ZHCSH20 October 2017 TAS5634
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Closed-Loop Architecture
- 8.3.2 Power Supplies
- 8.3.3 System Power-Up / Power-Down Sequence
- 8.3.4 Startup and Shutdown Ramp Sequence (C_START)
- 8.3.5 Device Protection System
- 8.3.6 Overload and Short Circuit Current Protection
- 8.3.7 DC Speaker Protection
- 8.3.8 Pin-To-Pin Short Circuit Protection (PPSC)
- 8.3.9 Overtemperature Protection
- 8.3.10 Overtemperature Warning, OTW
- 8.3.11 Undervoltage Protection (UVP) and Power-On Reset (POR)
- 8.3.12 Error Reporting
- 8.3.13 Fault Handling
- 8.3.14 System Design Consideration
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
- PWM 输入、D 类放大器功率级,与 TI 数字输入 (I2S) 音频处理器和调制器兼容
- 高清集成闭环反馈,具备以下特性:
- 在为 6Ω 负载提供 1W 功率时,THD 为 0.025%
- PSRR 大于 70dB(无输入信号)
- SNR 大于 105dB(A 加权)
- 10% THD+N 时的输出功率
- 600W/3Ω(PBTL 单声道配置)
- 300W/6Ω(BTL 立体声配置)
- 230W/8Ω(BTL 立体声配置)
- 1% THD+N 时的输出功率
- 465W/3Ω(PBTL 单声道配置)
- 240W/6Ω(BTL 立体声配置)
- 180W/8Ω(BTL 立体声配置)
- 集成式 80 mΩ MOSFET,可降低散热器尺寸
- 满量程输出功率下的效率大于 91%
- 1/8 量程输出功率下的效率大于 75%
- 启动时无喀哒声
- 器件保护:欠压保护、过热保护、过流保护、短路保护和直流扬声器保护
- 适用于 G 类电源控制的预削波输出信号
- 44 引脚 HTSSOP (DDV) 封装,顶部带有散热焊盘
2 应用
- 电动扬声器
- 低音炮
- 微型组件系统
- 条形音箱
- 专业和公共广播 (PA) 扬声器
3 说明
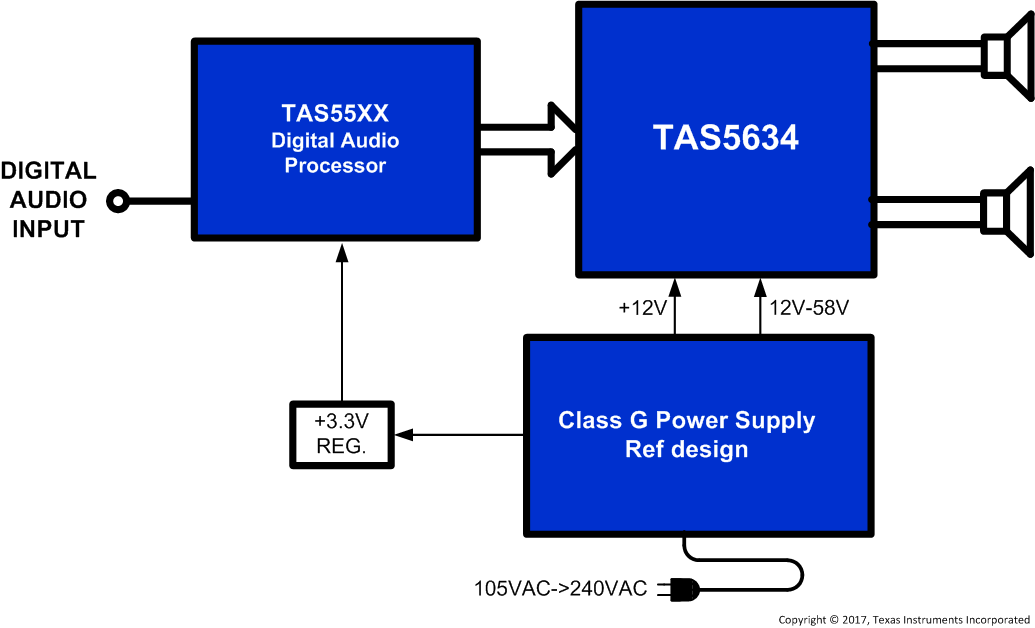
TAS5634 是一款 PWM 输入 D 类放大器功率级,可在 58V 标称电源电压下提供 2 x 300W (6Ω) 或 1 x 600W (3Ω) 的输出功率。58V 电源电压支持较高阻抗的扬声器负载,其中 BTL 为 6Ω,PBTL 为 3Ω。集成式 MOSFET 和全新栅极驱动方案具有较高的峰值效率和较低的空闲损耗,能够减小散热器解决方案尺寸。
TAS5634 使用闭环反馈设计,具有恒定的电压增益。开关模式电源 (SMPS) 的使用,使得内部匹配的增益电阻器可确保实现较高的电源抑制比 (PSRR) 和较低的输出噪声。
TAS5634 是一款兼容 TI 的数字输入 (I2S) 音频处理器和调制器产品组合的全集成式功率级,与 TAS5548 和 TAS5558 类似,也是一个完整的数字输入 D 类放大器。TAS5634 采用表面安装 44 引脚 HTSSOP 封装,是 PWM 输入 D 类功率级兼容引脚产品系列(包括 TAS5612LA、TAS5614LA 和 TAS5624A)中的一员。 PowerPAD™ PurePath™ 高清
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| TAS5634 | HTSSOP | 14.00mm x 6.10mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
简化电路原理图
4 修订历史记录
| 日期 | 修订版本 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 年 10 月 | * | 首次公开发布。 |