SBOA391A March 2020 – April 2021 INA199-Q1 , INA210-Q1 , INA211-Q1 , INA212-Q1 , INA213-Q1 , INA214-Q1 , INA215-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a Failure Mode Analysis (FMA) for the pins of the INA21x-Q1 and INA199-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to Ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to V+ (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance |
Figure 4-1 shows the INA21x-Q1 and INA199-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins please refer to the 'Pin Configuration and Functions' section in either of the INA21x-Q1 and INA199-Q1 datasheets.
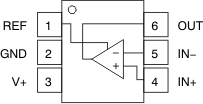 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- TA = -40°C to +125°C
- VV+ = 5 V
- VIN+ = 12 V
- VREF = VV+ / 2
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| REF | 1 | Normal operation if REF pin is at GND potential by design; otherwise the system measurement will be incorrect. | D if REF=GND by design; C otherwise |
| GND | 2 | Normal operation. | D |
| V+ | 3 | Power supply shorted to GND. | B |
| OUT | 4 | Output will be pulled down to GND and output current will be short circuit limited. When left in this configuration for a long time, under high supplies self-heating could cause die junction temperature to exceed 150°C. | B |
| IN- | 5 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to GND will occur (through RSHUNT). High current will flow from bus supply to GND. The shunt may be damaged. In low-side configuration, normal operation. | B for high-side; D for low-side |
| IN+ | 6 | In high-side configuration, a short from the bus supply to GND will occur. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| REF | 1 | Output common-mode voltage is not defined. Output will not maintain a linear relationship with differential input voltage. | C |
| GND | 2 | No power to device. Device may be biased through inputs. Output will no longer be referenced to GND. | B |
| V+ | 3 | No power to device. Device may be biased through inputs. Output will be incorrect and close to GND. | B |
| OUT | 4 | Output can be left open. There is no effect on the IC, but the output will not be measured. | C |
| IN- | 5 | Shunt resistor is not connected to amplifier. IN- pin may float to an unknown value. Output will go to an unknown value not to exceed V+ or GND. | B |
| IN+ | 6 | Shunt resistor is not connected to amplifier. IN+ pin may float to an unknown value. Output will go to an unknown value not to exceed V+ or GND. | B |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REF | 1 | 2 - GND | Normal operation if REF pin is at GND potential by design; otherwise the system measurement will be incorrect. | D if REF=GND by design; C otherwise |
| GND | 2 | 3 - V+ | Power supply shorted to GND. | B |
| V+ | 3 | 4 - OUT | Output will be pulled to V+ and output current will be short circuit limited. When left in this configuration for a long time, under high supplies self-heating could cause die junction temperature to exceed 150°C. | B |
| OUT | 4 | 5 - IN- | In high-side configuration, OUT shorted to bus supply with damage possible. In low-side configuration, OUT shorted to GND. | A for high-side; B for low-side. |
| IN- | 5 | 6 - IN+ | Inputs shorted together, so no sense voltage applied. Output will stay close to REF potential. | B |
| IN+ | 6 | 1 - REF | In high-side configuration, REF shorted to bus supply with damage possible. In low-side configuration, REF shorted to GND (normal operation if REF is at GND potential by design). | A for high-side; C for low-side (D if REF=GND by design) |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effect(s) | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| REF | 1 | Normal operation if REF pin is at V+ potential by design; otherwise the system measurement will be incorrect. | D if REF=V+ by design; C otherwise. |
| GND | 2 | Power supply shorted to GND. | B |
| V+ | 3 | Normal operation. | D |
| OUT | 4 | Output will be pulled to V+ and output current will be short circuit limited. When left in this configuration for a long time, under high supplies self-heating could cause die junction temperature to exceed 150°C. | B |
| IN- | 5 | In high-side configuration, device power supply shorted to bus supply. In low-side configuration, device power supply shorted to GND (through RSHUNT). | B |
| IN+ | 6 | In high-side configuration, device power supply shorted to bus supply (through RSHUNT). In low-side configuration, device power supply shorted to GND. | B |