SLUAAE4 May 2021 TPS563211
2.2 AECM Control Principle
The PWM mode control scheme is similar to PCM control. As shown in Figure 2-2 on the following page, the internal clock initials one on-pulse; the high-side FET then turns on, with current increasing in the inductor. When the emulated ramp voltage, feedback voltage and slope compensation voltage reach the integrated reference voltage, the high-side FET turns off and the low-side FET turns on until the next clock cycle. Therefore, in PWM mode, the switching frequency is truly fixed.
AECM control implements PFM mode to achieve high efficiency under light loads. With a load current decrease, the device enters into discontinuous conduction mode (DCM) from continuous conduction mode (CCM). In both modes, the switching frequency is fixed; the width of the on-pulse (Ton) depends on the load current. Lighter loads have a shorter Ton. AECM has an on-time generator like the D-CAP2 control topology, but that generator is disabled in PWM mode. With the load current further decreasing, the Ton decreases down to the internal clamped on-time, while the AECM device steps into PFM mode with the internal clock blocked and the on-time generator enabled. As shown in Figure 2-2, the control scheme of PFM mode is similar to the D-CAP2 control scheme.
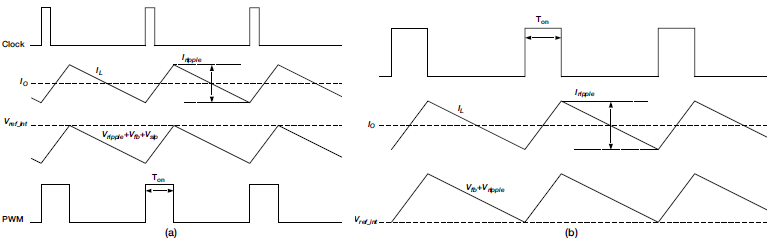 Figure 2-2 AECM Control Scheme Waveform:
PWM Operation Mode (a); PFM Operation Mode (b)
Figure 2-2 AECM Control Scheme Waveform:
PWM Operation Mode (a); PFM Operation Mode (b)