ZHCSOL0D December 2008 – November 2023 TPS714
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
- 6 Detailed Description
- 7 Application and Implementation
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- DRV|6
订购信息
7.2.2.1 Setting VOUT for the TPS71401 Adjustable LDO
The TPS714 contains an adjustable version, the TPS71401, which sets the output voltage using an external resistor divider, as shown in Figure 7-2. The output voltage operating range is 1.205 V to 8.8 V, and is calculated using:
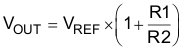
where:
- VREF = 1.205 V (typical)
Choosing resistors R1 and R2 allows approximately 1.5 μA of current through the resistor divider. Lower value resistors can be used for improved noise performance, but consume more power. Avoid higher resistor values because leakage current into or out of FB across R1 / R2 creates an offset voltage that is proportional to VOUT divided by VREF. The recommended design procedure is to choose R2 = 1 MΩ to set the divider current at 1.5 μA, and then calculate R1 using Equation 3:
Figure 7-2 depicts this configuration.