ZHCSPF9C December 2022 – August 2024 TLV2365 , TLV365
PRODUCTION DATA
8.1.2 达到零伏输出电平
某些单电源应用要求运算放大器输出的摆幅介于 0V 至正满标量程电压之间,而且需要出色的精度。一个示例是使用运算放大器驱动一个输入范围为 0V 至 3.3V 的单电源 ADC。具有极轻输出负载的轨至轨输出放大器可以达到非常接近于 0V(或在高端接近 V+)的输出电平,但不会完全等于 0V。而且,当需要的负载电流增加时,与 0V 之间的偏差也变得更大。偏离增加是受到 CMOS 输出级的限制所致。
在放大器输出和负电压源之间连接一个下拉电阻器时,TLVx365 可以实现 0V 的输出电平,甚至是比 0V 低数毫伏。图 8-3 显示了使用此技术的电路。
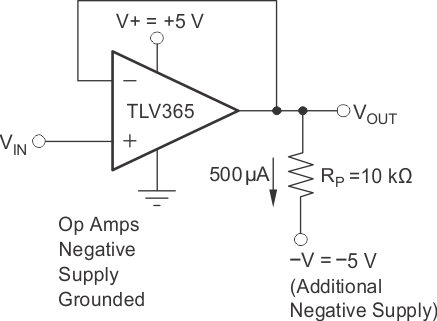 图 8-3 摆动到接地
图 8-3 摆动到接地当 TLVx365 作为单位增益缓冲器连接时,需要大概 500μA 的下拉电流。下拉电阻器 RL 的计算方式是 RL = [(VO − VNEG) / (500μA)]。
图 8-4 展示了失调电压与输出摆幅间的关系。

| VS = ±2.75V |