ZHCSHD7A January 2018 – April 2020 ADC12DJ2700
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics: DC Specifications
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics: Power Consumption
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Dual-Channel Mode)
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics: AC Specifications (Single-Channel Mode)
- 6.9 Timing Requirements
- 6.10 Switching Characteristics
- 6.11 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Device Comparison
- 7.3.2 Analog Inputs
- 7.3.3 ADC Core
- 7.3.4 Temperature Monitoring Diode
- 7.3.5 Timestamp
- 7.3.6 Clocking
- 7.3.7 Digital Down Converters (Dual-Channel Mode Only)
- 7.3.8 JESD204B Interface
- 7.3.9 Alarm Monitoring
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1 Dual-Channel Mode
- 7.4.2 Single-Channel Mode (DES Mode)
- 7.4.3 JESD204B Modes
- 7.4.4 Power-Down Modes
- 7.4.5 Test Modes
- 7.4.6 Calibration Modes and Trimming
- 7.4.7 Offset Calibration
- 7.4.8 Trimming
- 7.4.9 Offset Filtering
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Memory Map
- 7.6.2
Register Descriptions
- 7.6.2.1
Standard SPI-3.0 (0x000 to 0x00F)
- Table 46. Standard SPI-3.0 Registers
- 7.6.2.1.1 Configuration A Register (address = 0x000) [reset = 0x30]
- 7.6.2.1.2 Device Configuration Register (address = 0x002) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.1.3 Chip Type Register (address = 0x003) [reset = 0x03]
- 7.6.2.1.4 Chip ID Register (address = 0x004 to 0x005) [reset = 0x0020]
- 7.6.2.1.5 Chip Version Register (address = 0x006) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.1.6 Vendor Identification Register (address = 0x00C to 0x00D) [reset = 0x0451]
- 7.6.2.2 User SPI Configuration (0x010 to 0x01F)
- 7.6.2.3
Miscellaneous Analog Registers (0x020 to 0x047)
- 7.6.2.3.1 Clock Control Register 0 (address = 0x029) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.3.2 Clock Control Register 1 (address = 0x02A) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.3.3 SYSREF Capture Position Register (address = 0x02C-0x02E) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.3.4 INA Full-Scale Range Adjust Register (address = 0x030-0x031) [reset = 0xA000]
- 7.6.2.3.5 INB Full-Scale Range Adjust Register (address = 0x032-0x033) [reset = 0xA000]
- 7.6.2.3.6 Internal Reference Bypass Register (address = 0x038) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.3.7 TMSTP± Control Register (address = 0x03B) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.4 Serializer Registers (0x048 to 0x05F)
- 7.6.2.5
Calibration Registers (0x060 to 0x0FF)
- 7.6.2.5.1 Input Mux Control Register (address = 0x060) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.5.2 Calibration Enable Register (address = 0x061) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.5.3 Calibration Configuration 0 Register (address = 0x062) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.5.4 Calibration Status Register (address = 0x06A) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.5 Calibration Pin Configuration Register (address = 0x06B) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.5.6 Calibration Software Trigger Register (address = 0x06C) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.5.7 Low-Power Background Calibration Register (address = 0x06E) [reset = 0x88]
- 7.6.2.5.8 Calibration Data Enable Register (address = 0x070) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.5.9 Calibration Data Register (address = 0x071) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.10 Channel A Gain Trim Register (address = 0x07A) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.11 Channel B Gain Trim Register (address = 0x07B) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.12 Band-Gap Reference Trim Register (address = 0x07C) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.13 VINA Input Resistor Trim Register (address = 