ZHCSFA8 May 2016 TUSB501-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) (1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage range (2) | VCC | –0.5 | 4 | V |
| Voltage range at any input or output terminal | Differential I/O | –0.5 | 4 | V |
| CMOS inputs | –0.5 | VCC + 0.5 | V | |
| Storage temperature, TSTG | –65 | 150 | °C | |
| Maximum junction temperature, TJ | -40 | 125 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values are with respect to the GND terminals.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±5000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±1500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Main power supply | 3 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | –40 | 105 | °C | |
| CAC | AC coupling capacitor | 75 | 100 | 200 | nF |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TUSB501-Q1 | UNITS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRF (WSON) | ||||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 105.5 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case(top) thermal resistance | 47.5 | °C/W | |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 70.9 | °C/W | |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 10.0 | °C/W | |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 70.9 | °C/W | |
| RθJC(bottom) | Junction-to-case(bottom) thermal resistance | 51.8 | °C/W | |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the IC Package Thermal Metrics application report, SPRA953.
7.5 Power Supply Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP(1) | MAX(2) | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC-ACTIVE | Average active current | Link in U0 with SuperSpeed USB data transmission, OS = Low | 38.1 | mA | ||
| Link in U0 with SuperSpeed USB data transmission, OS = High | 43.8 | 65 | ||||
| ICC-IDLE | Average current in idle state | Link has some activity, not in U0, OS = Low | 29.8 | mA | ||
| ICC-U2U3 | Average current in U2/U3 | Link in U2 or U3 | 6.1 | mA | ||
| ICC-NC | Average current with no connection | No SuperSpeed USB device is connected to TXP, TXN | 1.3 | mA | ||
| PD | Power Dissipation in U0 | OS = Low | 126 | mW | ||
| OS = High | 145 | 234 | ||||
(1) TYP values use VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C.
(2) MAX values use VCC = 3.6 V, TA = –40°C.
7.6 DC Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-State CMOS Inputs (EQ, DE) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2.8 | V | |||
| VIM | Mid-level input voltage | VCC / 2 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.6 | V | |||
| VF | Floating voltage | VIN = High impedance | VCC / 2 | V | ||
| RPU | Internal pull-up resistance | 190 | kΩ | |||
| RPD | Internal pull-down resistance | 190 | kΩ | |||
| IIH | High-level input current | VIN = 3.6 V | 36 | µA | ||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VIN = GND, VCC = 3.6 V | -36 | µA | ||
| 2-State CMOS Input (OS) | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2 | V | |||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.5 | V | |||
| VF | Floating voltage | VIN = High impedance | GND | V | ||
| RPD | Internal pull-down resistance | 270 | kΩ | |||
| IIH | High-level input current | VIN = 3.6 V | 26 | µA | ||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VIN = GND | -1 | µA | ||
7.7 AC Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Differential Receiver (RXP, RXN) | ||||||
