-
MSP430FR604x、MSP430FR504x 16MHz MCU 高达 64KB FRAM,12 位高速 8-MSPS Σ-Δ ADC 和集成传感器 AFE ZHCSJA6B January 2019 – December 2021 MSP430FR5041 , MSP430FR5043 , MSP430FR50431 , MSP430FR6041 , MSP430FR6043 , MSP430FR60431
PRODUCTION DATA
-
MSP430FR604x、MSP430FR504x 16MHz MCU 高达 64KB FRAM,12 位高速 8-MSPS Σ-Δ ADC 和集成传感器 AFE
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 功能方框图
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 8.5 Typical Characteristics, Active Mode Supply Currents
- 8.6 Low-Power Mode (LPM0, LPM1) Supply Currents Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 8.7 Low-Power Mode (LPM2, LPM3, LPM4) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.8 Low-Power Mode With LCD Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.9 Low-Power Mode (LPMx.5) Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.10 Typical Characteristics, Low-Power Mode Supply Currents
- 8.11 Current Consumption per Module
- 8.12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 8.13
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.1 Power Supply Sequencing
- 8.13.2 Reset Timing
- 8.13.3 Clock Specifications
- 8.13.4 Wake-up Characteristics
- 8.13.5 Digital I/Os
- 8.13.6 LEA
- 8.13.7 Timer_A and Timer_B
- 8.13.8
eUSCI
- 8.13.8.1 eUSCI (UART Mode) Clock Frequency
- 8.13.8.2 eUSCI (UART Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.3 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Clock Frequency
- 8.13.8.4 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.5 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Timing Diagrams
- 8.13.8.6 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.7 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Timing Diagrams
- 8.13.8.8 eUSCI (I2C Mode) Switching Characteristics
- 8.13.8.9 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode) Timing Diagrams
- 8.13.9 Segment LCD Controller
- 8.13.10
ADC12_B
- 8.13.10.1 12-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- 8.13.10.2 12-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- 8.13.10.3 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
- 8.13.10.4 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With External Reference
- 8.13.10.5 12-Bit ADC, Dynamic Performance With Internal Reference
- 8.13.10.6 12-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In V1/2
- 8.13.10.7 12-Bit ADC, External Reference
- 8.13.10.8 Temperature Sensor Typical Characteristics
- 8.13.11 Reference
- 8.13.12 Comparator
- 8.13.13 FRAM
- 8.13.14 USS
- 8.13.15 Emulation and Debug
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 CPU
