ZHCSH31B August 2017 – February 2018 DRV10987
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Motor Parameters
- 8.4.2 Starting the Motor Under Different Initial Conditions
- 8.4.3 Motor Start Sequence
- 8.4.4 Align Current
- 8.4.5 Start-Up Current Setting
- 8.4.6 Closed Loop
- 8.4.7 Current Limits
- 8.4.8 Lock Detect and Fault Handling
- 8.4.9 Anti-Voltage Surge Function
- 8.4.10 PWM Output
- 8.4.11 FG Customized Configuration
- 8.4.12
Diagnostics and Visibility
- 8.4.12.1 Motor-Status Readback
- 8.4.12.2 Motor-Speed Readback
- 8.4.12.3 Motor Electrical-Period Readback
- 8.4.12.4 BEMF Constant Readback
- 8.4.12.5 Motor Estimated Position by IPD
- 8.4.12.6 Supply-Voltage Readback
- 8.4.12.7 Speed-Command Readback
- 8.4.12.8 Speed-Command Buffer Readback
- 8.4.12.9 Fault Diagnostics
- 8.5
Register Maps
- 8.5.1 I2C Serial Interface
- 8.5.2 Register Map
- 8.5.3
Register Descriptions
- 8.5.3.1 FaultReg Register (address = 0x00) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.2 MotorSpeed Register (address = 0x01) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.3 MotorPeriod Register (address = 0x02) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.4 MotorKt Register (address = 0x03) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.5 MotorCurrent Register (address = 0x04) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.6 IPDPosition–SupplyVoltage Register (address = 0x05) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.7 SpeedCmd–spdCmdBuffer Register (address = 0x06) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.8 AnalogInLvl Register (address = 0x07) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.9 DeviceID–RevisionID Register (address = 0x08) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.10 Unused Registers (addresses = 0x011 Through 0x2F)
- 8.5.3.11 SpeedCtrl Register (address = 0x30) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.12 EEPROM Programming1 Register (address = 0x31) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.13 EEPROM Programming2 Register (address = 0x32) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.14 EEPROM Programming3 Register (address = 0x33) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.15 EEPROM Programming4 Register (address = 0x34) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.16 EEPROM Programming5 Register (address = 0xYY) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.17 EEPROM Programming6 Register (address = 0x36) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.18 Unused Registers (addresses = 0x37 Through 0x5F)
- 8.5.3.19 EECTRL Register (address = 0x60) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.20 Unused Registers (addresses = 0x61 Through 0x8F)
- 8.5.3.21 CONFIG1 Register (address = 0x90) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.22 CONFIG2 Register (address = 0x91) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.23 CONFIG3 Register (address = 0x92) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.24 CONFIG4 Register (address = 0x93) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.25 CONFIG5 Register (address = 0x94) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.26 CONFIG6 Register (address = 0x95) [reset = 0x00]
- 8.5.3.27 CONFIG7 Register (address = 0x96) [reset = 0x00]
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.4.3.6 Start-Up Timing
Start-up timing is determined by the align and accelerate time. The align time can be set by AlignTime[2:0]. The accelerate time is defined by the open-loop to closed-loop threshold Op2ClsThr[4:0] along with the first-order acceleration coefficient StAccel[2:0](A1) and second-order acceleration coefficient StAccel2[2:0](A2) acceleration coefficients. Figure 24 shows the motor start-up process.
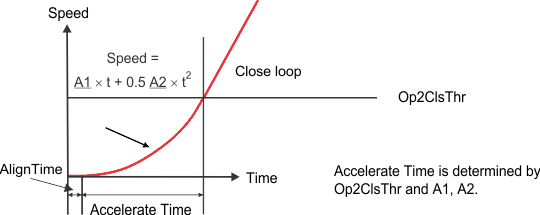 Figure 24. Motor Start-Up Process
Figure 24. Motor Start-Up Process
Select the first-order and second-order acceleration coefficients to allow the motor to reliably accelerate from zero velocity up to the closed-loop threshold in the shortest time possible. Using slow acceleration coefficients for open loop stage can help improve reliability in applications where it is difficult to initialize the motor accurately with either align or IPD.
Select the open- to closed-loop threshold to allow the motor to accelerate to a speed that generates sufficient BEMF for closed-loop control. This is determined by the BEMF constant of the motor based on the relationship described in Equation 2.