ZHCSGO1 August 2017 AM5718-HIREL
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 器件概述
- 2 修订历史记录
- 3 Device Comparison
-
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Terminal Assignment
- 4.2 Ball Characteristics
- 4.3 Multiplexing Characteristics
- 4.4
Signal Descriptions
- 4.4.1 Video Input Ports (VIP)
- 4.4.2 Display Subsystem - Video Output Ports
- 4.4.3 Display Subsystem - High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 4.4.4 Camera Serial Interface 2 CAL bridge (CSI2)
- 4.4.5 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 4.4.6 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 4.4.7 Timers
- 4.4.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 4.4.9 HDQ / 1-Wire Interface (HDQ1W)
- 4.4.10 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 4.4.11 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (McSPI)
- 4.4.12 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 4.4.13 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 4.4.14 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 4.4.15 SATA
- 4.4.16 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 4.4.17 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 4.4.18 Ethernet Interface (GMAC_SW)
- 4.4.19 Media Local Bus (MLB) Interface
- 4.4.20 eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 4.4.21 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 4.4.22 Keyboard controller (KBD)
- 4.4.23 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Interface
- 4.4.24 Programmable Real-Time Unit Subsystem and Industrial Communication Subsystem (PRU-ICSS)
- 4.4.25 Test Interfaces
- 4.4.26 System and Miscellaneous
- 4.4.27 Power Supplies
-
5 Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power On Hours (POH) Limits
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Operating Performance Points
- 5.6 Power Consumption Summary
- 5.7
Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.1 LVCMOS DDR DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.2 HDMIPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.3 Dual Voltage LVCMOS I2C DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.4 IQ1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.5 IHHV1833 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.6 LVCMOS OSC Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.7 LVCMOS CSI2 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.8 BMLB18 Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.9 BC1833IHHV Buffers DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.10 USBPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.11 Dual Voltage SDIO1833 DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.12 Dual Voltage LVCMOS DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.13 SATAPHY DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7.14 SERDES DC Electrical Characteristics
- 5.8 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.9 Power Supply Sequences
- 6 Clock Specifications
-
7 Timing Requirements and Switching Characteristics
- 7.1 Timing Test Conditions
- 7.2 Interface Clock Specifications
- 7.3 Timing Parameters and Information