- 9.3 Ultrasonic Sensing Solution (USS_A)
- 9.4 Low-Energy Accelerator (LEA) for Signal Processing
- 9.5 Operating Modes
- 9.6 Interrupt Vector Table and Signatures
- 9.7 Bootloader (BSL)
- 9.8 JTAG Operation
- 9.9 FRAM Controller A (FRCTL_A)
- 9.10 RAM
- 9.11 Tiny RAM
- 9.12 Memory Protection Unit (MPU) Including IP Encapsulation
- 9.13
Peripherals
- 9.13.1 Digital I/O
- 9.13.2 Oscillator and Clock System (CS)
- 9.13.3 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 9.13.4 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 9.13.5 Real-Time Clock (RTC_C)
- 9.13.6 Measurement Test Interface (MTIF)
- 9.13.7 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 9.13.8 System Module (SYS)
- 9.13.9 DMA Controller
- 9.13.10 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI)
- 9.13.11 TA0, TA1, and TA4
- 9.13.12 TA2 and TA3
- 9.13.13 TB0
- 9.13.14 ADC12_B
- 9.13.15 USS_A
- 9.13.16 Comparator_E
- 9.13.17 CRC16
- 9.13.18 CRC32
- 9.13.19 AES256 Accelerator
- 9.13.20 True Random Seed
- 9.13.21 Shared Reference (REF)
- 9.13.22 LCD_C
- 9.13.23 Embedded Emulation
- 9.14
Input/Output Diagrams
- 9.14.1 Port Function Select Registers (PySEL1 , PySEL0)
- 9.14.2 Port P1 (P1.0 and P1.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.3 Port P1 (P1.2 to P1.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.4 Port P1 (P1.6 to P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.5 Port P2 (P2.0 to P2.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.6 Port P2 (P2.2 to P2.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.7 Port P2 (P2.4 to P2.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.8 Port P2 (P2.6 to P2.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.9 Port P3 (P3.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.10 Port P3 (P3.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.11 Port P3 (P3.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.12 Port P3 (P3.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.13 Port P3 (P3.4 to P3.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.14 Port P3 (P3.6 to P3.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.15 Port P4 (P4.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.16 Port P4 (P4.1 to P4.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.17 Port P5 (P5.0 to P5.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.18 Port P6 (P6.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.19 Port P6 (P6.1 to P6.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.20 Port P6 (P6.