6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
see (1)
|
MIN |
MAX |
UNIT |
| PWR |
Supply voltage |
–28 |
33 |
V |
|
Voltage at sensor input pins: INP+, INP–, INT+, INT– |
–0.3 |
2 |
V |
|
Voltage at AVDD, AVSS, BRG+, BRG–, COMP, DACCAP, DVDD, DVDD_MEM, DVSS, FB–, GATE, REFCAP |
–0.3 |
3.6 |
V |
|
Voltage at FB+ pin |
–2 |
VPWR + 0.3 |
V |
|
Voltage at OUT pin |
-0.3 |
33 |
V |
| IPWR, short on OUT pin |
Supply current |
|
25 |
mA |
| TJmax |
Maximum junction temperature |
|
155 |
°C |
| Tstg |
Storage temperature |
–40 |
150 |
°C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
|
VALUE |
UNIT |
| V(ESD) |
Electrostatic discharge |
Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) |
±2000 |
V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) |
±500 |
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
|
MIN |
NOM |
MAX |
UNIT |
| VPWR |
Power supply voltage |
3.3 |
|
30 |
V |
|
Slew rate |
VDD = 0 to 30 V |
|
|
0.5 |
V/µs |
| IPWR |
Power supply current - normal operation |
No load on BRG, no load on DAC |
|
2.5 |
|
mA mA |
| Power supply current - EEPROM programming |
While EEPROM is being programmed, no load on BRG, no load on DAC |
|
|
9(1) |
| TA |
Operating ambient temperature |
–40 |
|
150 |
°C |
|
Programming temperature |
EEPROM |
–40 |
|
140 |
°C |
|
Start-up time (including analog and digital) |
VPWR ramp rate 0.5 V/µs |
|
|
1 |
ms |
|
Capacitor on PWR pin |
10 |
|
|
nF |
(1) Programming of the EEPROM results in an additional 6 mA of current on the PWR pin.
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) |
PGA300 |
UNIT |
| RHH (VQFN) |
| 36 PINS |
| RθJA |
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance |
30.6 |
°C/W |
| RθJC(top) |
Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance |
16.4 |
°C/W |
| RθJB |
Junction-to-board thermal resistance |
5.4 |
°C/W |
| ψJT |
Junction-to-top characterization parameter |
0.2 |
°C/W |
| ψJB |
Junction-to-board characterization parameter |
5.4 |
°C/W |
| RθJC(bot) |
Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance |
0.7 |
°C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the
Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report,
SPRA953.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics – Reverse Voltage Protection
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Reverse voltage |
|
–28 |
|
|
V |
|
Voltage drop across reverse voltage protection element |
|
|
20 |
|
mV |
6.6 Electrical Characteristics – Regulators
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| VAVDD |
AVDD voltage |
CAVDD = 100 nF |
|
3 |
|
V |
| VDVDD |
DVDD voltage – operating |
CDVDD = 100 nF |
|
1.8 |
|
V |
6.7 Electrical Characteristics – Internal Reference
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
High-voltage reference voltage(1) |
|
|
1.2 |
|
V |
|
Accurate reference voltage |
|
|
2.5 |
|
V |
|
Capacitor value on REFCAP pin |
|
|
100 |
|
nF |
(1) TEMP_DRIFT = [(Value at TEMP – Value at 25³C) / (Value at 25³C × ΔTEMP)] × 106
6.8 Electrical Characteristics – Bridge Sensor Supply
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| BRG SUPPLY FOR RESISTIVE BRIDGE SENSORS |
| VBRG+ – VBRG– |
Bridge supply voltage |
Bridge supply control bit = 0b00, no load |
|
2.5 |
|
V |
| Bridge supply control bit = 0b01, no load |
|
2 |
|
V |
| Bridge supply control bit = 0b10, no load |
|
1.25 |
|
V |
| IBRG |
Current supply to the bridge |
|
|
|
1.5 |
mA |
| CBRG |
Capacitive load |
RBRG = 20 kΩ |
|
|
2 |
nF |
6.9 Electrical Characteristics – Temperature Sensor Supply
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| ITEMP SUPPLY FOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR |
| ITEMP |
Current supply to temperature sensor |
Control bit = 0b000 |
|
25 |
|
µA |
| Control bit = 0b001 |
|
50 |
|
| Control bit = 0b010 |
|
100 |
|
| Control bit = 0b011 |
|
500 |
|
| Control bit = 0b1xx |
|
OFF |
|
|
| CTEMP |
Capacitive load |
|
|
|
100 |
nF |
|
Output impedance |
|
|
15 |
|
MΩ |
6.10 Electrical Characteristics – Internal Temperature Sensor
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Temperature range |
|
–40 |
|
150 |
°C |
6.11 Electrical Characteristics – P Gain (Chopper Stabilized)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Gain steps (5 bits) |
00000, at dc |
|
5 |
|
V/V |
| 00001 |
|
5.48 |
|
| 00010 |
|
5.97 |
|
| 00011 |
|
6.56 |
|
| 00100 |
|
7.02 |
|
| 00101 |
|
8 |
|
| 00110 |
|
9.09 |
|
| 00111 |
|
10 |
|
| 01000 |
|
10.53 |
|
| 01001 |
|
11.11 |
|
| 01010 |
|
12.5 |
|
| 01011 |
|
13.33 |
|
| 01100 |
|
14.29 |
|
| 01101 |
|
16 |
|
| 01110 |
|
17.39 |
|
| 01111 |
|
18.18 |
|
| 10000 |
|
19.05 |
|
| 10001 |
|
20 |
|
| 10010 |
|
22.22 |
|
| 10011 |
|
25 |
|
| 10100 |
|
30.77 |
|
| 10101 |
|
36.36 |
|
| 10110 |
|
40 |
|
| 10111 |
|
44.44 |
|
| 11000 |
|
50 |
|
| 11001 |
|
57.14 |
|
| 11010 |
|
66.67 |
|
| 11011 |
|
80 |
|
| 11100 |
|
100 |
|
| 11101 |
|
133.33 |
|
| 11110 |
|
200 |
|
| 11111 |
|
400 |
|
|
Gain bandwidth product |
|
|
10 |
|
MHz |
|
Input-referred noise density(1) |
f = 0.1 Hz to 2 kHz, gain = 400 V/V, sampling rate = 128 µs, across temperature |
|
15 |
|
nV/√Hz |
|
Input offset voltage |
|
|
10 |
|
µV |
|
Input bias current |
|
|
5 |
|
nA |
|
Frequency response |
Gain = 400 V/V, <1 kHz |
|
|
±0.1 |
%V/V |
|
Common-mode voltage range |
|
|
Depends on selected gain, bridge supply and sensor span (2) |
|
V |
|
Common-mode rejection ratio |
fCM = 50 Hz at gain = 5 V/V |
|
110 |
|
dB |
|
Input impedance |
|
10 |
|
|
MΩ |
(1) Total input-referred noise including gain noise, ADC reference noise, ADC thermal noise, and ADC quantization noise
(2)
Common Mode at P Gain Input and Output: There are two constraints:
- The single-ended voltage of the positive and negative pins at the P gain input must be between 0.3 V and 1.8 V
- The single-ended voltage of the positive and negative pins at the P gain output must be between 0.1 V and 2 V
6.12 Electrical Characteristics – P Analog-to-Digital Converter
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Sigma-delta modulator frequency |
|
|
1 |
|
MHz |
|
ADC voltage input range |
|
–2.5 |
|
2.5 |
V |
|
Number of bits |
|
|
16 |
|
bits |
|
ADC 2s complement code for –2.5-V differential input |
|
|
8000hex |
|
|
|
ADC 2s complement code for 0-V differential input |
|
|
0000hex |
|
|
|
ADC 2s complement code for 2.5-V differential input |
|
|
7FFFhex |
|
|
| INL |
Integral nonlinearity |
|
|
|
±0.5 |
LSB |
6.13 Electrical Characteristics – T Gain (Chopper Stabilized)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Gain steps (2 bits) |
Gain control bits = 0b00 at dc |
|
1.33 |
|
V/V |
| Gain control bits = 0b01 |
|
2 |
|
| Gain control bits = 0b10 |
|
5 |
|
| Gain control bits = 0b11 |
|
20 |
|
|
Gain bandwidth product |
|
|
350 |
|
kHz |
|
Noise density(1) |
f = 0.1 Hz to 100 Hz
at gain = 5 V/V, across temperature |
|
110 |
|
nV/√Hz |
|
Input offset voltage |
|
|
95 |
|
µV |
|
Input bias current |
|
|
5 |
|
nA |
|
Frequency response |
Gain = 20 V/V, <100 Hz |
|
|
0.335 |
%V/V |
|
Common mode voltage range |
|
|
Depends on selected gain and current supply (2) |
|
|
|
Common-mode rejection ratio |
fCM = 50 Hz |
|
110 |
|
dB |
|
Input impedance |
|
1 |
|
|
MΩ |
(1) Total input-referred noise including gain noise, ADC reference noise, ADC thermal noise, and ADC quantization noise
(2)
Common Mode at T Gain Input and Output: There are two constraints:
- The single-ended voltage of positive/negative pin at the T gain input should be between 5 m V and 1.8 V
- The single-ended voltage of positive/negative pin at the T gain output should be between 0.1 V and 2 V
6.14 Electrical Characteristics – T Analog-to-Digital Converter
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Sigma-delta modulator frequency |
|
|
1 |
|
MHz |
|
ADC voltage input range |
|
–2.5 |
|
2.5 |
V |
|
Number of bits |
|
|
16 |
|
bits |
|
ADC 2s complement code for –2.5-V differential input |
2s complement |
|
8000hex |
|
LSB |
|
ADC 2s complement code for 0-V differential input |
|
|
0000hex |
|
LSB |
|
ADC 2s complement code for 2.5-V differential input |
|
|
7FFFhex |
|
LSB |
| INL |
Integral nonlinearity |
|
|
|
±0.5 |
LSB |
6.15 Electrical Characteristics – One-Wire Interface
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Communication Baud Rate(1) |
|
600 |
|
9600 |
bits per second |
| OWI_ENH |
OWI activation high |
|
5.95 |
|
|
V |
| OWI_ENL |
OWI activation low |
|
|
|
5.75 |
V |
| OWI_VIH |
OWI transceiver Rx threshold for high |
|
4.8 |
|
5.1 |
V |
| OWI_VIL |
OWI transceiver Rx threshold for low |
|
3.9 |
|
4.2 |
V |
| OWI_IOH |
OWI transceiver Tx threshold for high |
|
500 |
|
1379 |
µA |
| OWI_IOL |
OWI transceiver Tx threshold for low |
|
2 |
|
5 |
µA |
(1) OWI over power line does not work if there is an LDO between the supply to the sensor and the PWR pin, or if the OWI high and low voltages are greater than the regulated voltage.
6.16 Electrical Characteristics – DAC Output
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
DAC reference voltage |
Reference bit = 1 |
|
1.25 |
|
V |
| Reference bit = 0 (ratiometric) |
|
0.25 × VPWR |
|
|
DAC resolution |
|
|
14 |
|
bits |
6.17 Electrical Characteristics – DAC Gain
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
|
Buffer gain (see Figure 16) |
2× |
|
2 |
|
V/V |
| 4× |
|
4 |
|
| 6.67× |
|
6.67 |
|
| 10× |
|
10 |
|
|
Current loop gain |
|
|
1001 |
|
mA/mA |
|
Gain-bandwidth product |
|
|
1 |
|
MHz |
|
Zero-code voltage (gain = 4×) |
DAC code = 0000h, IDAC = 2.5 mA |
|
|
20 |
mV |
|
Full-code voltage (gain = 4×) |
DAC code is 1FFFh, IDAC = –2.5 mA |
4.8 |
|
|
V |
|
Output current |
DAC code = 1FFFh , DAC code = 0000h |
|
|
±2.5 |
mA |
|
Short-circuit source current |
DAC code = 1FFFh |
|
27 |
|
mA |
|
Short-circuit sink current |
DAC code = 0000h |
|
27 |
|
mA |
|
Maximum capacitance |
Without compensation |
|
|
100 |
pF |
|
With compensation |
|
|
100 |
nF |
6.18 Electrical Characteristics – Non-Volatile Memory
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| EEPROM |
Size |
|
|
128 |
|
Bytes |
| Erase-write cycles |
|
|
|
1000 |
Cycles |
| Programming time |
1 8-byte page |
|
|
8 |
ms |
| Data retention |
|
10 |
|
|
Years |
6.19 Electrical Characteristics – Diagnostics
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| OSC_PWR_OV |
Oscillator circuit supply overvoltage threshold |
|
|
3.3 |
|
V |
| OSC_PWR_UV |
Oscillator circuit supply undervoltage threshold |
|
|
2.7 |
|
V |
| BRG_OV |
Resistive bridge sensor supply overvoltage threshold |
|
|
10 |
|
%. VBRG |
| BRG_UV |
Resistive bridge sensor supply undervoltage threshold |
|
|
–10 |
|
%Prog. VBRG |
| AVDD_OV |
AVDD overvoltage threshold |
|
|
3.3 |
|
V |
| AVDD_UV |
AVDD undervoltage threshold |
|
|
2.7 |
|
V |
| DVDD_OV |
DVDD overvoltage threshold |
|
|
2 |
|
V |
| DVDD_UV |
DVDD undervoltage threshold |
|
|
1.53 |
|
V |
| REF_OV |
Reference overvoltage threshold |
|
|
2.75 |
|
V |
| REF_UV |
Reference undervoltage threshold |
|
|
2.25 |
|
V |
| P_DIAG_PU |
P gain input diagnostics pulldown resistor value |
|
PD2 |
PD1 |
|
|
|
MΩ |
|
0 |
0 |
|
1 |
|
|
0 |
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
1 |
0 |
|
3 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
4 |
|
| INP_OV |
P gain input overvoltage threshold value |
INP+ and INP– each has threshold comparator |
THRS[2] |
THRS[1] |
THRS[0] |
|
|
|
% VBRG |
| VBRG = 2.5 V |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
72.5 |
|
| 0 |
0 |
1 |
|
70 |
|
| 0 |
1 |
0 |
|
65 |
|
