SLVAEY9 October 2020 TPS23730 , TPS23731 , TPS23734
1 Introduction
While the active clamp forward topology enables high efficiencies for PoE DC/DC designs, there are certain design considerations or component selections that require special attention. One such consideration is the stress on the switching MOSFETs. When power is removed, the behavior of the controller can create situations that cause either high voltage or high current in the circuit (or both).
To address this condition, one approach is to increase the ratings of parts (example: a higher voltage MOSFET). While this quickly solves the problem with little design effort, this approach leads to higher system cost. As the output voltage of the DC/DC converter increases, the stress on the MOSFETs increases, driving the cost up disproportionately to the output voltage increase. Since the voltage and current spikes are not the nominal values of the switching voltages and currents, the opportunity for lower cost parts is possible if the spikes are addressed in another way. This will also drive the cost ramp down for higher output voltage active clamp forward designs.
The TPS23730, TPS23734, and TPS23734 devices introduce a new approach, called soft-stop. This approach consists of controlling the discharge of the output capacitor of the converter, and subsequently sending the energy back to the input bulk capacitor.
Figure 1-1 illustrates an active clamp forward design.
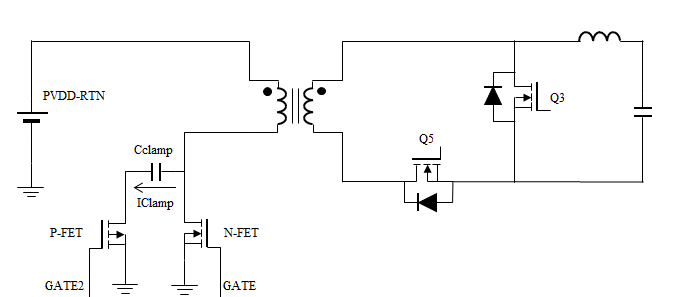 Figure 1-1 Active Clamp Forward Design.
Figure 1-1 Active Clamp Forward Design.