0x07E) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.14 VINB Input Resistor Trim Register (address = 0x07F) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.15 Timing Adjust for A-ADC, Single-Channel Mode, Foreground Calibration Register (address = 0x080) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.16 Timing Adjust for B-ADC, Single-Channel Mode, Foreground Calibration Register (address = 0x081) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.17 Timing Adjust for A-ADC, Single-Channel Mode, Background Calibration Register (address = 0x082) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.18 Timing Adjust for C-ADC, Single-Channel Mode, Background Calibration Register (address = 0x083) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.19 Timing Adjust for C-ADC, Single-Channel Mode, Background Calibration Register (address = 0x084) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.20 Timing Adjust for B-ADC, Single-Channel Mode, Background Calibration Register (address = 0x085) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.21 Timing Adjust for A-ADC, Dual-Channel Mode Register (address = 0x086) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.22 Timing Adjust for C-ADC Acting for A-ADC, Dual-Channel Mode Register (address = 0x087) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.23 Timing Adjust for C-ADC Acting for B-ADC, Dual-Channel Mode Register (address = 0x088) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.24 Timing Adjust for B-ADC, Dual-Channel Mode Register (address = 0x089) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.25 Offset Adjustment for A-ADC and INA Register (address = 0x08A-0x08B) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.26 Offset Adjustment for A-ADC and INB Register (address = 0x08C-0x08D) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.27 Offset Adjustment for C-ADC and INA Register (address = 0x08E-0x08F) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.28 Offset Adjustment for C-ADC and INB Register (address = 0x090-0x091) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.29 Offset Adjustment for B-ADC and INA Register (address = 0x092-0x093) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.30 Offset Adjustment for B-ADC and INB Register (address = 0x094-0x095) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.5.31 Offset Filtering Control 0 Register (address = 0x097) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.5.32 Offset Filtering Control 1 Register (address = 0x098) [reset = 0x33]
- 7.6.2.6
ADC Bank Registers (0x100 to 0x15F)
- 7.6.2.6.1 Timing Adjustment for Bank 0 (0° Clock) Register (address = 0x102) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.2 Timing Adjustment for Bank 0 (–90° Clock) Register (address = 0x103) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.3 Timing Adjustment for Bank 1 (0° Clock) Register (address = 0x112) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.4 Timing Adjustment for Bank 1 (–90° Clock) Register (address = 0x113) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.5 Timing Adjustment for Bank 2 (0° Clock) Register (address = 0x122) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.6 Timing Adjustment for Bank 2 (–90° Clock) Register (address = 0x123) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.7 Timing Adjustment for Bank 3 (0° Clock) Register (address = 0x132) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.8 Timing Adjustment for Bank 3 (–90° Clock) Register (address = 0x133) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.9 Timing Adjustment for Bank 4 (0° Clock) Register (address = 0x142) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.10 Timing Adjustment for Bank 4 (–90° Clock) Register (address = 0x143) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.11 Timing Adjustment for Bank 5 (0° Clock) Register (address = 0x152) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.6.12 Timing Adjustment for Bank 5 (–90° Clock) Register (address = 0x153) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.7 LSB Control Registers (0x160 to 0x1FF)
