SLVS710C January 2007 – February 2017 TPS65050
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Options
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagrams
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Operation of DCDC Converters
- 8.3.2 Power-Save Mode
- 8.3.3 Dynamic Voltage Positioning
- 8.3.4 Soft Start
- 8.3.5 100% Duty Cycle Low Dropout Operation
- 8.3.6 Undervoltage Lockout
- 8.3.7 Mode Selection
- 8.3.8 Enable
- 8.3.9 RESET
- 8.3.10 Push-Button ON-OFF (PB-ON-OFF)
- 8.3.11 Short-Circuit Protection
- 8.3.12 Thermal Shutdown
- 8.3.13 Low Dropout Voltage Regulators
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2 Typical Application
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
- The input capacitors for the DC-DC converters should be placed as close as possible to the VINDCDC1/2 pin and the PGND1 and PGND2 pins.
- The inductor of the output filter should be placed as close as possible to the device to provide the shortest switch node possible, reducing the noise emitted into the system and increasing the efficiency.
- Sense the feedback voltage from the output at the output capacitors to ensure the best DC accuracy. Feedback should be routed away from noisy sources such as the inductor. If possible route on the opposing side as the switch node and inductor and place a GND plane between the feedback and the noisy sources or keepout underneath them entirely.
- Place the output capacitors as close as possible to the inductor to reduce the feedback loop as much as possible. This will ensure best regulation at the feedback point.
- Place the device as close as possible to the most demanding or sensitive load. The output capacitors should be placed close to the input of the load. This will ensure the best AC performance possible.
- The input and output capacitors for the LDOs should be placed close to the device for best regulation performance.
- TI recommends using the common ground plane for the layout of this device. The AGND can be separated from the PGND but, a large low parasitic PGND is required to connect the PGNDx pins to the CIN and external PGND connections. If the AGND and PGND planes are separated, have one connection point to reference the grounds together. Place this connection point close to the IC.
11.2 Layout Example
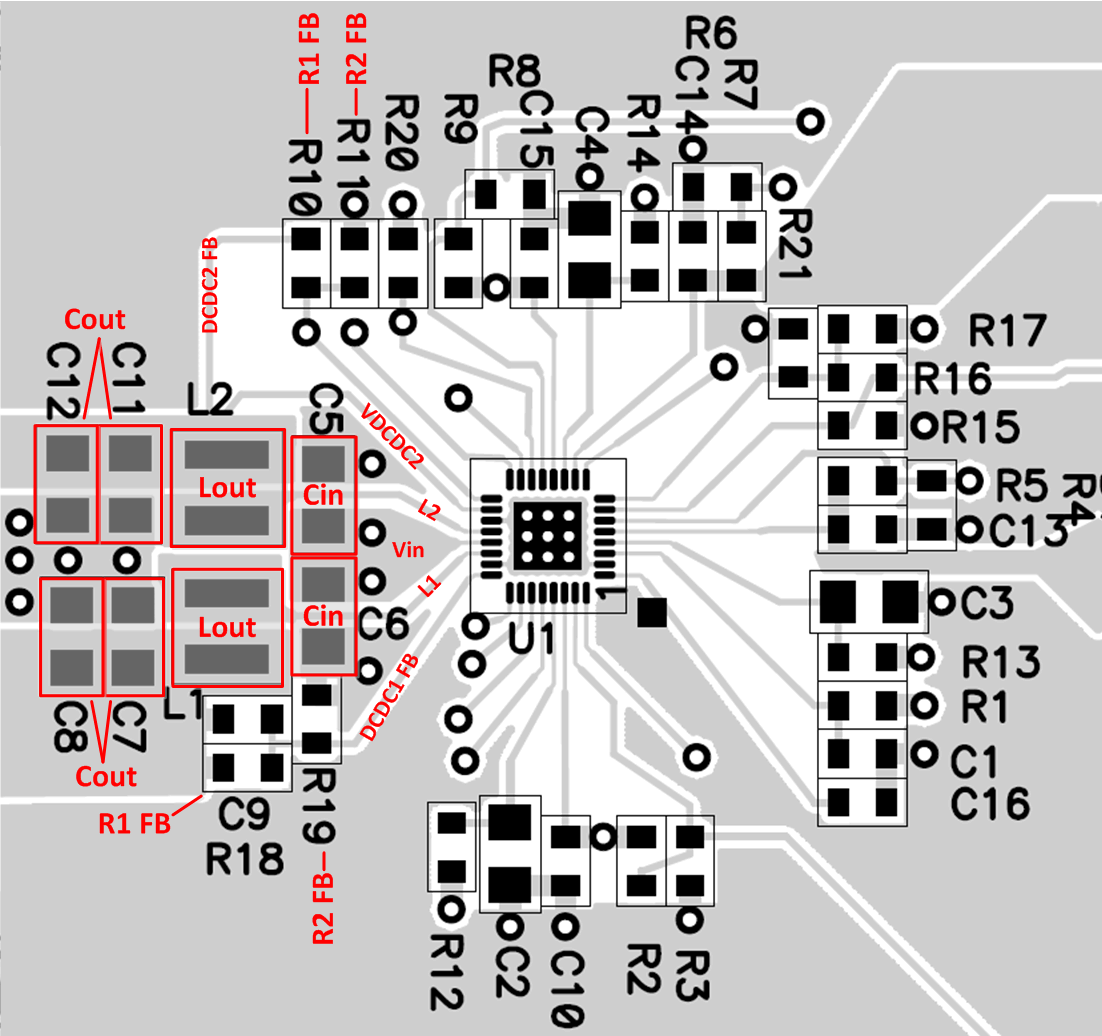 Figure 32. Layout Example from EVM for TPS6505x
Figure 32. Layout Example from EVM for TPS6505x