SNVS009H November 1999 – March 2016 LM2665
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The LM2665 CMOS charge-pump voltage converter operates as a voltage doubler for an input voltage in the range of 2.5 V to 5.5 V. Two low-cost capacitors and a diode (needed during start-up) are used in this circuit to provide up to 40 mA of output current. The LM2665 can also work as a voltage divider to split a voltage in the range of 1.8 V to 11 V in half.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
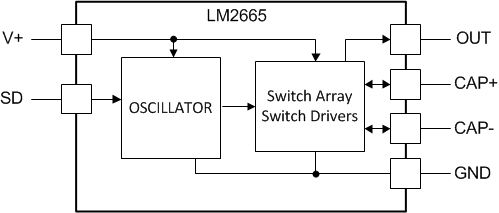
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Circuit Description
The LM2665 contains four large CMOS switches which are switched in a sequence to double the input supply voltage. Energy transfer and storage are provided by external capacitors. Figure 10 illustrates the voltage conversion scheme. When S2 and S4 are closed, C1 charges to the supply voltage V+. During this time interval, switches S1 and S3 are open. In the next time interval, S2 and S4 are open; at the same time, S1 and S3 are closed, the sum of the input voltage V+ and the voltage across C1 gives the 2-V+ output voltage when there is no load. The output voltage drop when a load is added is determined by the parasitic resistance (RDS(on) of the MOSFET switches and the ESR of the capacitors) and the charge transfer loss between capacitors. Details are discussed in Application and Implementation.
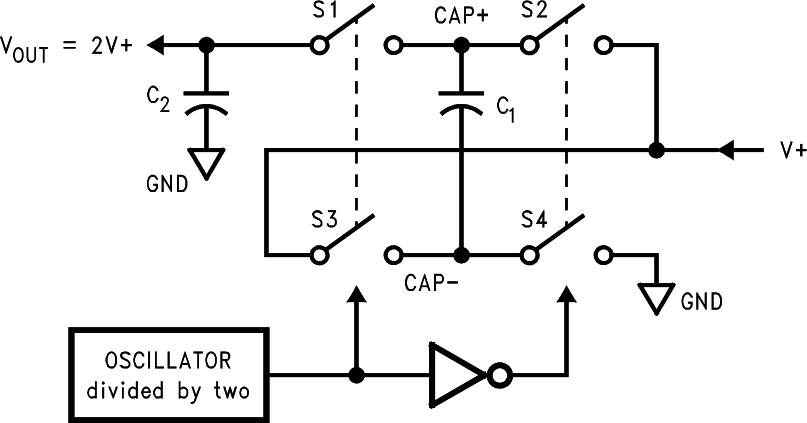 Figure 10. Voltage Doubling Principle
Figure 10. Voltage Doubling Principle
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Shutdown Mode
A shutdown (SD) pin is available to disable the device and reduce the quiescent current to 1 µA. In normal operating mode, the SD pin is connected to ground. The device can be brought into the shutdown mode by applying to the SD pin a voltage greater than 40% of the V+ pin voltage.