ZHCSDK4C September 2014 – January 2020 TPS92638-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 典型应用原理图
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
- 9 Detailed Description
-
10Application and Implementation
- 10.1 Application Information
- 10.2 Typical Applications
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
12.3 Thermal Information
This device operates a thermal shutdown (TSD) circuit as a protection from overheating. For continuous normal operation, the junction temperature should not exceed the thermal-shutdown trip point. If the junction temperature exceeds the thermal-shutdown trip point, the output turns off. When the junction temperature falls below the thermal-shutdown trip point minus hysteresis, the output turns on again.
Calculate the power dissipated by the device according to the following formula:
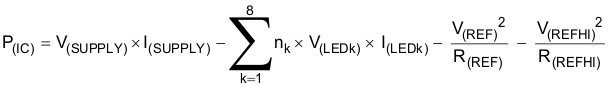
where:
nk = Number of LEDs for x channel
V(LEDk)= Voltage drop across one LED for x channel
V(REF) = Reference voltage, typically 1.24 V
I(LEDk) = Average LED current for channel k
After determining the power dissipated by the device, calculate the junction temperature from the ambient temperature and the device thermal impedance.
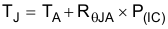
where:
TA = Ambient temperature
RθJA = Junction-to-ambient thermal impedance
P(IC) = Dissipated power