SNVS536F October 2007 – July 2015 LM2757
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The LM2757 is a switched capacitor converter that produces a regulated output voltage of either 5 V, 4.5 V or 4.1 V, depending on the mode selected. The core of the part is a highly efficient charge pump that utilizes fixed frequency pre-regulation to minimize ripple and power losses over wide input voltage and output current ranges. A description of the principal operational characteristics of the LM2757 is shown in the Functional Block Diagram and detailed in Feature Description.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
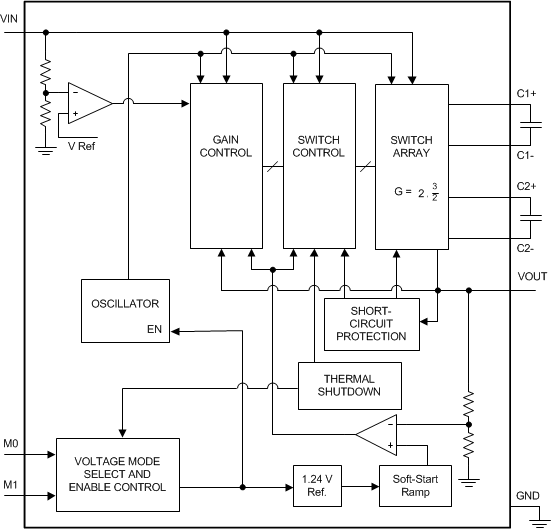
8.3 Feature Description
The core of the LM2757 is a two-phase charge pump controlled by an internally generated non-overlapping clock. The charge pump operates by using external flying capacitors C1 and C2 to transfer charge from the input to the output. At input voltages below 3.9 V (typical) for the 5-V mode, the LM2757 operates in a 2× gain, with the input current being equal to 2× the load current. At input voltages above 3.9 V (typical) for the 5-V mode, the part utilizes a gain of 3/2×, resulting in an input current equal to 3/2 times the load current. For the 4.5-V mode, the LM2757 operates in a 2× gain when the input voltage is below 3.35 V (typical) and transitions to a 3/2× gain when the input voltage is above 3.35 V (typical). For the 4.1-V mode, the device utilizes the 3/2× gain for the entire input voltage range.
The two phases of the switched capacitor switching cycle are referred to as the phase one and the phase two. During phase one, one flying capacitor is charged by the input supply while the other flying capacitor is connected to the output and delivers charge to the load . After half of the switching cycle [ t = 1/(2 × ƒSW)], the LM2757 switches to phase two. In this configuration, the capacitor that supplied charge to the load in phase one is connected to the input to be recharged while the capacitor that had been charged in the previous phase is connected to the output to deliver charge. With this topology, output ripple is reduced by delivering charge to the output in every phase.
The LM2757 uses fixed frequency pre-regulation to regulate the output voltage. The input and output connections of the flying capacitors are made with internal MOS switches. Pre-regulation limits the gate drive of the MOS switch connected between the voltage input and the flying capacitors. Controlling the on resistance of this switch limits the amount of charge transferred into and out of each flying capacitor during the charge and discharge phases, and in turn helps to keep the output ripple very low.
8.3.1 Efficiency Performance
Charge-pump efficiency is derived in Equation 1 and Equation 2 (supply current and other losses are neglected for simplicity):
where
- G = the charge pump gain
- E = efficiency
Efficiency is at its highest as G × VIN approaches VOUT. Refer to Typical Characteristics for detailed efficiency data. The transition between gains of 3/2 and 2 are clearly distinguished by the sharp discontinuity in the efficiency curve.
8.3.2 Soft Start
The LM2757 employs soft-start circuitry to prevent excessive input inrush currents during start-up. At start-up, the output voltage gradually rises from 0 V to the nominal output voltage. This occurs in 300 µs (typical). Soft-start is engaged when the device is enabled.
8.3.3 Thermal Shutdown
Protection from damage related to overheating is achieved with a thermal shutdown feature. When the junction temperature rises to 145°C (typical), the device switches into shutdown mode. The LM2757 disengages thermal shutdown when the junction temperature of the part is reduced to 135°C (typical). Due to the high efficiency of the LM2757, thermal shutdown and/or thermal cycling are not encountered when the part is operated within specified input voltage, output current, and ambient temperature operating ratings. If thermal cycling is seen under these conditions, the most likely cause is an inadequate PCB layout that does not allow heat to be sufficiently dissipated out of the device.
8.3.4 Current-Limit Protection
The LM2757 charge pump contains current-limit protection circuitry that protects the device during VOUT fault conditions where excessive current is drawn. Output current is limited to 250 mA (typical).
8.4 Device Functional Modes
8.4.1 Enable and Voltage Mode Selection
The LM2757 is enabled when either one of the mode select pins (M0, M1) has a logic High voltage applied to it. There are 450-kΩ pulldown resistors connected internally to each of the mode select pins. The voltage mode is selected according to Table 1.
8.4.2 Shutdown With Output High Impedance
The LM2757 is in shutdown mode when there is a logic Low voltage on both mode select pins (M0, M1). There are also 450-kΩ pulldown resistors connected to both mode select pins, pulling the nodes down to ground when there is no signal present. When in shutdown, the output of the LM2757 is high impedance, allowing an external supply to drive the output line such as in USB OTG or mobile HDMI applications. Refer to the output leakage current graphs in Typical Characteristics for typical leakage currents into the VOUT pin, when driven by a separate supply during shutdown. Output leakage increases with temperature, with the lowest leakage occurring at –30°C and the highest leakage at 85°C (on which the graph is based). It should be noted when looking at the graphs as the input voltage falls the leakage peaks at around an input voltage of 1.5 V, then goes down as the input voltage decrease to 0 V. The leakage at an input voltage of 0 V is the same as the leakage current when the battery is disconnected from the circuit.