SFFS492 august 2023 AMC3336-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the AMC3336-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 shows the AMC3336-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the AMC3336-Q1 data sheet.
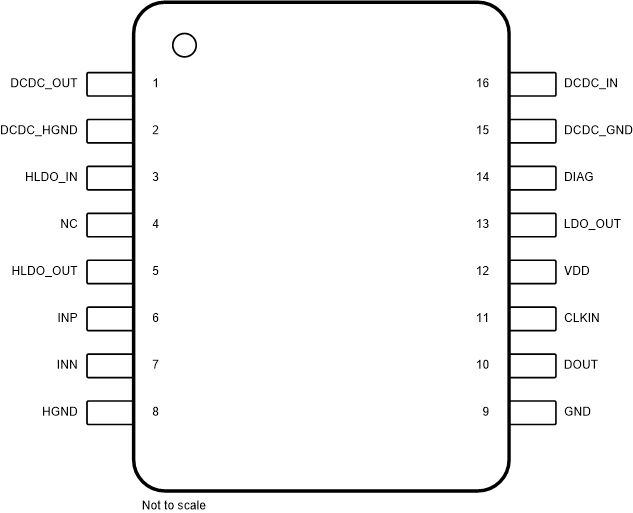 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- INN is connected to HGND.
- INP is connected to a resistive divider and the resitors are sized to limit the input current into INP to <10 mA under all circumstances (for example, if the device is powered off and the input signal is applied).
- For pins on input side (hot side):
Short-circuited to ground means short to HGND.
As the input side is powered internally from the output side (cold side), Short-circuited to supply does not apply. - For pins on output side (cold side):
Short-circuited to ground means short to GND.
Short-circuited to supply means short to VDD.
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCDC_OUT | 1 | Signal chain on input side powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Observe that the absolute maximum ratings for INP and INN of the device are met, otherwise device damage plausible. | A |
| DCDC_HGND | 2 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| HLDO_IN | 3 | Signal chain on input side powered off. Increased power consumption. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| NC | 4 | No effect. Pin has no internal connection. | D |
| HLDO_OUT | 5 | Signal chain on input side powered off. Increased power consumption. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| INP | 6 | INP stuck low (GND1) resulting in zero differential input voltage. DOUT output bitstream is mid-scale (50% zeros, 50% ones). | C |
| INN | 7 | INN stuck low (HGND). Value of DOUT output bitstream proportional to voltage difference (VINP – VHGND). Normal operation for the assumed use case. | D |
| HGND | 8 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| GND | 9 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| DOUT | 10 | DOUT stuck low (GND). No valid DOUT output bitstream. DOUT output bitstream looks like fail-safe output response (see data sheet for details). Excess current consumption from VDD source when DOUT tries to drive high. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| CLKIN | 11 | CLKIN stuck low (GND). Device not functional due to missing clock input. DOUT stuck in same state (high or low) as when CLKIN stopped. No valid DOUT output bitstream. | A |
| VDD | 12 | Device is powered off. DOUT is driven to GND. | B |
| LDO_OUT | 13 | DC/DC converter is powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DIAG | 14 | DIAG stuck low (GND). Device operates normally but falsely indicates that high-side in non-operational (see data sheet for details). | B |
| DCDC_GND | 15 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| DCDC_IN | 16 | DC/DC converter converter is powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCDC_OUT | 1 | Signal chain on input side powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). | B |
| DCDC_HGND | 2 | DCDC_HGND internally connected to HGND through diode. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). | B |
| HLDO_IN | 3 | Signal chain on input side powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| NC | 4 | No effect. Pin has no internal connection. | D |
| HLDO_OUT | 5 | No decoupling capacitor connected to the output of the high-side LDO. Device remains functional, parametric degradation plausible. | C |
| INP | 6 | Differential input (VINP – VINN) undetermined. DOUT output bitstream is undetermined. | B |
| INN | 7 | Differential input (VINP – VINN) undetermined. DOUT output bitstream is undetermined. | B |
| HGND | 8 | HGND internally connected to DCDC_HGND through diode. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). | B |
| GND | 9 | GND internally connected to DCDC_GND through diode. Device remains functional but common-mode output voltage shifts up (out of specification). | C |
| DOUT | 10 | DOUT undetermined. No valid DOUT output bitstream. | B |
| CLKIN | 11 | CLKIN floating. Device not functional due to missing clock input. DOUT stuck in same state (high or low) as when CLKIN stopped. No valid DOUT output bitstream. | B |
| VDD | 12 | Device is periodically powered through ESD diode of the CLKIN pin when CLKIN is driven high. DOUT output bitstream is undetermined. | B |
| LDO_OUT | 13 | DC/DC converter is powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). | B |
| DIAG | 14 | Pull-up resistor disconnected. No effect on primary function of the device. Diagnostic output not observable (see data sheet for details). | B |
