ZHCSEB8 October 2015 TPS63020-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 典型应用电路原理图
- 5 修订历史记录
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
- 9 Detailed Description
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
12 Layout
12.1 Layout Guidelines
For all switching power supplies, the layout is an important step in the design, especially at high peak currents and high switching frequencies. If the layout is not carefully done, the regulator could show stability problems as well as EMI problems. Therefore, use wide and short traces for the main current path and for the power ground tracks. The input capacitor, output capacitor, and the inductor should be placed as close as possible to the IC. Use a common ground node for power ground and a different one for control ground to minimize the effects of ground noise. Connect these ground nodes at any place close to one of the ground pins of the IC.
The feedback divider should be placed as close as possible to the control ground pin of the IC. To lay out the control ground, short traces are recommended as well, separation from the power ground traces. This avoids ground shift problems, which can occur due to superimposition of power ground current and control ground current.
12.2 Layout Example
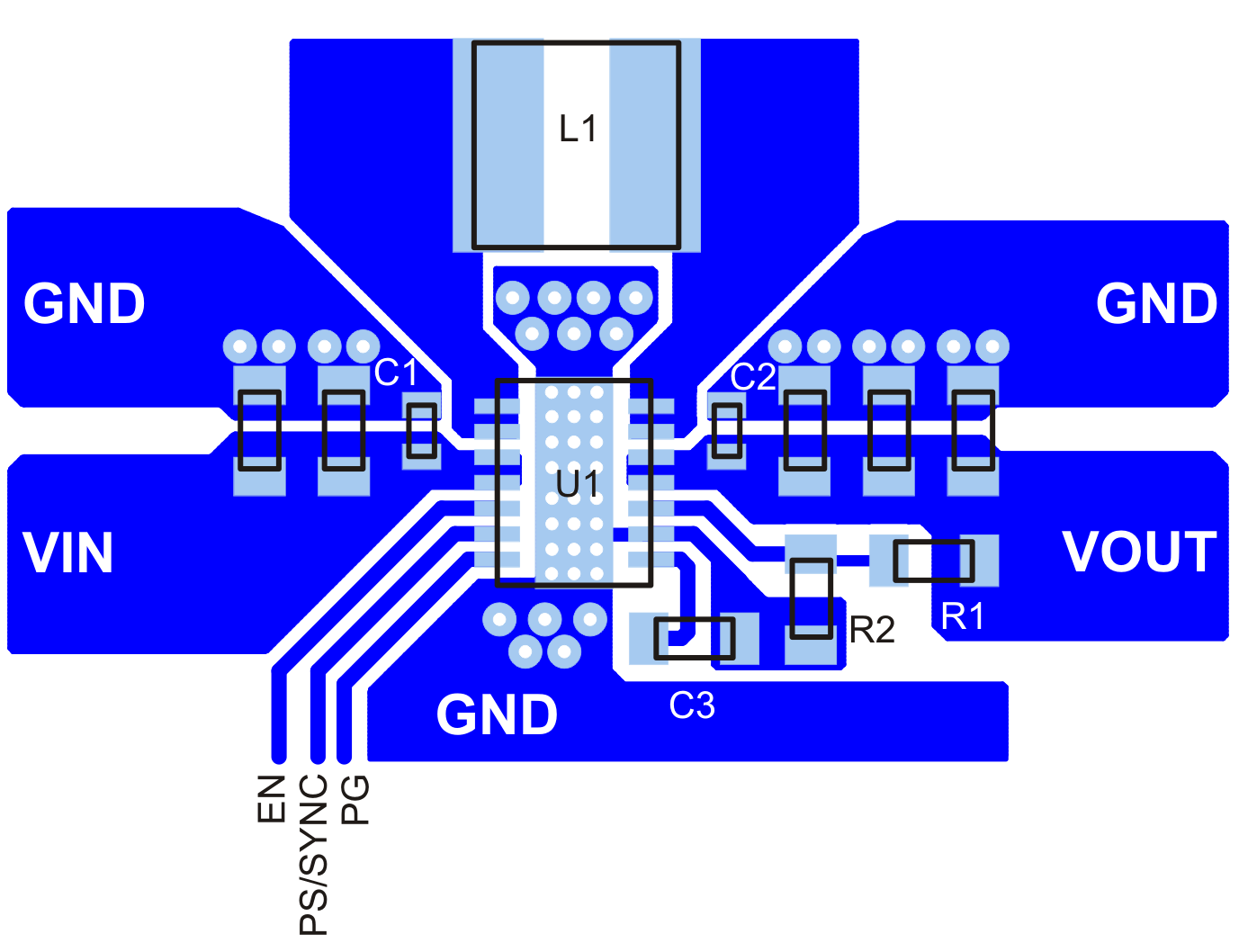 Figure 20. PCB Layout Suggestion
Figure 20. PCB Layout Suggestion
12.3 Thermal Considerations
Implementation of integrated circuits in low-profile and fine-pitch surface-mount packages typically requires special attention to power dissipation. Many system-dependent issues such as thermal coupling, airflow, added heat sinks and convection surfaces, and the presence of other heat-generating components affect the power-dissipation limits of a given component.
Three basic approaches for enhancing thermal performance are listed below:
- Improving the power dissipation capability of the PCB design
- Improving the thermal coupling of the component to the PCB by soldering the exposed thermal pad
- Introducing airflow in the system
For more details on how to use the thermal parameters, see the application notes: Thermal Characteristics Application Note (SZZA017), and Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics Application Note (SPRA953).