SLUSC99A July 2016 – January 2017 UCD3138128A
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parametric Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1 System Module
- 9.3.2 Peripherals
- 9.3.3 Automatic Mode Switching
- 9.3.4 DPWMC, Edge Generation, Intramux
- 9.3.5 Synchronous Rectifier MOSFET Ramp And IDE Calculation
- 9.3.6 Filter
- 9.3.7 Communication Ports
- 9.3.8 Real Time Clock
- 9.3.9 External Crystal Interface
- 9.3.10 Timers
- 9.3.11 General Purpose ADC12
- 9.3.12 Miscellaneous Analog
- 9.3.13 Brownout
- 9.3.14 Global I/O
- 9.3.15 Temperature Sensor Control
- 9.3.16 I/O Mux Control
- 9.3.17 Current Sharing Control
- 9.3.18 Temperature Reference
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5 Register Maps
- 10Applications and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13Device and Documentation Support
- 14Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
12 Layout
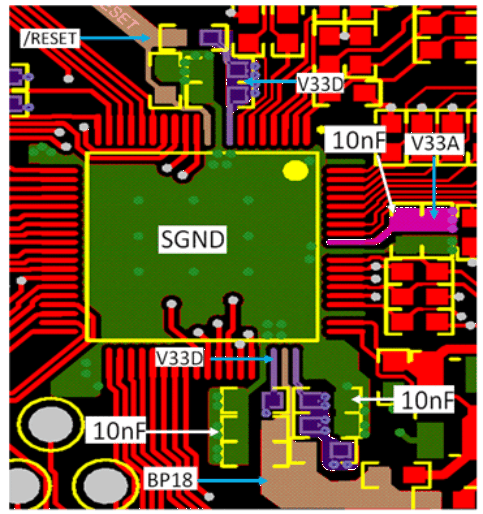
12.1 Device Grounding and Layout Guidelines
- Single ground is recommended: SGND. A multilayer such as 4 layers board is recommended so that one solid SGND is dedicated for return current path, referred to the layout example.
- Apply multiple different capacitors for different frequency range on decoupling circuits. Each capacitor has different ESL, Capacitance and ESR, and they have different frequency response.
- Avoid long traces close to radiation components, and place them into an internal layer, and it is preferred to have grounding shield.
- Analog circuits and digital circuits should have separate return to ground; although with a single plane, still try to avoid mixing analog current and digital current.
- Do not use a ferrite bead or larger than 3-Ω resistor to connect between V33A and V33D.
- Both 3.3VD and 3.3VA should have local decoupling capacitors close to the device power pins, add vias to connect decoupling caps directly to SGND.
- Avoid negative current/negative voltage on all pins, so Schottky clamping diodes may be needed to limit the voltage; avoid more than 3.8 V or less than –0.3 V voltage spikes on all pins; add Schottky diodes on the pins which could have voltage spikes during surge test; be aware that a Schottky has relatively higher leakage current, which can affect the voltage sensing at high temperature.
- If V33 slew rate is less than 2.5 V/ms the RESET pin should have a 2.21-kΩ resistor between the reset pin and V33D and a 2.2-µF capacitor from RESET to ground. For more details please refer to the UCD3138 Family - Practical Design Guideline This capacitor must be located close to the device RESET pin.
- If the XTAL_IN (Pin 61) and XTAL_OUT (Pin 62) are not used for external clock, tie them to 1.8 V (Pin BP18) through a 1-kΩ resistor respectively.
- Configure unused GPIO pins to be inputs or connect them to the ground (DGND or SGND); when an external pull-up resistor is used for GPIO, the pull-up resistor needs to be 1 kΩ or higher.
For detailed practical design guidelines, refer to (UCD3138 Family - Practical Design Guideline).