ZHCSEN4E September 2015 – April 2018 LMK03318
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 器件比较表
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Thermal Information
- 8.5 Thermal Information
- 8.6 Electrical Characteristics - Power Supply
- 8.7 Pullable Crystal Characteristics (SECREF_P, SECREF_N)
- 8.8 Non-Pullable Crystal Characteristics (SECREF_P, SECREF_N)
- 8.9 Clock Input Characteristics (PRIREF_P/PRIREF_N, SECREF_P/SECREF_N)
- 8.10 VCO Characteristics
- 8.11 PLL Characteristics
- 8.12 1.8-V LVCMOS Output Characteristics (OUT[7:0])
- 8.13 LVCMOS Output Characteristics (STATUS[1:0])
- 8.14 Open-Drain Output Characteristics (STATUS[1:0])
- 8.15 AC-LVPECL Output Characteristics
- 8.16 AC-LVDS Output Characteristics
- 8.17 AC-CML Output Characteristics
- 8.18 HCSL Output Characteristics
- 8.19 Power-On Reset Characteristics
- 8.20 2-Level Logic Input Characteristics (HW_SW_CTRL, PDN, GPIO[5:0])
- 8.21 3-Level Logic Input Characteristics (REFSEL, GPIO[3:1])
- 8.22 Analog Input Characteristics (GPIO[5])
- 8.23 I2C-Compatible Interface Characteristics (SDA, SCL)
- 8.24 Typical 156.25-MHz Closed-Loop Output Phase Noise Characteristics
- 8.25 Typical 161.1328125-MHz Closed-Loop Output Phase Noise Characteristics
- 8.26 Closed-Loop Output Jitter Characteristics
- 8.27 PCIe Clock Output Jitter
- 8.28 Typical Power Supply Noise Rejection Characteristics
- 8.29 Typical Power-Supply Noise Rejection Characteristics
- 8.30 Typical Closed-Loop Output Spur Characteristics
- 8.31 Typical Characteristics
- 9 Parameter Measurement Information
-
10Detailed Description
- 10.1 Overview
- 10.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 10.3 Feature Description
- 10.4
Device Functional Modes
- 10.4.1 Smart Input MUX
- 10.4.2 Universal Input Buffer (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
- 10.4.3 Crystal Input Interface (SEC_REF)
- 10.4.4 Reference Doubler
- 10.4.5 Reference Divider (R)
- 10.4.6 Input Divider (M)
- 10.4.7 Feedback Divider (N)
- 10.4.8 Phase Frequency Detector (PFD)
- 10.4.9 Charge Pump
- 10.4.10 Loop Filter
- 10.4.11 VCO Calibration
- 10.4.12 Fractional Circuitry
- 10.4.13 Post Divider
- 10.4.14 High-Speed Output MUX
- 10.4.15 High-Speed Output Divider
- 10.4.16 High-Speed Clock Outputs
- 10.4.17 Output Synchronization
- 10.4.18 Status Outputs
- 10.5 Programming
- 10.6
Register Maps
- 10.6.1 VNDRID_BY1 Register; R0
- 10.6.2 VNDRID_BY0 Register; R1
- 10.6.3 PRODID Register; R2
- 10.6.4 REVID Register; R3
- 10.6.5 PARTID Register; R4
- 10.6.6 PINMODE_SW Register; R8
- 10.6.7 PINMODE_HW Register; R9
- 10.6.8 SLAVEADR Register; R10
- 10.6.9 EEREV Register; R11
- 10.6.10 DEV_CTL Register; R12
- 10.6.11 INT_LIVE Register; R13
- 10.6.12 INT_MASK Register; R14
- 10.6.13 INT_FLAG_POL Register; R15
- 10.6.14 INT_FLAG Register; R16
- 10.6.15 INTCTL Register; R17
- 10.6.16 OSCCTL2 Register; R18
- 10.6.17 STATCTL Register; R19
- 10.6.18 MUTELVL1 Register; R20
- 10.6.19 MUTELVL2 Register; R21
- 10.6.20 OUT_MUTE Register; R22
- 10.6.21 STATUS_MUTE Register; R23
- 10.6.22 DYN_DLY Register; R24
- 10.6.23 REFDETCTL Register; R25
- 10.6.24 STAT0_INT Register; R27
- 10.6.25 STAT1 Register; R28
- 10.6.26 OSCCTL1 Register; R29
- 10.6.27 PWDN Register; R30
- 10.6.28 OUTCTL_0 Register; R31
- 10.6.29 OUTCTL_1 Register; R32
- 10.6.30 OUTDIV_0_1 Register; R33
- 10.6.31 OUTCTL_2 Register; R34
- 10.6.32 OUTCTL_3 Register; R35
- 10.6.33 OUTDIV_2_3 Register; R36
- 10.6.34 OUTCTL_4 Register; R37
- 10.6.35 OUTDIV_4 Register; R38
- 10.6.36 OUTCTL_5 Register; R39
- 10.6.37 OUTDIV_5 Register; R40
- 10.6.38 OUTCTL_6 Register; R41
- 10.6.39 OUTDIV_6 Register; R42
- 10.6.40 OUTCTL_7 Register; R43
- 10.6.41 OUTDIV_7 Register; R44
- 10.6.42 CMOSDIVCTRL Register; R45
- 10.6.43 CMOSDIV0 Register; R46
- 10.6.44 STATUS_SLEW Register; R49