- 7.4 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 7.5 Virtual and Manual I/O Timing Modes
- 7.6 Video Input Ports (VIP)
- 7.7 Display Subsystem - Video Output Ports
- 7.8 Display Subsystem - High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI)
- 7.9 Camera Serial Interface 2 CAL bridge (CSI2)
- 7.10 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 7.11 General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
- 7.12 Timers
- 7.13 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface (I2C)
- 7.14 HDQ / 1-Wire Interface (HDQ1W)
- 7.15 Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART)
- 7.16 Multichannel Serial Peripheral Interface (McSPI)
- 7.17 Quad Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
- 7.18 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
- 7.19 Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- 7.20 Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA)
- 7.21 Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
- 7.22 Controller Area Network Interface (DCAN)
- 7.23 Ethernet Interface (GMAC_SW)
- 7.24
eMMC/SD/SDIO
- 7.24.1
MMC1-SD Card Interface
- 7.24.1.1 Default speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.2 High speed, 4-bit data, SDR, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.3 SDR12, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.4 SDR25, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.5 UHS-I SDR50, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.6 UHS-I SDR104, 4-bit data, half-cycle
- 7.24.1.7 UHS-I DDR50, 4-bit data
- 7.24.2 MMC2 - eMMC
- 7.24.3 MMC3 and MMC4-SDIO/SD
- 7.24.1
MMC1-SD Card Interface
- 7.25 General-Purpose Interface (GPIO)
- 7.26 PRU-ICSS Interfaces
- 7.27 System and Miscellaneous interfaces
- 7.28 Test Interfaces
-
8 Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8.1 Power Supply Mapping
- 8.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.1 DDR3 General Board Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.2
DDR3 Board Design and Layout Guidelines
- 8.2.2.1 Board Designs
- 8.2.2.2 DDR3 EMIF
- 8.2.2.3 DDR3 Device Combinations
- 8.2.2.4 DDR3 Interface Schematic
- 8.2.2.5 Compatible JEDEC DDR3 Devices
- 8.2.2.6 PCB Stackup
- 8.2.2.7 Placement
- 8.2.2.8 DDR3 Keepout Region
- 8.2.2.9 Bulk Bypass Capacitors
- 8.2.2.10 High-Speed Bypass Capacitors
- 8.2.2.11 Net Classes
- 8.2.2.12 DDR3 Signal Termination
- 8.2.2.13 VREF_DDR Routing
- 8.2.2.14 VTT
- 8.2.2.15 CK and ADDR_CTRL Topologies and Routing Definition
- 8.2.2.16 Data Topologies and Routing Definition
- 8.2.2.17 Routing Specification
- 8.3 High Speed Differential Signal Routing Guidance
- 8.4 Power Distribution Network Implementation Guidance
- 8.5 Single-Ended Interfaces
- 8.6 Clock Routing Guidelines
- 9 器件和文档支持
- 10机械封装和可订购信息
9 器件和文档支持
TI 提供各式各样的开发工具,包括用于评估处理器性能、生成代码、促进算法实现以及完全集成和调试软硬件模块的各种工具,如下所示。
9.1 器件命名规则
为了指出产品开发周期所处的阶段,TI 为所有微处理器 (MPU) 和支持工具的产品型号分配了前缀。每个器件都具有以下三个前缀之一:X、P 或无(无前缀),例如 AM571x。德州仪器 (TI) 建议为其支持的工具使用三个可用前缀指示符中的两个:TMDX 和 TMDS。这些前缀代表了产品开发的发展阶段,即从工程原型 (TMDX) 直到完全合格的生产器件和工具 (TMDS)。
器件开发进化流程:
-
X 试验器件不一定代表最终器件的电气规范标准并且不可使用生产组装流程。
-
P 原型器件不一定是最终芯片模型并且不一定符合最终电气标准规范。
