
The following inductor series from different suppliers have been used with the TPS61253x converters.
| MANUFACTURER(1) | SERIES | DESCRIPTION | DIMENSIONS (W × L × H) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colicraft | XEL3515-561MEB | 0.56 μH, 21.5 mΩ DCR, 6.5 A Isat | 3.2 mm × 3.5 mm × 1.5 mm |
| Murata | 1277AS-H-1R0M=P2 | 1 μH, 34 mΩ DCR, 4.6 A Isat | 3.2 mm × 2.5 mm × 1.2 mm |