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.21 Port P6 (P6.4) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.22 Port P6 (P6.5 and P6.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.23 Port P7 (P7.0) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.24 Port PJ (PJ.0 to PJ.3) JTAG Pins TDO, TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.25 Port PJ (PJ.4 and PJ.5) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.14.26 Port PJ (PJ.6 and PJ.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.15 Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 9.16 Memory Map
- 9.17 Identification
-
10Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 10.1
Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 10.1.1 Power Supply and Bulk Capacitors
- 10.1.2 External Oscillator (HFXT and LFXT)
- 10.1.3 USS Oscillator (USSXT)
- 10.1.4 Transducer Connection to the USS Module
- 10.1.5 Charge Pump Control of Input Multiplexer
- 10.1.6 JTAG
- 10.1.7 Reset
- 10.1.8 Unused Pins
- 10.1.9 General Layout Recommendations
- 10.1.10 Do's and Don'ts
- 10.2 Peripheral- and Interface-Specific Design Information
- 10.1
Device Connection and Layout Fundamentals
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
- 重要声明
MSP430FR604x、MSP430FR504x 16MHz MCU 高达 64KB FRAM,12 位高速 8-MSPS Σ-Δ ADC 和集成传感器 AFE
1 特性
- 功耗超低的一流超声波水流和气流测量
- 水
- 在低流速到高流速的情况下以及工作温度范围内的差分飞行时间 (dToF) 精度为 ±12.5ps
- 可在 500:1 的宽动态范围内实现 ±1% 精度
- 在直径为 25mm 的管道上,能够测量的最大流速为 8800 升/小时(40 加仑/分钟)
- 能够检测的最小流速小于 1 升/小时(0.005 加仑/分钟)
- 高精度时间测量分辨率小于 5ps
- 在每秒获取一组结果的条件下总体电流消耗大约为 3µA
- 能够支持直径为 15mm 至 1000mm 的宽管道尺寸
- 气体
- 在低流速到高流速的情况下以及工作温度范围内的差分飞行时间 (dToF) 精度为 ±250ps
- 可在流速高达 12000 升/小时的条件下实现 ±1% 的精度,具有 200:1 的宽动态范围
- 能够测量的流速大于 25000 升/小时
- 能够检测的最小流速小于 3 升/小时
- 高精度时间测量分辨率小于 100ps
- 在每秒获取一组结果的条件下总体电流消耗大约为 20µA
- 水
- 符合并超出 ISO4064、OIML R49、EN 14236 和 EN 1434 精度标准
- 能够直接与标准超声波传感器(高达 2.5MHz)连接
- 集成模拟前端 – 超声波传感解决方案 (USS_A),包括
- 用于在各种频率下生成多音调脉冲的可编程脉冲发生器 (PPG)
- 用于控制输入和输出通道且具有低阻抗输出驱动器 (4Ω) 的集成 PHY
- 具有高达 8Msps 输出数据速率的高性能高速 12 位模数转换器 (SDHS)
- 具有 –6.5dB 至 30.8dB 增益的可编程增益放大器 (PGA)
- 输出范围为 68MHz 至 80MHz 的高性能 PLL
- 计量测试接口 (MTIF)
- 脉冲发生器和脉冲计数器
- 脉冲率高达 1024 次脉冲/秒 (p/s)
- 计数容量高达 65535(16 位)
- 在 LPM3.5 下以 200nA(典型值)运行
- 低功耗加速器 (LEA)
- 独立于 CPU 运行
- 与 CPU 共享 8KB RAM
- 高效的 256 点复数 FFT:比 Arm®Cortex®-M0+ 内核最多快 40 倍
- 嵌入式微控制器
- 时钟频率高达 16MHz 的 16 位精简指令集计算机 (RISC) 架构
- 宽电源电压范围:1.8V 至 3.6V (1)
- 优化的超低功耗模式
- 激活模式:大约 120 µA/MHz
- 具有实时时钟 (RTC) 的待机模式 (LPM3.5):450nA (2)
- 关断 (LPM4.5):30nA
- 铁电随机存取存储器 (FRAM)
- 容量高达 64KB 的非易失性存储器
- 超低功耗写入
- 以 125ns/字(4ms 内写入 64KB)的速度快速写入
- 统一的存储器 = 程序 + 数据 + 存储都处于同一存储空间
- 耐写次数达 1015 次