| VBRG = 2 V |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
90 |
|
| 1 |
0 |
0 |
|
87.5 |
|
| 1 |
0 |
1 |
|
82.5 |
|
| VBRG = 1.25 V |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
100 |
|
| 1 |
1 |
1 |
|
95 |
|
| INP_UV |
P gain input undervoltage threshold value |
INP+ and INP– each has threshold comparator |
THRS[2] |
THRS[1] |
THRS[0] |
|
|
|
% VBRG |
| VBRG = 2.5 V |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
7.5 |
|
| 0 |
0 |
1 |
|
10.0 |
|
| 0 |
1 |
0 |
|
15.0 |
|
| VBRG = 2.V |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
10.0 |
|
| 1 |
0 |
0 |
|
12.5 |
|
| 1 |
0 |
1 |
|
17.5 |
|
| VBRG = 1.25 V |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
17.5 |
|
| 1 |
1 |
1 |
|
22.5 |
|
| INT_OV |
T gain input overvoltage |
INT+ and INT– each has threshold comparator |
|
2.1 |
|
V |
| PGAIN_OV |
Output overvoltage (single-ended) threshold for P gain |
|
|
2.25 |
|
V |
| PGAIN_UV |
Output undervoltage (single-ended) threshold for P gain |
|
|
0.15 |
|
V |
| TGAIN_OV |
Output overvoltage (single-ended) threshold for T gain |
|
|
2.25 |
|
V |
| TGAIN_UV |
Output undervoltage (single-ended) threshold for T gain |
|
|
0.15 |
|
V |
| HARNESS_FAULT1 |
Open-wire leakage current 1. Open PWR with pullup on OUT |
|
|
2 |
|
µA |
| HARNESS_FAULT2 |
Open-wire leakage current 2. Open GND with pulldown on OUT |
|
|
20 |
|
µA |
6.20 Operating Characteristics
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
| PARAMETER |
TEST CONDITIONS |
MIN |
TYP |
MAX |
UNIT |
| Start-up time(1) |
No IIR filter, |
|
180 |
|
µs |
| Start-up time(2) |
IIR filter = 1000 Hz |
|
1158 |
|
µs |
| Output rate |
|
|
128 |
|
µs |
| Response time(3) |
No IIR filter |
|
211 |
|
µs |
| Response time(4) |
IIR filter = 1000 Hz |
|
1050 |
|
µs |
| Absolute-voltage mode, overall accuracy (PGA300 only, no sense element)(5) |
3 pressure - 1 temperature calibration, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.2 |
|
%FSO |
| 3 pressure - 3 temperature calibration, input voltage not subject to temperature variation, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.1 |
|
%FSO |
| 4 pressure - 4 temperature calibration, input voltage not subject to temperature variation, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.08 |
|
%FSO |
| Ratiometric-voltage mode, overall accuracy (PGA300, no sense element)(5) |
3 pressure - 1 temperature calibration, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.5 |
|
%FSO |
| 3 pressure - 3 temperature calibration, input voltage not subject to temperature variation, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.25 |
|
%FSO |
| 4 pressure - 4 temperature calibration, input voltage not subject to temperature variation, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.2 |
|
%FSO |
| Current mode, overall accuracy (PGA300, no sense element)(5) |
3 pressure - 1 temperature calibration, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.2 |
|
%FSO |
| 3 pressure - 3 temperature calibration, input voltage not subject to temperature variation, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.1 |
|
%FSO |
| 4 pressure - 4 temperature calibration, input voltage not subject to temperature variation, overall accuracy calculated using points different from points used for calibration |
|
0.09 |
|
%FSO |
(1) Time from power up to reach 90% of valid output
(2) Time from power up to reach valid output, including settling time
(3) Time to reach 90% of valid output
(4) Time to reach valid output, including settling time
(5) Sense element held at constant temperature while the PGA300 device was calibrated at –25ºC, 25ºC, 85ºC and 125ºC. Accuracy was then measured at –40ºC, 50ºC and 150 ºC.
6.21 Typical Characteristics
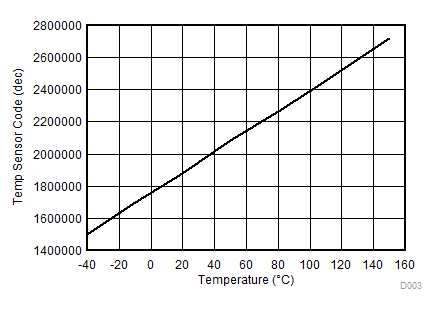 Figure 1. Temperature Sensor Code vs Temperature
Figure 1. Temperature Sensor Code vs Temperature
