ZHCSFJ5 September 2016 ISO5852S-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Function
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Power Ratings
- 7.6 Insulation Specifications
- 7.7 Safety Limiting Values
- 7.8 Safety-Related Certifications
- 7.9 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.10 Switching Characteristics
- 7.11 Safety and Insulation Characteristics Curves
- 7.12 Typical Characteristics
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2
Typical Applications
- 10.2.1 Design Requirements
- 10.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 10.2.2.1 Recommended ISO5852S-Q1 Application Circuit
- 10.2.2.2 FLT and RDY Pin Circuitry
- 10.2.2.3 Driving the Control Inputs
- 10.2.2.4 Local Shutdown and Reset
- 10.2.2.5 Global-Shutdown and Reset
- 10.2.2.6 Auto-Reset
- 10.2.2.7 DESAT Pin Protection
- 10.2.2.8 DESAT Diode and DESAT Threshold
- 10.2.2.9 Determining the Maximum Available, Dynamic Output Power, POD-max
- 10.2.2.10 Example
- 10.2.2.11 Higher Output Current Using an External Current Buffer
- 10.2.3 Application Curves
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
- 适用于汽车电子 应用
- 具有符合 AEC-Q100 标准的下列结果:
- 器件温度 1 级:-40°C 至 125°C 的环境运行温度范围
- 器件人体模型 (HBM) 分类等级 3A
- 器件充电器件模型 (CDM) 分类等级 C6
- VCM = 1500V 时,共模瞬态抗扰度 (CMTI) 的最小值为 100kV/μs
- 分离输出,可提供 2.5A 峰值拉电流和 5A 峰值灌电流
- 短暂传播延迟:76ns(典型值),
110ns(最大值) - 2A 有源米勒钳位
- 输出短路钳位
- 短路期间的软关断 (STO)
- 在检测到去饱和故障时通过 FLT 发出故障报警,并通过 RST 复位
- 具有就绪 (RDY) 引脚指示的输入和输出欠压锁定 (UVLO)
- 有源输出下拉特性,在低电源或输入悬空的情况下默认输出低电平
- 2.25V 至 5.5V 输入电源电压
- 15V 至 30V 输出驱动器电源电压
- 互补金属氧化物半导体 (CMOS) 兼容输入
- 抑制短于 20ns 的输入脉冲和瞬态噪声
- 可承受的浪涌隔离电压达 12800VPK ”
- 安全相关认证:
- 符合 DIN V VDE V 0884-10 (VDE V 0884-10):2006-12 标准的 8000 VPK VIOTM 和 2121 VPK VIORM 增强型隔离
- 符合 UL 1577 标准且长达 1 分钟的 5700 VRMS 隔离
- CSA 组件验收通知 5A,IEC 60950-1 和 IEC 60601-1 终端设备标准
- 符合 EN 61010-1 和 EN 60950-1 标准的 TUV 认证
- GB4943.1-2011 CQC 认证
- 已通过 UL、VDE、CQC、TUV 认证并规划进行 CSA 认证
2 应用
- 隔离式绝缘栅双极型晶体管 (IGBT) 和金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管 (MOSFET) 驱动器:
- 混合动力汽车 (HEV) 和电动车 (EV) 电源模块
- 工业电机控制驱动
- 工业电源
- 太阳能逆变器
- 感应加热
3 说明
ISO5852S-Q1 器件是一款用于 IGBT 和 MOSFET 的 5.7 kVRMS 增强型隔离栅极驱动器,具有分离输出(OUTH 和 OUTL)以及 2.5A 的拉电流能力和 5A 的灌电流能力。输入端由 2.25V 至 5.5V 的单电源供电运行。输出端允许的电源范围为 15V 至 30V。两个互补 CMOS 输入控制栅极驱动器的输出状态。76ns 的短暂传播时间保证了对于输出级的精确控制。中的文本由“3V 至 5.5V 单电源”更改为“2.25V 至 5.5V 单电源”中的文本由“IGBT 处于过载状态”更改为“IGBT 处于过流状态”
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| ISO5852S-Q1 | SOIC (16) | 10.30mm x 7.50mm |
- 要了解所有可用封装,请见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
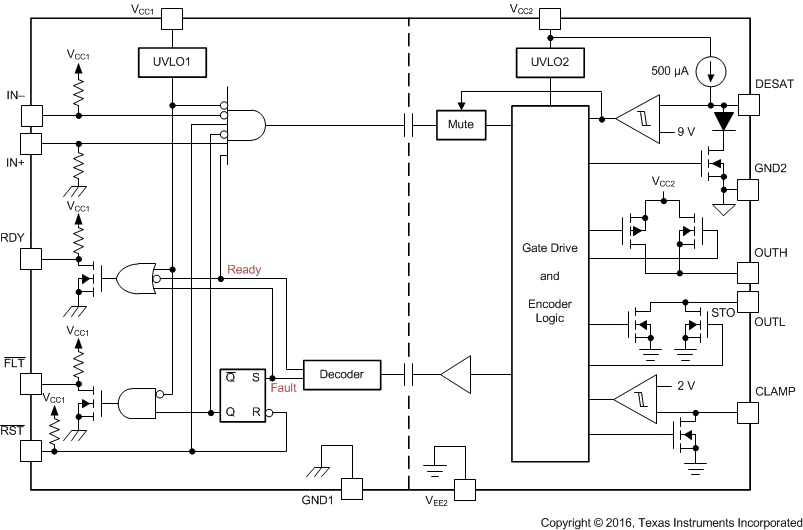
功能方框图
4 修订历史记录
| 日期 | 修订版本 | 注释 |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 年 9 月 | * | 最初发布。 |