- 抗辐射和非磁性
- 智能数字外设
- 32 位硬件乘法器 (MPY)
- 6 通道内部 DMA
- 带有日历和报警功能的 RTC
- 6 个 16 位计时器,每个计时器具有多达 7 个捕捉/比较寄存器
- 32 位和 16 位循环冗余校验 (CRC)
- 高性能模拟
- 12 通道模拟比较器
- 12 位 ADC,具有窗口比较器、内部基准和采样保持功能以及多达 8 条外部输入通道
- 具有高达 248 段对比度控制的集成 LCD 驱动器
- 多功能输入/输出端口
- 所有引脚均支持电容式触控功能,无需外部组件
- 可按位、字节和字进行访问(成对访问)
- 所有端口均可从 LPM 进行边沿可选唤醒
- 所有端口均具有可设定的上拉电阻或下拉电阻
- 代码安全性和加密
- 128 位或 256 位 AES 安全加密和解密协处理器
- 用于随机数生成算法的随机数种子
- IP 封装可保护存储器免遭外部访问
- FRAM 可提供固有安全性优势
- 增强型串行通信
- 多达 4 个 eUSCI_A 串行通信端口
- 支持自动波特率检测的 UART
- IrDA 编码和解码
- 多达 2 个 eUSCI_B 串行通信端口
- 支持多从器件寻址的 I2C
- 硬件 UART 或 I2C 引导加载程序 (BSL)
- 多达 4 个 eUSCI_A 串行通信端口
- 灵活的时钟系统
- 具有 10 个可选厂家调整频率的固定频率数控振荡器 (DCO)
- 低功耗低频内部时钟源 (VLO)
- 32kHz 晶振 (LFXT)
- 高频晶振 (HFXT)
- 开发工具和软件
- 器件比较汇总了可用的器件型号和封装选项
3 说明
德州仪器 (TI) MSP430FR604x 和 MSP430FR504x SoC 属于 MSP430 超声波传感微控制器 (MCU) 系列,且功能强大、集成度高,专为各种工业应用而设计:
这些 MCU 提供集成的超声波传感解决方案 (USS_A) 模块,该模块可针对多种流速提供高精度测量。USS 模块高度集成,需要的外部组件极少,因而有助于实现超低功耗计量并降低系统成本。
MSP430FR604x 和 MSP430FR504x 器件采用低功耗加速器 (LEA),可实现基于 ADC 的高速信号采集以及后续优化数字信号处理,为电池供电型计量应用提供了一款理想的超低功耗、高精度计量解决方案。
USS_A 模块包括可编程脉冲发生器 (PPG) 和具有低阻抗输出驱动器的物理接口 (PHY),以实现最佳传感器激励和准确的阻抗匹配,从而在零流量漂移 (ZFD) 方面达到最佳效果。USS_A 模块还包含可编程增益放大器 (PGA) 和高速 12 位 8Msps Σ-Δ ADC (SDHS),便于通过行业标准超声波传感器实现精确的信号采集。
此外,MSP430FR604x 和 MSP430FR504x 还集成了其他外设,可提高系统在计量方面的集成度。它具有计量测试接口 (MTIF) 模块,能够通过脉冲生成来指示仪表测量的流量。它还具有片上 8 通道多路复用器 LCD 驱动器(仅限 MSP430FR604x)、实时时钟 (RTC)、12 位 SAR ADC、模拟比较器、高级加密 (AES256) 模块和循环冗余校验 (CRC) 模块。
MSP430FR604x 和 MSP430FR504x MCU 由广泛的硬件和软件生态系统提供支持,随附参考设计和代码示例,便于您快速开始设计。开发套件包括 MSP-TS430PN80C 80 引脚目标开发板和 EVM430-FR6043 超声波气流计 EVM。TI 还提供免费软件,包括超声波感应设计中心、超声波感应软件库和 MSP430Ware™ 软件。
MSP430FR604x 和 MSP430FR504x MCU 系列集成了 TI 的 FRAM(铁电 RAM)和功耗整体超低 MSP 系统架构,从而使系统设计人员能够在降低能耗的同时提升性能。FRAM 技术兼有 RAM 的低功耗快速写入、灵活性、耐用性和闪存非易失性等特性。
有关完整的模块说明,请参阅《MSP430FR58xx、MSP430FR59xx 和 MSP430FR6xx 系列用户指南》。
| 器件型号(1) | 封装(2) | 封装尺寸(3) |
|---|---|---|
| MSP430FR6043IPN | LQFP (80) | 12mm x 12mm |
| MSP430FR60431IPN | LQFP (80) | 12mm x 12mm |
| MSP430FR6041IPN | LQFP (80) | 12mm x 12mm |
| MSP430FR5043IPM | LQFP (64) | 10mm x 10mm |
| MSP430FR50431IPM | LQFP (64) | 10mm x 10mm |
| MSP430FR5041IPM | LQFP (64) | 10mm x 10mm |
| MSP430FR5043IRGC | VQFN (64) | 9mm x 9mm |
| MSP430FR50431IRGC | VQFN (64) | 9mm x 9mm |
| MSP430FR5041IRGC | VQFN (64) | 9mm x 9mm |
4 功能方框图
图 4-1 给出了功能方框图。
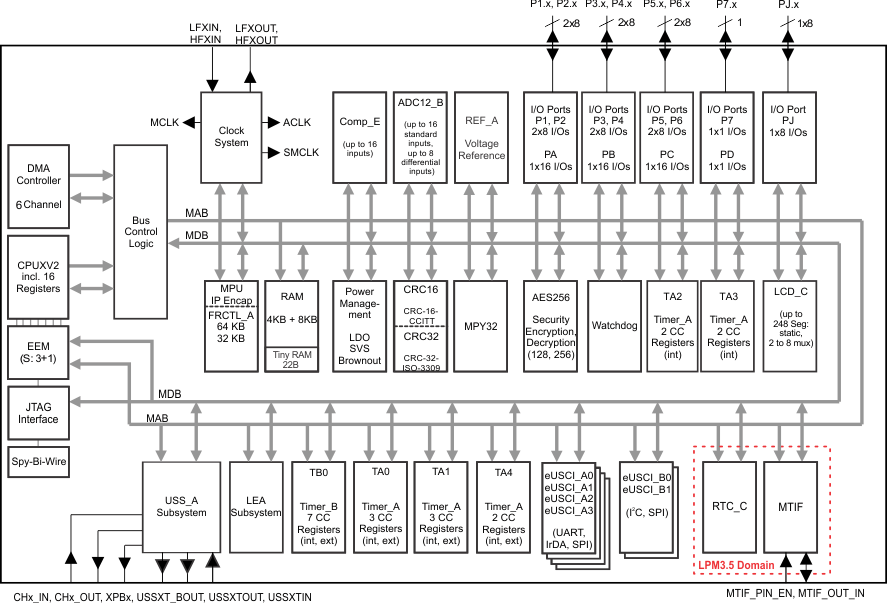
注意:该器件具备 12KB RAM,其中 8KB RAM 与 LEA 子系统共享。
图 4-1 功能方框图5 Revision History
Changed from revision A to revision B
Changes from December 2, 2020 to December 1, 2021
- 更改了文档标题Go
- 在说明 中添加了指向应用资源的链接Go
- Updated Section 11.5, Support Resources Go
Changed from initial release to revision A
