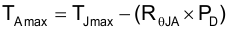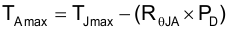ZHCSFK1C July 2016 – June 2018
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.2.2.3 Thermal Calculation
Equation 1 shows the thermal calculation.
Equation 1. 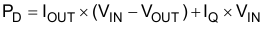
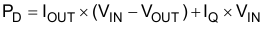
where
- PD = continuous power dissipation
- IOUT = output current
- VIN = input voltage
- VOUT = output voltage
- Because IQ << IOUT, the term IQ × VIN is always ignored
For a device under operation at a given ambient air temperature (TA), use Equation 2 to calculate the junction temperature (TJ).
Equation 2. 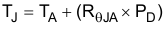
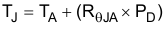
where
- ZθJA = junction-to-ambient air thermal impedance
Use Equation 3 to calculate the rise in junction temperature because of power dissipation.
Equation 3. 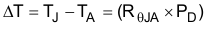
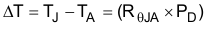
For a given maximum junction temperature (TJmax), use Equation 4 to calculate the maximum ambient air temperature (TAmax) at which the device can operate.
Equation 4.