-
无完全合格的芯片模型的生产版本。
支持工具开发进化流程:
-
TMDX 还未经德州仪器 (TI) 完整内部质量测试的开发支持产品.
-
TMDS 完全合格的开发支持产品。
X 和 P 器件和 TMDX 开发支持工具在供货时附带如下免责条款:
“开发的产品用于内部评估用途。”
生产器件和 TMDS 开发支持工具已进行完全特性描述,并且器件的质量和可靠性已经完全论证。TI 的标准保修证书适用。
预测显示原型器件(X 或者 P)的故障率大于标准生产器件。由于它们的预计的最终使用故障率仍未定义,德州仪器 (TI) 建议不要将这些器件用于任何生产系统。只有合格的产品器件将被使用。
如需 ZBO 封装类型的 AM571x 器件的可订购器件号,请参阅本文档的“封装选项附录”、访问 TI 网站 (www.ti.com.cn) 或联系您的 TI 销售代表。
有关模具器件命名规则 的 详细说明,请参阅《器件勘误表》(文献编号 SPRZ436)。
9.1.1 标准封装编号法
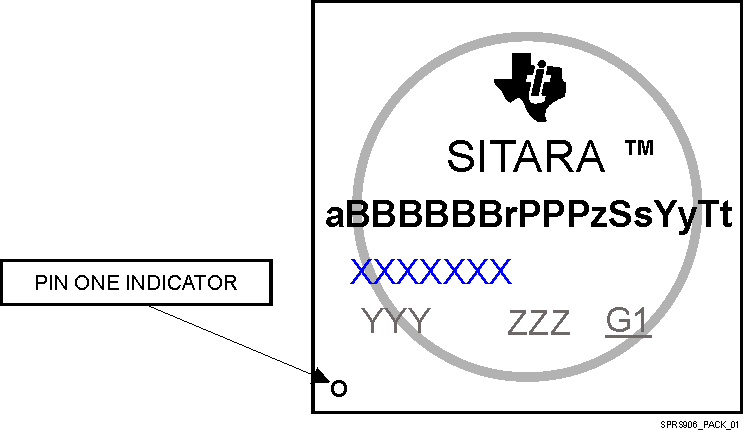 Figure 9-1 印刷器件参考
Figure 9-1 印刷器件参考
NOTE
某些器件的器件封装顶部的表面有一个圆形标记,该标记是在生产测试过程中产生的。这些标记只在表面显示,不会影响可靠性。
9.1.2 器件命名约定
Table 9-1 命名规则 说明
| 字段参数 | 字段 说明 | 值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 器件演变阶段 | X | 原型 |
| P | 预生产(生产测试流程,无可靠性数据) | ||
| 空白 | 生产 | ||
| BBBBBB | 基本生产器件号 | AM5718 | 高阶(请参阅Table 3-1,器件比较) |
| r | 器件版本 | 空白 | SR 1.0 |
| A | SR 2.0 | ||
| PPP | 封装符号 | ZBO | ZBO S-PBGA-N760 (23mm × 23mm) 封装 |
| z | 器件速度 | X | 表示器件中每个内核的速度等级。有关详细信息,请参阅Table 5-5,速度等级最大频率 |
| D | |||
| Ss | 安全标识符 | TU | 虚拟密钥安保器件 |
| 空白 | 通用器件 | ||
| Yy | 器件类型 | E | 支持所有工业协议(基本协议加 EtherCAT 从属协议和 POWERLINK 从属协议) |
| 空白 | 支持基本工业协议 | ||
| Yn | 字母后接数字表示带有客户密码的 HS 器件 | ||
| Tt | 温度 (2) | EP | 工作温度范围(请参阅Table 5-4,建议运行条件) |
| XXXXXXX | 批次追踪代码 (LTC) | ||
| YYY | 生产代码;仅供 TI 使用 | ||
| ZZZ | 生产代码;仅供 TI 使用 | ||
| O | 引脚 1 符号 | ||
- 为了标明产品开发周期的阶段,TI 为所有部件号分配了前缀。这些前缀代表了产品开发的发展阶段,即从工程原型直到完全合格的生产器件。
原型器件依据以下免责声明供应:
“此产品尚在开发中,供内部评估使用。”
无论是否有相反规定,TI 均不作任何明示、暗示或法定的担保,包括对此器件特定用途的适用性和适销性的任何暗示担保。 - 适用于器件最高结温。
NOTE
符号和器件号中的空白将折叠显示,以防字符间存在间隙。
9.2 工具与软件
以下产品支持面向 AM571x 平台的开发工作:
AM571x 寄存器描述符工具是一款交互式器件寄存器配置工具,便于用户查看寄存器的开通复位状态,然后针对特定用例定制器件配置。
AM571x 时钟树工具是一款交互式时钟树配置软件。借助这款软件,用户可以查看器件时钟树、与时钟树元件和 PRCM 寄存器交互、查看对 PRCM 寄存器和器件时钟树的影响,还可查看用户与时钟树进行交互影响到的所有器件寄存器的迹线。
AM571x Pin Mux 实用程序是一款交互式应用,可帮助系统设计人员在进行基于器件的产品设计时选择适当的引脚多路复用配置。借助 Pin Mux 实用程序,设计人员可选择特定外设接口的有效 IO 集,从而确保为设计选择的引脚多路复用配置只使用器件支持的有效 IO 集。
有关处理器平台开发支持工具的完整列表,请访问德州仪器 (TI) 网站 www.ti.com.cn。有关定价和购买信息,请联系最近的 TI 销售办事处或授权分销商。
9.3 文档支持
以下文档对 AM571x 器件进行了介绍。
9.4 接收文档更新通知
要接收文档更新通知(包括器件勘误表),请转至 www.ti.com.cn 上相关器件的产品文件夹。单击右上角的“提醒我”(Alert me) 按钮。点击后,您将每周定期收到已更改的产品信息(如果有的话)。有关更改的详细信息,请查阅已修订文档的修订历史记录。
9.5 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
-
TI Embedded Processors WikiTexas Instruments Embedded Processors Wiki.
Established to help developers get started with Embedded Processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
9.6 商标
ICEPick 和 SmartReflex 是德州仪器 (TI) 公司的商标。
ARM 和 Cortex 是 ARM Limited 的注册商标。
ETB、ARM9、CoreSight 和 Neon 是 ARM Limited 的商标。
HDMI 是 HDMI Licensing, LLC. 的商标。
HDQ 是 Benchmarq 的商标。
1-Wire 是 Maxim Integrated 的注册商标。
PowerVR 是 Imagination Technologies Ltd. 的注册商标。
SD 是 Toshiba Corporation 的注册商标。
MMC 和 eMMC 是 MultiMediaCard Association 的商标。
MIPI 是移动产业处理器接口 (MIPI) 联盟的注册商标。
PCI Express 是 PCI-SIG 的注册商标。
MediaLB 是 Standard Microsystems Corporation 的商标。
Vivante 是 Vivante Corporation 的注册商标。
所有其他商标均为其各自所有者的财产。
9.7 静电放电警告

ESD 可能会损坏该集成电路。德州仪器 (TI) 建议通过适当的预防措施处理所有集成电路。如果不遵守正确的处理措施和安装程序 , 可能会损坏集成电路。
ESD 的损坏小至导致微小的性能降级 , 大至整个器件故障。 精密的集成电路可能更容易受到损坏 , 这是因为非常细微的参数更改都可能会导致器件与其发布的规格不相符。
9.8 Glossary
-
TI Glossary This glossary lists and explains terms, acronyms, and definitions.