- 10.6.45 IPCLKSEL Register; R50
- 10.6.46 IPCLKCTL Register; R51
- 10.6.47 PLL_RDIV Register; R52
- 10.6.48 PLL_MDIV Register; R53
- 10.6.49 PLL_CTRL0 Register; R56
- 10.6.50 PLL_CTRL1 Register; R57
- 10.6.51 PLL_NDIV_BY1 Register; R58
- 10.6.52 PLL_NDIV_BY0 Register; R59
- 10.6.53 PLL_FRACNUM_BY2 Register; R60
- 10.6.54 PLL_FRACNUM_BY1 Register; R61
- 10.6.55 PLL_FRACNUM_BY0 Register; R62
- 10.6.56 PLL_FRACDEN_BY2 Register; R63
- 10.6.57 PLL_FRACDEN_BY1 Register; R64
- 10.6.58 PLL_FRACDEN_BY0 Register; R65
- 10.6.59 PLL_MASHCTRL Register; R66
- 10.6.60 PLL_LF_R2 Register; R67
- 10.6.61 PLL_LF_C1 Register; R68
- 10.6.62 PLL_LF_R3 Register; R69
- 10.6.63 PLL_LF_C3 Register; R70
- 10.6.64 SEC_CTRL Register; R72
- 10.6.65 XO_MARGINING Register; R86
- 10.6.66 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_1_BY1 Register; R88
- 10.6.67 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_1_BY0 Register; R89
- 10.6.68 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_2_BY1 Register; R90
- 10.6.69 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_2_BY0 Register; R91
- 10.6.70 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_3_BY1 Register; R92
- 10.6.71 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_3_BY0 Register; R93
- 10.6.72 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_4_BY1 Register; R94
- 10.6.73 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_4_BY0 Register; R95
- 10.6.74 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_5_BY1 Register; R96
- 10.6.75 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_5_BY0 Register; R97
- 10.6.76 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_6_BY1 Register; R98
- 10.6.77 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_6_BY0 Register; R99
- 10.6.78 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_7_BY1 Register; R100
- 10.6.79 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_7_BY0 Register; R101
- 10.6.80 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_8_BY1 Register; R102
- 10.6.81 XO_OFFSET_GPIO5_STEP_8_BY0 Register; R103
- 10.6.82 XO_OFFSET_SW_BY1 Register; R104
- 10.6.83 XO_OFFSET_SW_BY0 Register; R105
- 10.6.84 PLL_CTRL2 Register; R117
- 10.6.85 PLL_CTRL3 Register; R118
- 10.6.86 PLL_CALCTRL0 Register; R119
- 10.6.87 PLL_CALCTRL1 Register; R120
- 10.6.88 NVMCNT Register; R136
- 10.6.89 NVMCTL Register; R137
- 10.6.90 NVMLCRC Register; R138
- 10.6.91 MEMADR_BY1 Register; R139
- 10.6.92 MEMADR_BY0 Register; R140
- 10.6.93 NVMDAT Register; R141
- 10.6.94 RAMDAT Register; R142
- 10.6.95 ROMDAT Register; R143
- 10.6.96 NVMUNLK Register; R144
- 10.6.97 REGCOMMIT_PAGE Register; R145
- 10.6.98 XOCAPCTRL_BY1 Register; R199
- 10.6.99 XOCAPCTRL_BY0 Register; R200
- 10.6.100 EEPROM Map
- 11Application and Implementation
- 12Power Supply Recommendations
- 13Layout
- 14器件和文档支持
- 15机械、封装和可订购信息
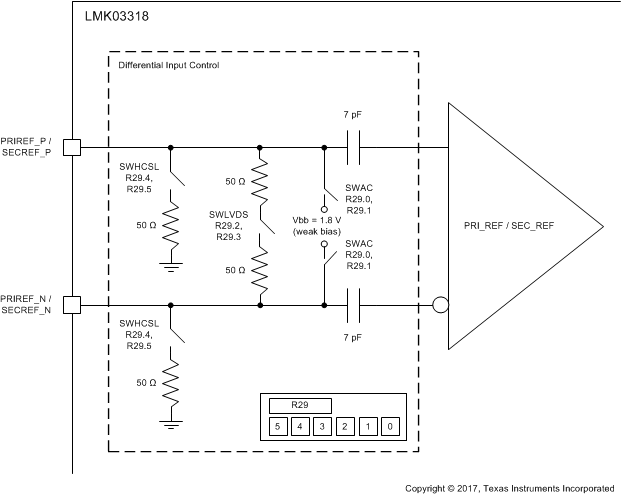
10.4.2 Universal Input Buffer (PRI_REF, SEC_REF)
The primary reference can support differential or single-ended clocks. The secondary reference can support differential or single-ended clocks or crystal. The differential input buffers on both primary and secondary support internal 50 Ω to ground or 100 Ω termination between P and N followed by on-chip AC-coupling capacitors to internal self-biased circuitry. Internal biasing is offered before the on-chip AC-coupling capacitors when the clock inputs are AC coupled externally, and this is enabled by setting R29.0 = 1 (for primary reference) or R29.1 = 1 (for secondary reference). When the clock inputs are DC coupled, the internal biasing before the on-chip AC-coupling capacitors is disabled by settings R29.0 = 0 (for primary reference) or R29.1 = 0 (for secondary reference). Figure 45 shows the differential input buffer termination options implemented on both primary and secondary and the switches (SWLVDS, SWHCSL, SWAC) are controlled by R29[5-0]. Table 4 shows the primary and secondary buffer configuration matrix for LVPECL, CML, LVDS, HCSL and LVCMOS inputs.
