SLVSC31D December 2013 – August 2015
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Description (continued)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
- For best performance, all traces should be as short as possible.
- Use wide traces for IN, OUT, and GND to minimize the parasitic electrical effects.
- TI recommends a minimum output capacitor of 10 μF with an ESR of 3 Ω or less to prevent oscillations. X7R dielectrics are preferred.
- Place the output capacitor (COUT) as close as possible to the OUT pin of the device.
- SHDN can be driven by 5-V logic, 3-V logic, or open-collector logic with a pullup resistor.The device is in the low-power shutdown state if SHDN is not connected.
- The exposed thermal vias of the HKU package should be connected to a wide ground plane for effective heat dissipation. Refer to Figure 29, Figure 30, and Figure 31 for the typical footprint of the HKU package.
11.2 Layout Example
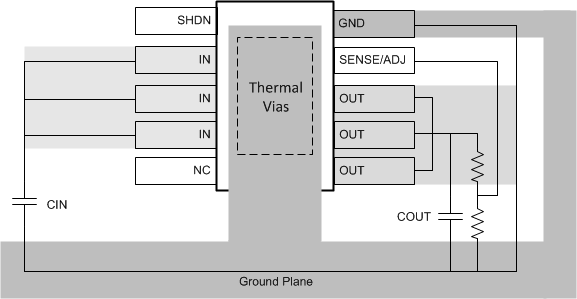 Figure 28. Example of Layout
Figure 28. Example of Layout
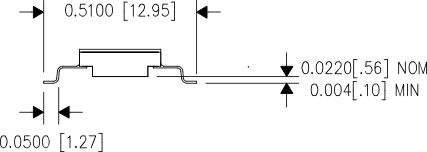 Figure 29. Typical HKU Package With Leads Form
Figure 29. Typical HKU Package With Leads Form
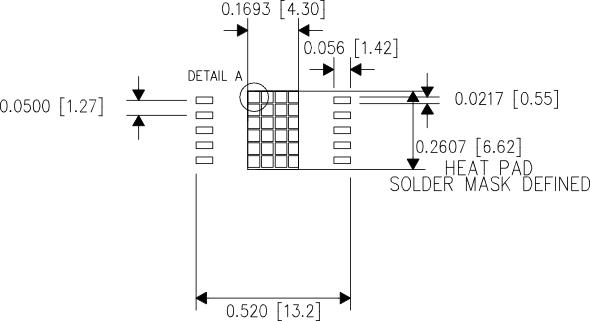 Figure 30. Typical Thermal Vias Footprint
Figure 30. Typical Thermal Vias Footprint
 Figure 31. Typical Thermal Vias Details
Figure 31. Typical Thermal Vias Details
11.3 Thermal Considerations
The power-handling capability of the device is limited by the maximum-rated junction temperature (125°C). The power dissipated by the device is made up of two components:
- Output current multiplied by the input/output voltage differential: IOUT(VIN – VOUT)
- GND pin current multiplied by the input voltage: IGNDVIN.
Find the GND pin current by using the GND pin current graphs in Typical Characteristics. Power dissipation is equal to the sum of the two components listed previously.
The TPS7A4501-SP regulators have internal thermal limiting designed to protect the device during overload conditions. For continuous normal conditions, do not exceed the maximum junction temperature rating of 125°C. It is important to give careful consideration to all sources of thermal resistance from junction to ambient. Also consider additional heat sources mounted nearby.
For surface-mount devices, heat sinking is accomplished by using the heat-spreading capabilities of the PCB and its copper traces. Copper board stiffeners and plated through-holes can also be used to spread the heat generated by power devices.
11.3.1 Calculating Junction Temperature
Example: Given an output voltage of 3.3 V, an input voltage range of 4 to 6 V, an output current range of 0 to 500 mA, and a maximum case temperature of 50°C, what is the maximum junction temperature?
The power dissipated by the device is equal to:
where
- IOUT(MAX) = 500 mA
- VIN(MAX) = 6 V
- IGND at (IOUT = 500 mA, VIN = 6 V) = 10 mA
So,
Using a U package, the thermal resistance is about 10.3°C/W. So the junction temperature rise above case is approximately equal to:
The maximum junction temperature is then equal to the maximum junction-temperature rise above case plus the maximum case temperature or: