ZHCSFV6E august 2016 – november 2020 DS90UB933-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.6 Recommended Serializer Timing For PCLK
- 6.7 AC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C-Compatible
- 6.8 Bidirectional Control Bus DC Timing Specifications (SCL, SDA) - I2C-Compatible
- 6.9 Serializer Switching Characteristics
- 6.10 Timing Diagrams
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
7.5.2 Description of Bidirectional Control Bus and I2C Modes
The I2C-compatible interface allows programming of the DS90UB933-Q1, DS90UB934-Q1, DS90UB964-Q1, or an external remote device (such as image sensor) through the bidirectional control channel. Register programming transactions to/from the DS90UB933/934/964 chipset are employed through the clock (SCL) and data (SDA) lines. These two signals have open drain I/Os, and both lines must be pulled up to V(VDDIO) by an external resistor. Pullup resistors or current sources are required on the SCL and SDA busses to pull them high when they are not being driven low. A logic LOW is transmitted by driving the output low. Logic HIGH is transmitted by releasing the output and allowing it to be pulled up externally. The appropriate pullup resistor values depend upon the total bus capacitance and operating speed. The DS90UB933-Q1 I2C bus data rate supports up to 400 kbps according to I2C fast mode specifications.
For further description of general I2C communication, refer to the Understanding the I2C Bus application note . For more information on choosing appropriate pullup resistor values, see the I2C Bus Pullup Resistor Calculation application note .
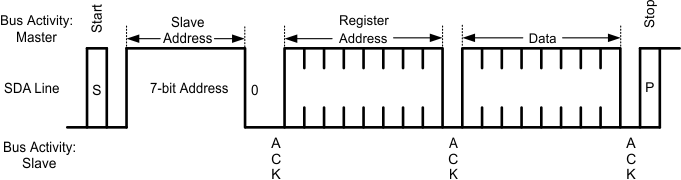 Figure 7-9 Write Byte
Figure 7-9 Write Byte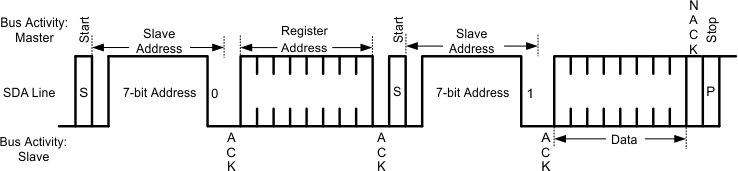 Figure 7-10 Read Byte
Figure 7-10 Read Byte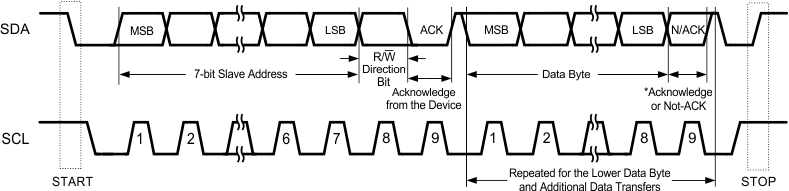 Figure 7-11 Basic Operation
Figure 7-11 Basic Operation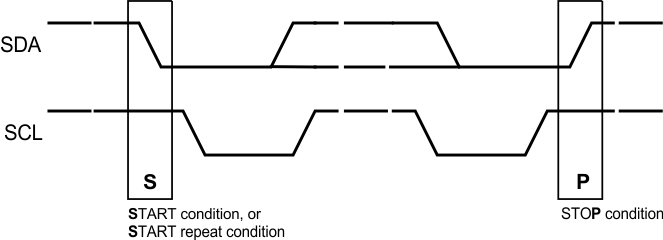 Figure 7-12 Start and Stop Conditions
Figure 7-12 Start and Stop Conditions