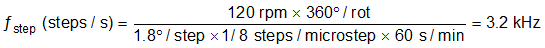ZHCSER7C October 2015 – November 2018 DRV8885
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Stepper Motor Driver Current Ratings
- 7.3.2 PWM Motor Drivers
- 7.3.3 Microstepping Indexer
- 7.3.4 Current Regulation
- 7.3.5 Controlling RREF With an MCU
- 7.3.6 Decay Modes
- 7.3.7 Blanking Time
- 7.3.8 Charge Pump
- 7.3.9 LDO Voltage Regulator
- 7.3.10 Logic and Multi-Level Pin Diagrams
- 7.3.11 Protection Circuits
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
8.2.2.1 Stepper Motor Speed
The first step in configuring the DRV8885 requires the desired motor speed and microstepping level. If the target application requires a constant speed, then a square wave with frequency ƒstep must be applied to the STEP pin.
If the target motor speed is too high, the motor will not spin. Make sure that the motor can support the target speed.
For a desired motor speed (v), microstepping level (nm), and motor full step angle (θstep),
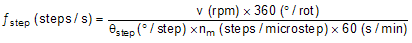
θstep can be found in the stepper motor data sheet, or written on the motor itself.
For the DRV8885, the microstepping level is set by the Mx pins and can be any of the settings in the table below. Higher microstepping will mean a smother motor motion and less audible noise, but will increase switching losses and require a higher fstep to achieve the same motor speed.
Table 11. Microstepping Indexer Settings
| M1 | M0 | STEP MODE |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Full step (2-phase excitation) with 71% current |
| 0 | 1 | 1/16 step |
| 1 | 0 | 1/2 step |
| 1 | 1 | 1/4 step |
| 0 | Z | 1/8 step |
| 1 | Z | Non-circular 1/2 step |
Example: Target 120 rpm at 1/8 microstep mode. The motor is 1.8°/step