| VDIFF-pp | Input differential voltage swing | AC-coupled differential peak-to-peak signal | 100 | 1200 | mVpp | |
| VCM-RX | Common-mode voltage bias in the receiver (DC) | 3.3 | V | |||
| ZRX-DIFF | Differential input impedance (DC) | Present after a SuperSpeed USB device is detected on TXP/TXN | 72 | 91 | 120 | Ω |
| ZRX-CM | Common-mode input impedance (DC) | Present after a SuperSpeed USB device is detected on TXP, TXN | 18 | 22.8 | 30 | Ω |
| ZRX-HIGH-IMP-DC-POS | Common-mode input impedance with termination disabled (DC) | Present when no SuperSpeed USB device is detected on TXP, TXN. Measured over the range of 0-500 mV with respect to GND. | 25 | 35 | kΩ | |
| VRX-LFPS-DET-DIFF-pp | Low Frequency Periodic Signaling (LFPS) Detect Threshold | Below the minimum is squelched | 100 | 300 | mVpp | |
| Differential Transmitter (TXP, TXN) | ||||||
| VTX-DIFF-PP | Transmitter differential voltage swing (transition-bit) | OS = Low, No load | 930 | mVpp | ||
| OS = High, No load | 1300 | |||||
| VTX-DE-RATIO | Transmitter de-emphasis | DE = Floating, OS = Low | -3.5 | dB | ||
| CTX | TX input capacitance to GND | At 2.5 GHz | 1.25 | pF | ||
| ZTX-DIFF | Differential impedance of the driver | 75 | 93 | 125 | Ω | |
| ZTX-CM | Common-mode impedance of the driver | Measured with respect to AC ground over 0-500 mV | 18.75 | 31.25 | Ω | |
| ITX-SC | TX short circuit current | TX ± shorted to GND | 60 | mA | ||
| VCM-TX | Common-mode voltage bias in the transmitter (DC) | 1.2 | 2.5 | V | ||
| VCM-TX-AC | AC common-mode voltage swing in active mode | Within U0 and within LFPS | 100 | mVpp | ||
| VTX-IDLE-DIFF -AC-pp | Differential voltage swing during electrical idle | Tested with a high-pass filter | 0 | 10 | mVpp | |
| VTX-CM-DeltaU1-U0 | Absolute delta of DC CM voltage during active and idle states | Restrict the test condition to meet 100 mV | 100 | mV | ||
| VTX-idle-diff-DC | DC electrical idle differential output voltage | Voltage must be low pass filtered to remove any AC component | 0 | 12 | mV | |
| Differential Transmitter (TXP, TXN) | ||||||
| tR, tF | Output rise, fall time see Figure 6 |
20%-80% of differential voltage measured 1 inch from the output pin | 80 | ps | ||
| tRF-MM | Output Rise, Fall time mismatch | 20%-80% of differential voltage measured 1 inch from the output pin | 20 | ps | ||
| tdiff-LH, tdiff-HL |
Differential propagation delay see Figure 4 |
De-emphasis = -3.5 dB propagation delay between 50% level at input and output | 290 | ps | ||
| tidleEntry, tidleExit | Idle entry and exit times see Figure 5 |
3.6 | ns | |||
| Timing | ||||||
| tREADY | Time from power applied until RX termination | Apply 0 V to VCC, connect SuperSpeed USB termination to TX±, apply 3.3 V to VCC, and measure when ZRX-DIFF is enabled. | 9 | ms | ||
| Jitter | ||||||
| TJTX-EYE | Total jitter (1) (2) | EQ = Floating, OS = High, DE = High See Figure 3. |
0.213 | UI (4) | ||
| DJTX | Deterministic jitter (2) | 0.197 | UI (4) | |||
| RJTX | Random jitter (2) (3) | 0.016 | UI (4) | |||
(1) Includes RJ at 10-12.
(2) Measured at the ends of reference channel in Figure 3 with K28.5 pattern, VID = 1000 mVpp, 5 Gbps, -3.5 dB de-emphasis from source.
(3) Rj calculated as 14.069 times the RMS random jitter for 10-12 BER.
(4) UI = 200 ps.
7.8 Typical Characteristics
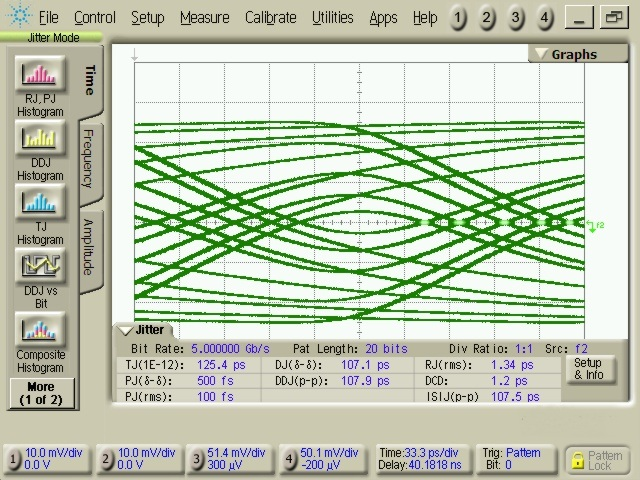
| TA = 25°C | ||
at TUSB501-Q1
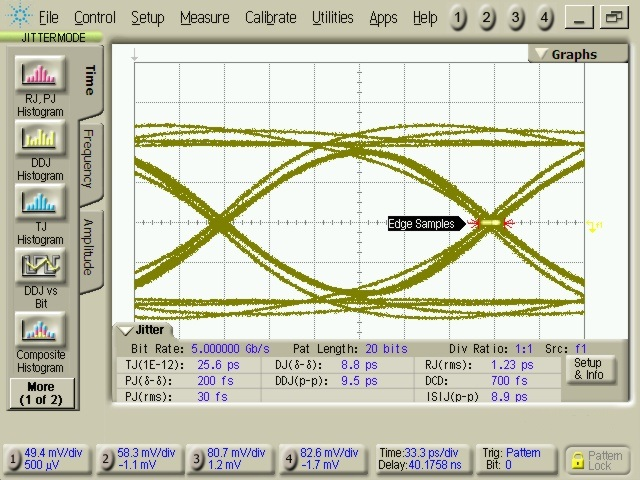
| TA = 25°C | DE = HIGH | OS = HIGH |
| EQ = NC |