ZHCSG52B March 2017 – May 2018 TPS543C20
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4
Device Functional Modes
- 8.4.1 Soft-Start Operation
- 8.4.2 Input and VDD Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO) Protection
- 8.4.3 Power Good and Enable
- 8.4.4 Voltage Reference
- 8.4.5 Prebiased Output Start-up
- 8.4.6 Internal Ramp Generator
- 8.4.7 Switching Frequency
- 8.4.8 Clock Sync Point Selection
- 8.4.9 Synchronization and Stackable Configuration
- 8.4.10 Dual-Phase Stackable Configurations
- 8.4.11 Operation Mode
- 8.4.12 API/BODY Brake
- 8.4.13 Sense and Overcurrent Protection
- 8.4.14 Output Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protection
- 8.4.15 Overtemperature Protection
- 8.4.16 RSP/RSN Remote Sense Function
- 8.4.17 Current Sharing
- 8.4.18 Loss of Synchronization
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application: TPS543C20 Stand-alone Device
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.3 System Example
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
9.2.2.8.1 Response to a Load Transient
The output capacitance must supply the load with the required current when current is not immediately provided by the regulator. When the output capacitor supplies load current, the impedance of the capacitor greatly affects the magnitude of voltage deviation (such as undershoot and overshoot) during the transient.
Use Equation 9 and Equation 10 to estimate the amount of capacitance needed for a given dynamic load step and release.
NOTE
There are other factors that can impact the amount of output capacitance for a specific design, such as ripple and stability.
Equation 9. 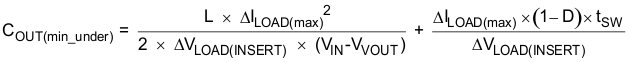
Equation 10. 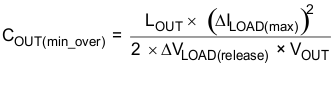
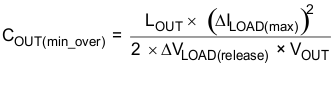
where
- COUT(min_under) is the minimum output capacitance to meet the undershoot requirement
- COUT(min_over)is the minimum output capacitance to meet the overshoot requirement
- D is the duty cycle
- L is the output inductance value (0.47 µH)
- ∆ILOAD(max) is the maximum transient step (10 A)
- VOUT is the output voltage value (900 mV)
- tSW is the switching period (2.0 µs)
- VIN is the minimum input voltage for the design (12 V)
- ∆VLOAD(insert) is the undershoot requirement (50 mV)
- ∆VLOAD(release) is the overshoot requirement (50 mV)
- This example uses a combination of POSCAP and MLCC capacitors to meet the overshoot requirement.
- POSCAP bank #1: 2 x 330 µF, 2.5 V, 3 mΩ per capacitor
- MLCC bank #2: 3 × 100 µF, 6.3 V, 1 mΩ per capacitor