- 7.6.2.8
JESD204B Registers (0x200 to 0x20F)
- 7.6.2.8.1 JESD204B Enable Register (address = 0x200) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.8.2 JESD204B Mode Register (address = 0x201) [reset = 0x02]
- 7.6.2.8.3 JESD204B K Parameter Register (address = 0x202) [reset = 0x1F]
- 7.6.2.8.4 JESD204B Manual SYNC Request Register (address = 0x203) [reset = 0x01]
- 7.6.2.8.5 JESD204B Control Register (address = 0x204) [reset = 0x02]
- 7.6.2.8.6 JESD204B Test Pattern Control Register (address = 0x205) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.8.7 JESD204B DID Parameter Register (address = 0x206) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.8.8 JESD204B Frame Character Register (address = 0x207) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.8.9 JESD204B, System Status Register (address = 0x208) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.8.10 JESD204B Channel Power-Down Register (address = 0x209) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.8.11 JESD204B Extra Lane Enable (Link A) Register (address = 0x20A) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.8.12 JESD204B Extra Lane Enable (Link B) Register (address = 0x20B) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.9
Digital Down Converter Registers (0x210-0x2AF)
- 7.6.2.9.1 DDC Configuration Register (address = 0x210) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.9.2 Overrange Threshold 0 Register (address = 0x211) [reset = 0xF2]
- 7.6.2.9.3 Overrange Threshold 1 Register (address = 0x212) [reset = 0xAB]
- 7.6.2.9.4 Overrange Configuration Register (address = 0x213) [reset = 0x07]
- 7.6.2.9.5 DDC Configuration Preset Mode Register (address = 0x214) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.9.6 DDC Configuration Preset Select Register (address = 0x215) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.2.9.7 Digital Channel Binding Register (address = 0x216) [reset = 0x02]
- 7.6.2.9.8 Rational NCO Reference Divisor Register (address = 0x217 to 0x218) [reset = 0x0000]
- 7.6.2.9.9 NCO Synchronization Register (address = 0x219) [reset = 0x02]
- 7.6.2.9.10 NCO Frequency (DDC A or DDC B and Preset x) Register (address = see ) [reset = see ]
- 7.6.2.9.11 NCO Phase (DDC A or DDC B and Preset x) Register (address = see ) [reset = see ]
- 7.6.2.10 Spin Identification Register (address = 0x297) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.2.1
Standard SPI-3.0 (0x000 to 0x00F)
- 7.6.3
SYSREF Calibration Registers (0x2B0 to 0x2BF)
- 7.6.3.1 SYSREF Calibration Enable Register (address = 0x2B0) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.3.2 SYSREF Calibration Configuration Register (address = 0x2B1) [reset = 0x05]
- 7.6.3.3 SYSREF Calibration Status Register (address = 0x2B2 to 0x2B4) [reset = Undefined]
- 7.6.3.4 DEVCLK Aperture Delay Adjustment Register (address = 0x2B5 to 0x2B7) [reset = 0x000000]
- 7.6.3.5 DEVCLK Timing Adjust Ramp Control Register (address = 0x2B8) [reset = 0x00]
- 7.6.4 Alarm Registers (0x2C0 to 0x2C2)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
- ADC 内核:
- 12 位分辨率
- 单通道模式下采样率高达 5.4GSPS
- 双通道模式下采样率高达 2.7GSPS
- 性能规格:
- 本底噪声(无信号,VFS = 1.0VPP-DIFF):
- 双通道模式:–151.6dBFS/Hz
- 单通道模式:–153.8dBFS/Hz
- HD2、HD3:–65dBc,高达 3GHz
- 本底噪声(无信号,VFS = 1.0VPP-DIFF):
- VCMI 为 0V 时的缓冲模拟输入:
- 模拟输入带宽 (-3dB):8.0GHz
- 可用输入频率范围:>10GHz
- 满量程输入电压(VFS,默认值):0.8VPP
- 模拟输入共模电压 (VICM):0V
- 无噪声孔径延迟 (TAD) 调节:
- 采样精度控制:19fs 步长
- 简化同步和交错
- 温度和电压不变延迟
- 简便易用的同步 特性:
- 自动 SYSREF 计时校准
- 样片标记时间戳
- JESD204B 串行数据接口:
- 支持子类 0 和 1
- 最大通道速率:12.8Gbps
- 多达 16 个通道可降低通道速率
- 双通道模式下的数字下变频器:
- 实际输出:DDC 旁路或双倍抽取
- 复杂输出:4 倍、8 倍或 16 倍抽取
- 每个 DDC 均具有四个独立的 32 位 NCO
- 功耗:2.7W
- 电源电压:1.1V、1.9V
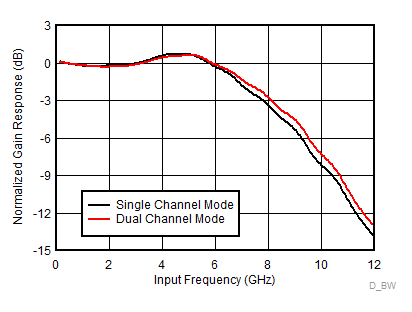
ADC12DJ2700 测量的输入带宽