Table 4. Input Buffer Configuration Matrix on Primary and/or Secondary Reference(1)
| R50.5 / R50.7 | R50.4 / R50.6 | R29.4 / R29.5 | R29.2 / R29.3 | R29.0 / R29.1 | MODE | EXTERNAL COUPLING | TERMINATION | BIASING |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | HCSL | AC | Internal | Internal |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | LVDS | AC | Internal | Internal |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | LVPECL | AC | Internal | Internal |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | CML | AC | Internal | Internal |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | HCSL | DC | Internal | External |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | LVDS | DC | Internal | External |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | LVPECL | DC | External | External |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | CML | DC | External | External |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | LVCMOS | DC | N/A | N/A |
Figure 46 through Figure 55 show recommendations for interfacing primary or secondary inputs of the LMK03318 with LVCMOS, LVPECL, LVDS, CML and HCSL drivers, respectively.
NOTE
The secondary reference accepts up to 2.6-V maximum swing when LVCMOS input option is selected.
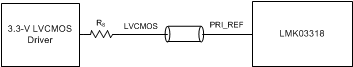 Figure 46. Interfacing LMK03318 Primary Input With 3.3-V LVCMOS Signal
Figure 46. Interfacing LMK03318 Primary Input With 3.3-V LVCMOS Signal
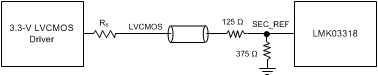 Figure 47. Interfacing LMK03318 Secondary Input With 3.3-V LVCMOS Signal
Figure 47. Interfacing LMK03318 Secondary Input With 3.3-V LVCMOS Signal
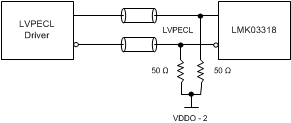 Figure 48. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVPECL Signal
Figure 48. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVPECL Signal
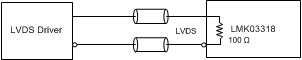 Figure 49. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVDS Signal
Figure 49. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVDS Signal
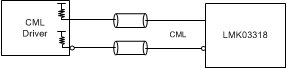 Figure 50. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With CML Signal
Figure 50. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With CML Signal
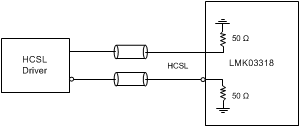 Figure 51. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With HCSL Signal
Figure 51. DC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With HCSL Signal
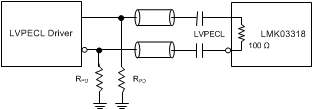 Figure 52. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVPECL Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
Figure 52. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVPECL Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
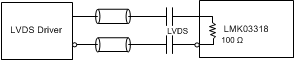 Figure 53. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVDS Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
Figure 53. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With LVDS Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
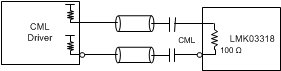 Figure 54. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With CML Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
Figure 54. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With CML Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
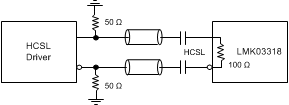 Figure 55. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With HCSL Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)
Figure 55. AC-Coupling LMK03318 Inputs With HCSL Signal (Internal Biasing Enabled)