ZHCSHQ2B November 2017 – May 2018 TPS62821 , TPS62822 , TPS62823
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
8.4.3 Minimum Duty Cycle and 100% Mode Operation
There is no limitation for small duty cycles, since even at very low duty cycles the switching frequency is reduced as needed to always ensure a proper regulation.
If the output voltage level comes close to the input voltage, the device enters 100% mode. While the high-side switch is constantly turned on, the low-side switch is switched off. The difference between VIN and VOUT is determined by the voltage drop across the high-side FET and the dc resistance of the inductor. The minimum VIN that is needed to maintain a specific VOUT value is estimated as:
space
Equation 3. 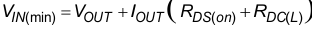
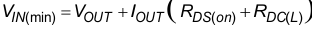
space