Changes from January 19, 2019 to December 1, 2020
- 更新了整个文档中的表格、图和交叉参考的编号格式。Go
- Added notes to Section 8.12, Thermal Resistance Characteristics Go
- Added the note that begins "XT1CLK and VLOCLK can be active during LPM4..." in Section 9.5, Operating Modes Go
- Added the INTERRUPT VECTOR REGISTER column, moved register names from the INTERRUPT FLAG column, and corrected interrupt flag names as necessary in Table 9-4, Interrupt Sources, Flags, Vectors, and Signatures Go
- Corrected the interrupt flag bit numbers for ports P4 to P7 (changed PxIFG.2 to PxIFG.7) in Table 9-4, Interrupt Sources, Flags, and Vectors Go
- Corrected a typo in the PySEL0.x column header in Table 9-24, I/O Function Selection Go
- Corrected the address range for "Main: interrupt vectors" in Table 9-52, Memory Organization Go
6 Device Comparison
Table 6-1 summarizes the available family members.
| DEVICE(1) | FRAM (KB)(2) |
SRAM (KB) |
CLOCK SYSTEM | LEA | LCD | MTIF | ADC12_B (Channels) | Comp_E (Channels) | Timer_A(3) | Timer_B(4) | eUSCI_A(5) | eUSCI_B(6) | AES | BSL | I/O | PACKAGE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSP430FR6043 | 64 | 12 | DCO HFXT LFXT |
Yes | Yes | Yes | 8 external, 2 internal | 12 | 3, 3(7) 2, 2,2(8) |
7 | 4 | 2 | Yes | UART | 57 | 80 PN (LQFP) |
| MSP430FR60431 | 64 | 12 | DCO HFXT LFXT |
Yes | Yes | Yes | 8 external, 2 internal | 12 | 3, 3(7) 2, 2,2(8) |
7 | 4 | 2 | Yes | I2C | 57 | 80 PN (LQFP) |
| MSP430FR6041 | 32 | 12 | DCO HFXT LFXT |
Yes | Yes | Yes | 8 external, 2 internal | 12 | 3, 3(7) 2, 2,2(8) |
7 | 4 | 2 | Yes | UART | 57 | 80 PN (LQFP) |
| MSP430FR5043 | 64 | 12 | DCO HFXT LFXT |
Yes | No | Yes | 7 external, 2 internal | 11 | 3, 3(7) 2, 2,2(8) |
7 | 4 | 2 | Yes | UART | 44 | 64 PM (LQFP) 64 RGC (VQFN) |
| MSP430FR50431 | 64 | 12 | DCO HFXT LFXT |
Yes | No | Yes | 7 external, 2 internal | 11 | 3, 3(7) 2, 2,2(8) |
7 | 4 | 2 | Yes | I2C | 44 | 64 PM (LQFP) 64 RGC (VQFN) |
| MSP430FR5041 | 32 | 12 | DCO HFXT LFXT |
Yes | No | Yes | 7 external, 2 internal | 11 | 3, 3(7) 2, 2,2(8) |
7 | 4 | 2 | Yes | UART | 44 | 64 PM (LQFP) 64 RGC (VQFN) |
6.1 Related Products
For information about other devices in this family of products or related products, see the following links.
TI 16-bit and 32-bit microcontrollers
High-performance, low-power solutions to enable the autonomous future
Products for MSP430 ultra-low-power sensing & measurement MCUs
One platform. One ecosystem. Endless possibilities.
Find reference designs leveraging the best in TI technology to solve your system-level challenges