ZHCSFI8C June 2016 – June 2021 TPS62135
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Operation
- 9.4.2 Power Save Mode Operation (PWM/PFM)
- 9.4.3 100% Duty-Cycle Operation
- 9.4.4 HICCUP Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (TPS62135 only)
- 9.4.5 Current Limit And Short Circuit Protection (TPS621351 only)
- 9.4.6 Soft-Start / Tracking (SS/TR)
- 9.4.7 Output Discharge Function (TPS62135 only)
- 9.4.8 Starting into a Pre-Biased Load (TPS621351 only)
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10.3.2 Powering Multiple Loads
In applications where TPS62135x is used to power multiple load circuits, it may be the case that the total capacitance on the output is very large. In order to properly regulate the output voltage, there needs to be an appropriate AC signal level on the VOS pin. Tantalum capacitors have a large enough ESR to keep output voltage ripple sufficiently high on the VOS pin. With low ESR ceramic capacitors, the output voltage ripple may get very low, so it is not recommended to use a large capacitance directly on the output of the device. If there are several load circuits with their associated input capacitor on a pcb, these loads are typically distributed across the board. This adds enough trace resistance (Rtrace) to keep a large enough AC signal on the VOS pin for proper regulation.
The minimum total trace resistance on the distributed load is 10 mΩ. The total capacitance n x Cin in the use case below was 32 x 47 uF of ceramic X7R capacitors.
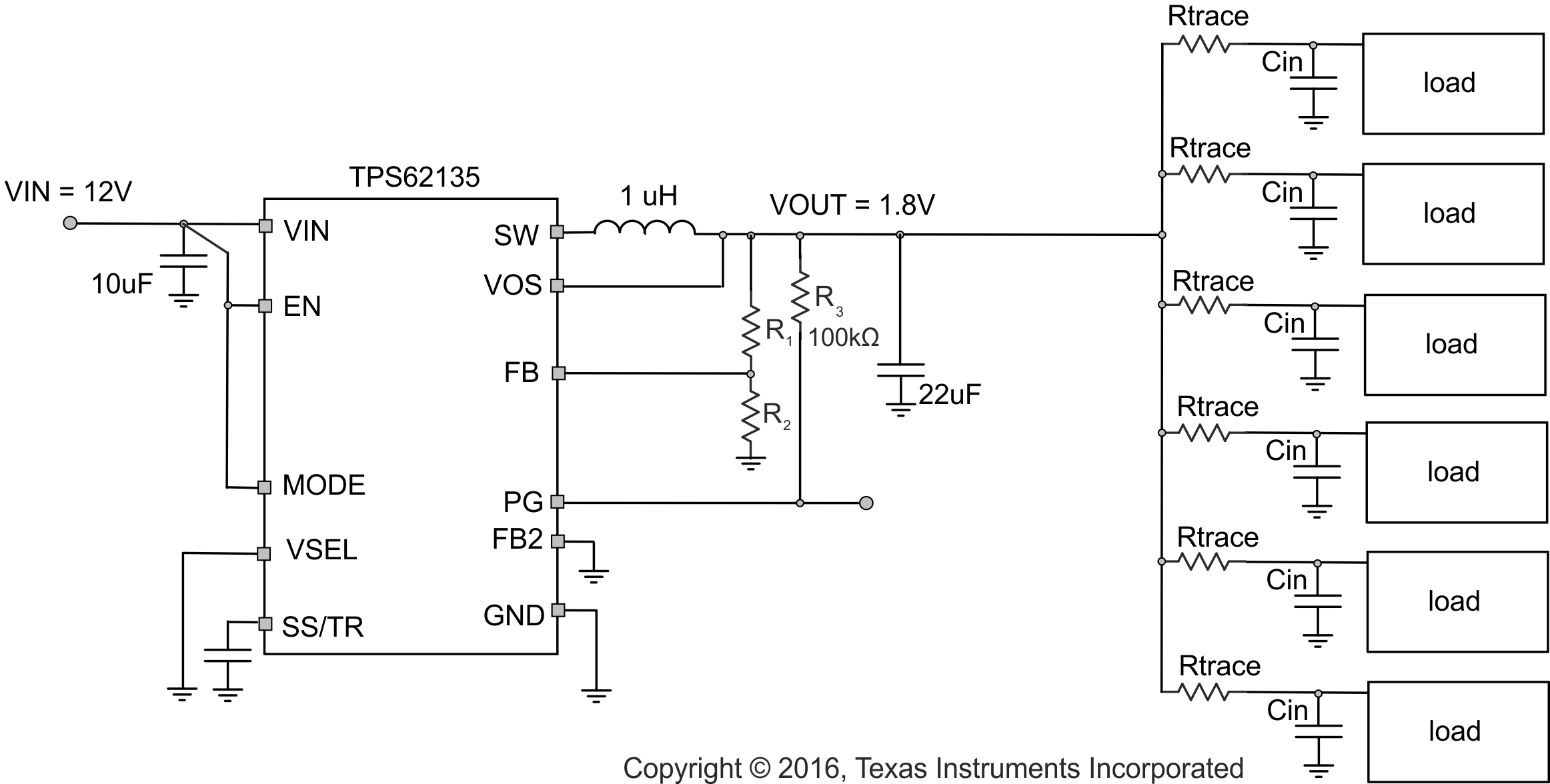 Figure 10-84 Multiple Loads
Figure 10-84 Multiple Loads