SLVSA48A April 2010 – September 2015 TPS65200
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3 Feature Description
- 7.4
Device Functional Modes
- 7.4.1
Charge Mode Operation
- 7.4.1.1 Input Current Limiting and D+/D- Detection
- 7.4.1.2 Bad Adaptor Detection/Rejection (CHBADI)
- 7.4.1.3 Input Current Limiting at Start-Up
- 7.4.1.4 Charge Profile
- 7.4.1.5 Precharge to Fast Charge Threshold (VSHORT)
- 7.4.1.6 PWM Controller in Charge Mode
- 7.4.1.7 Battery Charging Process
- 7.4.1.8 Thermal Regulation and Protection
- 7.4.1.9 Safety Timer in Charge and Boost Mode (CH32MI, BST32SI)
- 7.4.1.10 Input Voltage Protection in Charge Mode
- 7.4.1.11 Battery Protection in Charge Mode
- 7.4.1.12 Charge Status Output, STAT Pin
- 7.4.2 Boost Mode Operation
- 7.4.3 High Impedance Mode
- 7.4.1
Charge Mode Operation
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6
Register Maps
- 7.6.1 Control Register (CONTROL)
- 7.6.2 Charger Config Register A (CONFIG_A)
- 7.6.3 Charger Config Register B (CONFIG_B)
- 7.6.4 Charger Config Register C (CONFIG_C)
- 7.6.5 Charger Config Register D (CONFIG_D)
- 7.6.6 WLED Control Register (WLED)
- 7.6.7 Status Register A (STATUS_A)
- 7.6.8 Status Register B (STATUS_B)
- 7.6.9 Interrupt Register 1 (INT1)
- 7.6.10 Interrupt Register 2 (INT2)
- 7.6.11 Interrupt Register 3 (INT3)
- 7.6.12 Interrupt Mask Register 1 (MASK1)
- 7.6.13 Interrupt Mask Register 2 (MASK2)
- 7.6.14 Interrupt Mask Register 3 (MASK3)
- 7.6.15 Chip ID Register (CHIPID)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
5 Pin Configuration and Functions
YFF Package
36-Pin DSBGA
Bottom View, Top View
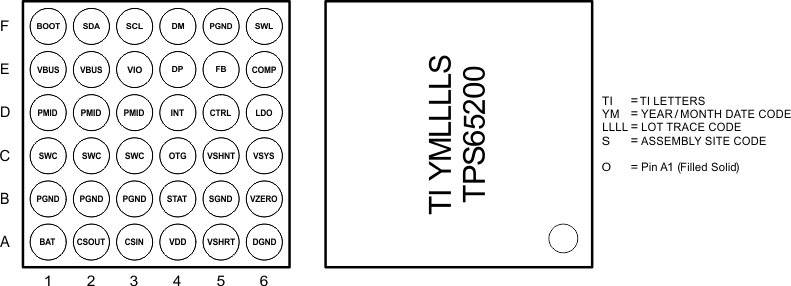
Pin Functions
| PIN | I/O | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | NAME | ||
| A1 | BAT | O | Output of the linear charger and battery voltage sense. Connect the battery from this pin to ground. |
| A2 | CSOUT | I | Charge current-sense input. Battery current is sensed through the voltage drop across an external sense resistor. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor to PGND is required. |
| A3 | CSIN | I | Charge current-sense input. Battery current is sensed through the voltage drop across an external sense resistor. A 0.1-μF ceramic capacitor to PGND is required. |
| A4 | VDD | O | Internal supply for battery charger. Connect a 1-mF ceramic capacitor from this output to PGND. External load on VDD is not recommended. |
| A5 | VSHRT | I | The voltage on this pin defines the battery voltage for transitioning from linear charge (pre-charge) to fast charge. A 10-µA current source is internally connected to this pin. Connect a resistor from this pin to ground to setup VSHORT reference. If the pin is left floating or tied to VDD an internal VSHORT reference of 2.1 V is used. |
| A6 | DGND | Digital ground | |
| B1 | PGND | Power ground | |
| B2 | |||
| B3 | |||
| B4 | STAT | O | Charge status pin. Pulled low when charge in progress. Open drain for other conditions. This pin can also be controlled through I2C register. STAT can be used to drive a LED or communicate with a host processor. |
| B5 | SGND | Signal ground | |
| B6 | VZERO | I | This pin sets the zero-current output voltage level of the current shunt monitor. |
| C1 | SWC | O | Internal switch to inductor connection (charger) |
| C2 | |||
| C3 | |||
| C4 | OTG | I | Boost control pin. Boost mode is turned on whenever this pin is active. Polarity is user defined through I2C register. The pin is disabled by default and can be enabled through I2C register bit. |
| C5 | VSHNT | O | Output of current shunt monitor. For positive currents (into battery) VSHNT > VZERO. For negative currents (out of the battery) VSHNT < VZERO. |
| C6 | VSYS | I | Input supply for WLED driver and current shunt monitor |
| D1 | PMID | O | Connection point between reverse blocking MOSFET and high-side switching MOSFET. Bypass it with a minimum of 1-μF capacitor from PMID to PGND. No other circuits are recommended to connect at PMID pin. |
| D2 | |||
| D3 | |||
| D4 | INT | O | Interrupt pin (open-drain). This pin is pulled low to signal to the main processor that a fault has occurred. |
| D5 | CTRL | I | Control pin of the LED boost regulator. It is a multi-functional pin which can be used for enable control and PWM dimming. |
| D6 | LDO | O | LDO output. LDO is regulated to 4.9 V and drives 60-mA of current. Bypass LDO to GND with at least a 1-μF ceramic capacitor. LDO is enabled when VBUS is above the VBUS UVLO threshold. |
| E1 | VBUS | I/O | Charger input voltage. Bypass it with a 1-μF ceramic capacitor from VBUS to PGND. It also provides power to the load in boost mode. |
| E2 | |||
| E3 | VIO | I | I/O reference voltage. A VIO level above 0.6 V disables automatic D+/D- detection. |
| E4 | DP | I | USB port D+ input connection |
| E5 | FB | I | Feedback pin for current. Connect the sense resistor from FB to GND. |
| E6 | COMP | O | Output of the transconductance error amplifier. Connect an external capacitor to this pin to compensate the regulator. |
| F1 | BOOT | O | Boot-strapped capacitor for the high-side MOSFET gate driver. Connect a 10-nF ceramic capacitor (voltage rating above 10 V) from BOOST pin to SWC pin. |
| F2 | SDA | I/O | I2C interface data |
| F3 | SCL | I | I2C interface clock |
| F4 | DM | I | USB port D- input connection |
| F5 | PGND | Power ground | |
| F6 | SWL | I | This is the switching node of the LED driver. Connect the inductor from the supply to the SWL pin. This pin is also used to sense the output voltage for open LED protection. |