| DCDC_GND | 15 | DCDC_GND internally connected to GND through diode. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details) with increased power consumption from VDD source. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DCDC_IN | 16 | DC/DC converter is powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCDC_OUT | 1 | DCDC_HGND | Signal chain on input side powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DCDC_HGND | 2 | HLDO_IN | Signal chain on input side powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| HLDO_IN | 3 | NC | No effect. Pin 4 has no internal connection. | D |
| NC | 4 | HLDO_OUT | No effect. Pin has no internal connection. | D |
| HLDO_OUT | 5 | INP | INP stuck high (HLDO_OUT). DOUT bitstream proportional to voltage difference (VHLDO_OUT – VINN). Overrange detection is likely to trigger (see data sheet for more details). | B |
| INP | 6 | INN | INP shorted to INN resulting in zero differential input voltage. DOUT output bitstream is mid-scale (50% zeros, 50% ones). | B |
| INN | 7 | HGND | INN stuck low (HGND). Value of DOUT output bitstream proportional to voltage difference (VINP – VHGND). Normal operation for the assumed use case. | D |
| HGND | 8 | GND | Not considered. Corner pin. | N/A |
| GND | 9 | DOUT | DOUT stuck low (GND). No valid DOUT output bitstream. DOUT output bitstream looks like fail-safe output response (see data sheet for details). Excess current consumption from VDD source when DOUT tries to drive high. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DOUT | 10 | CLKIN | DOUT output bit stream corrupted. Excess current consumption from DVDD source when DOUT tries to drive high, while CLKIN drives low and vice versa. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| CLKIN | 11 | VDD | CLKIN stuck high (VDD). Device not functional because of missing clock input. DOUT stuck in same state (high or low) as when CLKIN stopped. No valid DOUT output bitstream. | A |
| VDD | 12 | LDO_OUT | DC/DC converter is supplied from VDD. Device functions normally with increased power consumption from VDD source. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| LDO_OUT | 13 | DIAG | DIAG stuck high (LDO_OUT). Device operates normally with excessive power dissipation if DIAG is driven low (e.g. during startup). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DIAG | 14 | DCDC_GND | DIAG stuck low (GND). Device operates normally but falsely indicates that high-side in non-operational (see data sheet for details). | B |
| DCDC_GND | 15 | DCDC_IN | DC/DC converter powered off. Device outputs fail-safe state (see data sheet for details). | B |
| DCDC_IN | 16 | DCDC_OUT | Not considered. Corner pin. | N/A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCDC_OUT | 1 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| DCDC_HGND | 2 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| HLDO_IN | 3 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| NC | 4 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| HLDO_OUT | 5 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| INP | 6 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| INN | 7 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| HGND | 8 | Not considered. Input side (hot side) is not connected to external supply. | N/A |
| GND | 9 | Device is powered off. DOUT is driven to
GND. Observe that GND and DCDC_GND are diode connected and ESD protection on CLKIN can forward bias. Device damage plausible. |
A |
| DOUT | 10 | DOUT stuck high (VDD). No valid DOUT output bitstream. Excess current consumption from VDD source when DOUT tries to drive low. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| CLKIN | 11 | CLKIN stuck high (VDD). Device not functional because of missing clock input. DOUT stuck in same state (high or low) as when CLKIN stopped. No valid DOUT output bitstream. | B |
| VDD | 12 | No effect. Normal operation. | D |
| LDO_OUT | 13 | DC/DC converter is supplied from VDD. Device functions normally with increased power consumption from VDD source. Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DIAG | 14 | DIAG stuck high (VDD). Device operates normally with excessive power dissipation if DIAG is driven low (e.g. during startup). Long-term damage plausible. | A |
| DCDC_GND | 15 | DC/DC converter is powered off. Observe that GND and DCDC_GND are diode connected. Device damage plausible. | A |
| DCDC_IN | 16 | DC/DC converter is supplied from VDD. Device functions normally with increased power consumption from VDD source. Long-term damage plausible. | A |